Intel Core i7 12700K
Rated: 8/10
AMD Ryzen 7 5800X
Rated: 9/10
Pros And Cons
| CPUs | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Intel i7-12700K | ✅ More cores & threads and frequency ✅ Better productivity performance | ❌ Higher cost despite similar performance ❌ High power draw and temperatures |
| Ryzen 7 5800X | ✅ Exceptional price-to-performance ratio ✅ Better power & thermal efficiency | ❌ No support for DDR5 RAM ❌ Might not be vaible for future-proofing |
- We noticed that both processors performed similarly, with an average performance difference of under 1%.
- Despite the similar performance, the Ryzen 7 5800X proved 19% more power-efficient and 8.9% more thermally efficient than its Intel counterpart.
- In research, we analyzed that the Ryzen 7 5800X is available at only $231 apiece. This price is much cheaper than the Intel i7-12700K, with a 21.21% increased price tag of $280.
- We recommend the Ryzen 7 5800X due to its better performance, lower price, power & thermal efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Specifications | Intel i7-12700K | Ryzen 7 5800X |
|---|---|---|
| Cores & Threads | 12 Cores & 20 Threads | 8 Cores & 16 Threads |
| Hybrid Cores | P-Cores: 8 | E-Cores: 4 | - |
| Base Frequency | P Core: 3.6 GHz, E-Core: 2.7 GHz | 3.8 GHz |
| Boost Clock Speed | P Core: 4.9 GHz, E-Core: 3.8 GHz | 4.7 GHz |
| Memory Support | DDR4 up to 3200 MHz DDR5 up to 4800 MHz | DDR4 up to 3200 MHz |
| Best CPU Coolers | Best CPU Coolers for Intel i7-12700K | Best CPU Coolers for Ryzen 7 5800X |
| Best Motherboards | Best Motherboards for Intel i7-12700K | Best Motherboards for Ryzen 7 5800X |
| Best Memory | Best RAM for Intel i7-12700K | - |
Architectural Differences
- Process Node & Architecture: Intel’s CPU is based on the Hybrid Core architecture and uses a TMSC 10nm process node. Meanwhile, the Zen-3-based AMD processor has a process size of 7nm.
- Cache: The Core i7-12700K has an L2 Cache of 12MB over the Ryzen 7 5800X’s 4MB. For L3 Cache, Intel has 25MB of L3 cache, whereas AMD has 32MB.
- Socket & PCIe: The AM4-based Ryzen 7 5800X has PCIe 4.0 support, while the LGA 1700-based Core i7-12700K supports PCIe Gen 4.0 and 5.0.
- TDP & Integrated Graphics: The Core i7-12700K arrives with a slightly higher TDP of 125W. Meanwhile, the Ryzen 7 5800X’s TDP rating is 105W. The 12700K also arrives with integrated graphics of Intel UHD 770, whereas the Ryzen doesn’t come with any.
- Supported Motherboard Chipsets: The Intel i7-12700K supports the Z690, H670, B660, H610 motherboard chipsets whereas the Ryzen 7 5800X has support for X570, B550, X470 B450 A520 A320 chipsets.
Intel’s 12th generation chips are being compared against the Ryzen 5000 series, and one of the most interesting competitions is the Intel i7-12700K vs Ryzen 7 5800X. The 12700K is Intel’s highest-end i7 chip, and the 5800X was AMD’s most powerful Ryzen 7 chip at launch. In this comparison, we’ll show you how each processor performs and which prevails.
Intel i7 12700K Vs Ryzen 7 5800X – Gaming Benchmarks
Now that the specifications of each processor are discussed let’s dive deeper into the performance aspects of these two chips by conducting a benchmark test at 1080p.
