Building a computer requires consumers to know which product fits best. After all, compatibility is essential when buying components for your new PC. Of course, a sufficient power supply is equally important as the best graphics card you can fit with your budget. Nonetheless, many consumers try to build PCs that consume less power. So, what is the gaming PC power usage in reality?
Key Takeaways
- A PC’s main power consumption stems from the graphics card and processor, so create a build centred around products with better TDP.
- Usually, an AMD build consumes less power than an Intel build.
- Investing in a more robust power supply with an 80+ ranking is essential for current and future mid-range to high-end builds, ensuring optimal performance and scalability.
Wattage Intensive Components
When considering gaming PC power usage, focus on components with higher wattage requirements, namely the CPU and GPU. Assessing their power needs is crucial for building an energy-efficient system.
Graphics Card Power Requirements

- Analyzing mid-range graphics cards like the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 and AMD Radeon RX 6600 XT, their performance varies slightly while sharing similar power requirements. The RTX 3060 demands a minimum of 170W[1] with a recommended 350W power supply, while the RX 6600 XT requires at least 160W[2] with the same recommended power supply.
- Furthermore, looking at high-end options, we have the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 and the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090. However, few consumers are willing to buy the RTX 4090 due to its price and immense power requirements.
In conclusion, a graphics card usually requires over 300W power, up to 1000W.
Processor Power Requirements

- Firstly, analyzing the mid-range market, we have the AMD Ryzen 5 3600 and the Intel Core i5-11600K. Consequently, the 5 3600 has an expected TDP of 65W.[3] However, using a 400W power supply is recommended. Subsequently, the i5-11600K has a TDP of 125W.[4] Therefore, using a 500W power supply or higher is recommended with the 11600K.
- Secondly, moving towards the higher-end market, the AMD Ryzen 9 7900X and the Intel Core i9-13900K dominate. Notwithstanding, the 9 7900X has a TDP of 170W.[5] On the other hand, the i9-13900K has a TDP of 125-253W.[6] So, to properly utilize both processors, consumers need at least a 700W power supply.
Lastly, a processor may require 300W to 800W power to run efficiently. Although, if you plan to overclock your components, you will need even more power.
Low-End Gaming PC Power Usage
Let’s explore the power requirements of gaming PCs across various price ranges, considering both Intel and AMD options. Understanding the power efficiency of different categories is crucial for gamers with varying budgets. First, let’s delve into the power needs of low-end gaming PCs.
Low-End Intel Gaming PC