Testing Rig
- Motherboard 1: MSI MEG X570 ACE
- Motherboard 2: MSI Z690 Unify
- Memory: Patriot Viper LED 3600Mhz (2x16GB) – DDR4
- Graphics Card: MSI RTX 3080 GAMING X TRIO
- CPU Cooler: Corsair iCue H150i
- Power Supply: be quiet! Dark Power Pro 13 1300W
- Storage: XPG GAMMIX S70 BLADE 2TB NVMe
- OS: Windows 11
Shadow Of The Tomb Raider
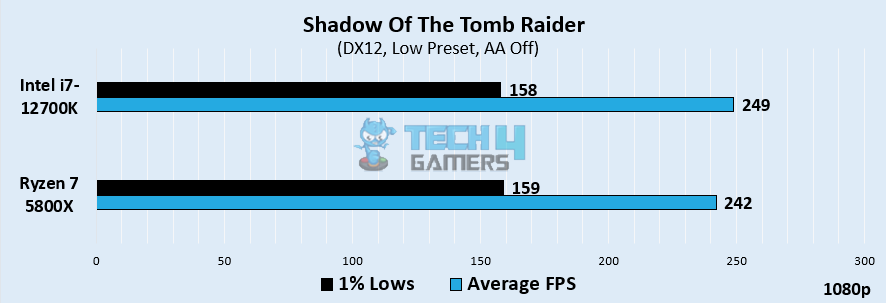
- In our first game, the two CPUs are quite neck and neck, with the Intel i7-12700K averaging 249 FPS over the 242 FPS gained by the Ryzen 7 5800X – displaying a 2.85% edge.
- As for the 1% lows, the Ryzen 7 5800X showed an average of 159 FPS, slightly higher than the 158 FPS acquired by the Core i7-12700K.
Cyberpunk 2077
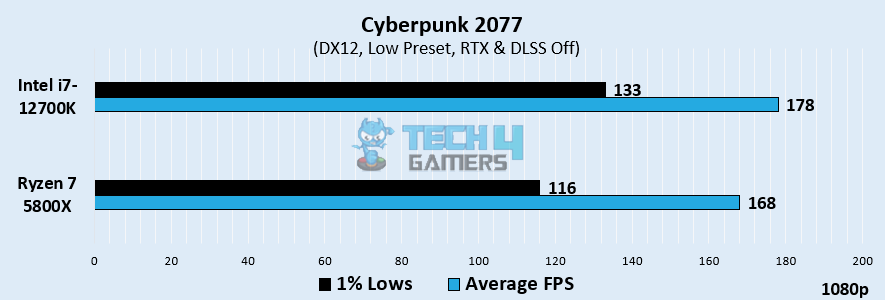
- In Cyberpunk 2077, we saw that the Intel i7-12700K outperformed the Ryzen 7 5800X by obtaining an average of 178 FPS over AMD’s 168 FPS, achieving a 5.78% gain in performance.
- For 1% lows, we observed that the Intel i7-12700K displayed an average of 133 FPS, whereas its AMD counterpart achieved 116 FPS.
F1 2021
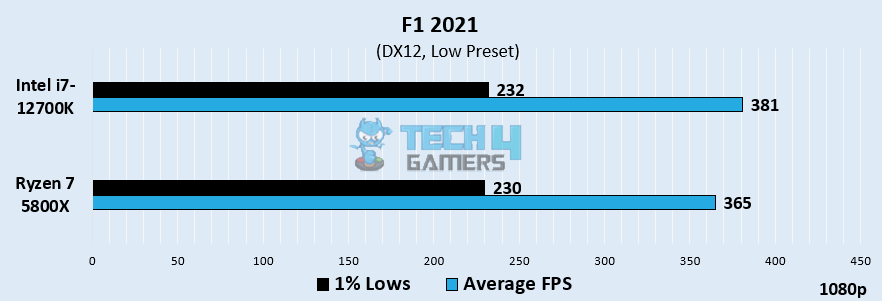
- The Core i7-12700K outshined the Ryzen 7 5800X by 4.28%, averaging 381 FPS over 365 FPS, respectively.
- Regarding the 1% lows, the Core i7-12700K averaged 232 FPS, while the Ryzen 7 5800X was a few FPS behind with an average of 230 FPS.
Far Cry 6
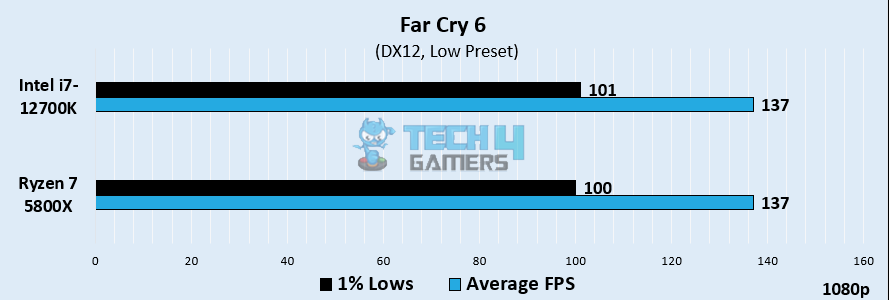
- In Far Cry 6, we noticed that both the processors rivaled equally, obtaining the same average of 137 FPS.
- Similar to the average FPS, the 1% lows were also similar, with the i7-12700K averaging 101 FPS over Ryzen’s 100 FPS.
Hitman 3
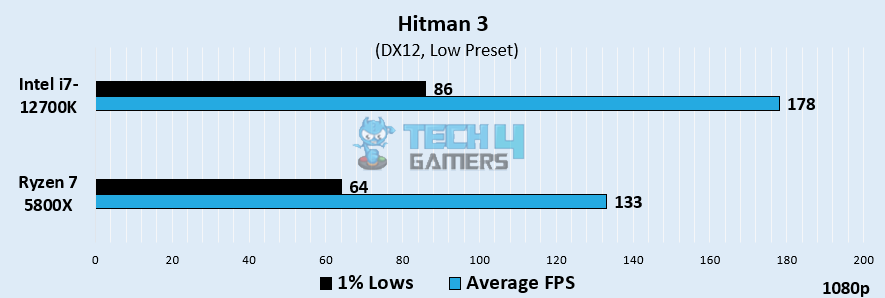
- Here, the Core i7-12700K acquired an average of 178 FPS, whereas the Ryzen 7 5800X lagged with 133 FPS, resulting in a substantial difference of 28.9% gained by Intel’s CPU.
- We observed that the 1% lows also favored the Intel i7-12700K, which averaged 86 FPS. In contrast, the Ryzen 7 5800X treaded lightly with 64 FPS.
Overall Gaming Performance
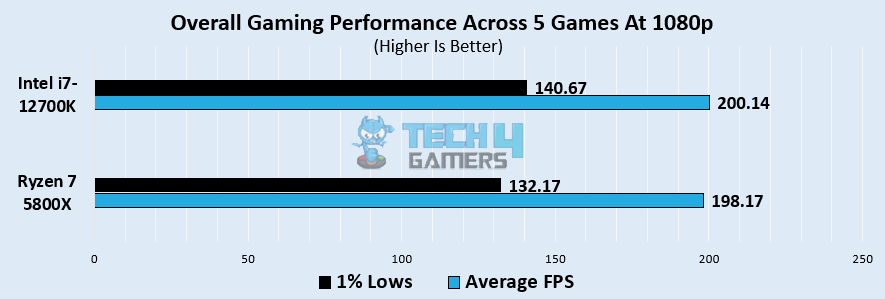
We calculated the average values across the games mentioned above and saw that the results were quite close. On average, the Intel i7-12700K obtained 200.1 FPS, whereas the Ryzen 7 5800X achieved 198.1 FPS, displaying a difference of less than 1%. As for the 1% lows, the i7-12700K outperformed by averaging 140.6 FPS over the Ryzen 7 5800X’s 132.1 FPS.
Winner: AMD Ryzen 7 5800X
Thermal Efficiency
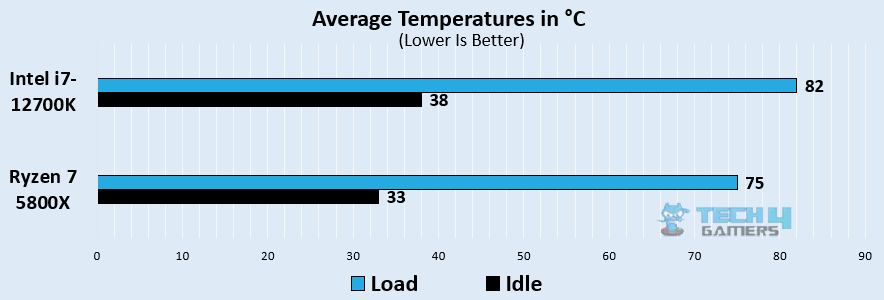
Comparing the temperatures between the two CPUs, we noticed that the i7 12700K runs considerably hotter at idle and under loads, operating at 38°C and 82°C, respectively. On the other hand, the Ryzen 7 5800X proves to be 8.9% more thermally efficient by running at 75°C under load and only 33°C when the system is idle.
Power Consumption
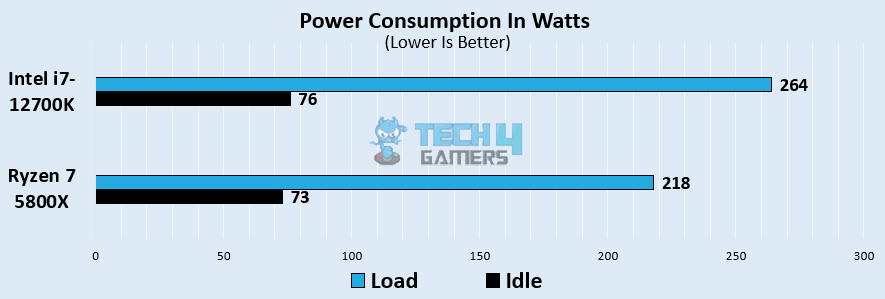
We observed that the i7 12700K draws a massive 264 watts over the Ryzen 7 5800X’s 218 watts – this makes the Ryzen 7 5800X 19% more power-efficient. However, the two CPUs have comparable idle power draws, drawing just around 75 watts.
Pricing And Availability
| CPUs | MSRP | Current Price |
|---|---|---|
| Intel i7-12700K | 💲409 | 💲280 |
| Ryzen 7 5800X | 💲449 | 💲231 |
| Price Difference | 9.3% | 21.21% |
Both the CPUs’ prices have been greatly reduced from their MSRP, with the Intel i7-12700K costing 34.3% less and the Ryzen 7 5800X costing 64.8% less. This makes the Ryzen 7 5800X 5% cheaper than its Intel rival. Both processors are readily available separately on online sites, but the Ryzen 7 5800X is also widely available as an entire PC bundle.
Ryzen 7 5800X Vs Intel i7-12700K: Which One Do We Recommend?
After reviewing the differences mentioned above, you might have already concluded this. But, we’ll highlight again that the Ryzen 7 5800X has proved to perform almost the same as the Intel i7-12700K. Not only that, but it also costs less, is more power-efficient, and is more thermally efficient. This is why I recommend you get the Ryzen 7 5800X without thinking twice.
Frequently Asked Questions
The i7 12700K is much better than the Ryzen 7 5800x in terms of productivity performance and marginally better in gaming performance. The 12700K also gives you DDR5 and PCIe 5.0 support, which the 5800x does not have.
No. DDR5 memory is not necessary for any Alder Lake CPU. Intel’s 600 series chipset boards come with DDR4 or DDR5 support, so you can choose a DDR4 motherboard to run DDR4 memory.
AMD’s Ryzen 9 5900x is more neck and neck with the 12700K in terms of productivity performance.
More From Ryzen 7 5800X
More From Intel i7-12700K
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Comparisons Expert]
Abdemanaf is a skilled creative writer who has been honing his craft since 2011. While initially working in different fields, he found a passion for technology and has been exploring the tech world since early 2015. Over the years, he has developed an in-depth knowledge of the latest tech trends and product offerings by various companies.
Abdemanaf’s writing reflects his analytical mindset and ability to think critically. He has a knack for breaking down complex technical information into easily digestible pieces, making his articles engaging and accessible to readers from all backgrounds. In February 2022, he joined Tech4Gamers as a blog and product comparison writer, where he has been able to hone his skills further.
As a writer, Abdemanaf is dedicated to staying up-to-date with the latest technological advancements and trends, enabling him to provide readers with the most relevant and accurate information. He is always eager to learn more and is constantly seeking new challenges to improve his skills.
Get In Touch: manaf@tech4gamers.com







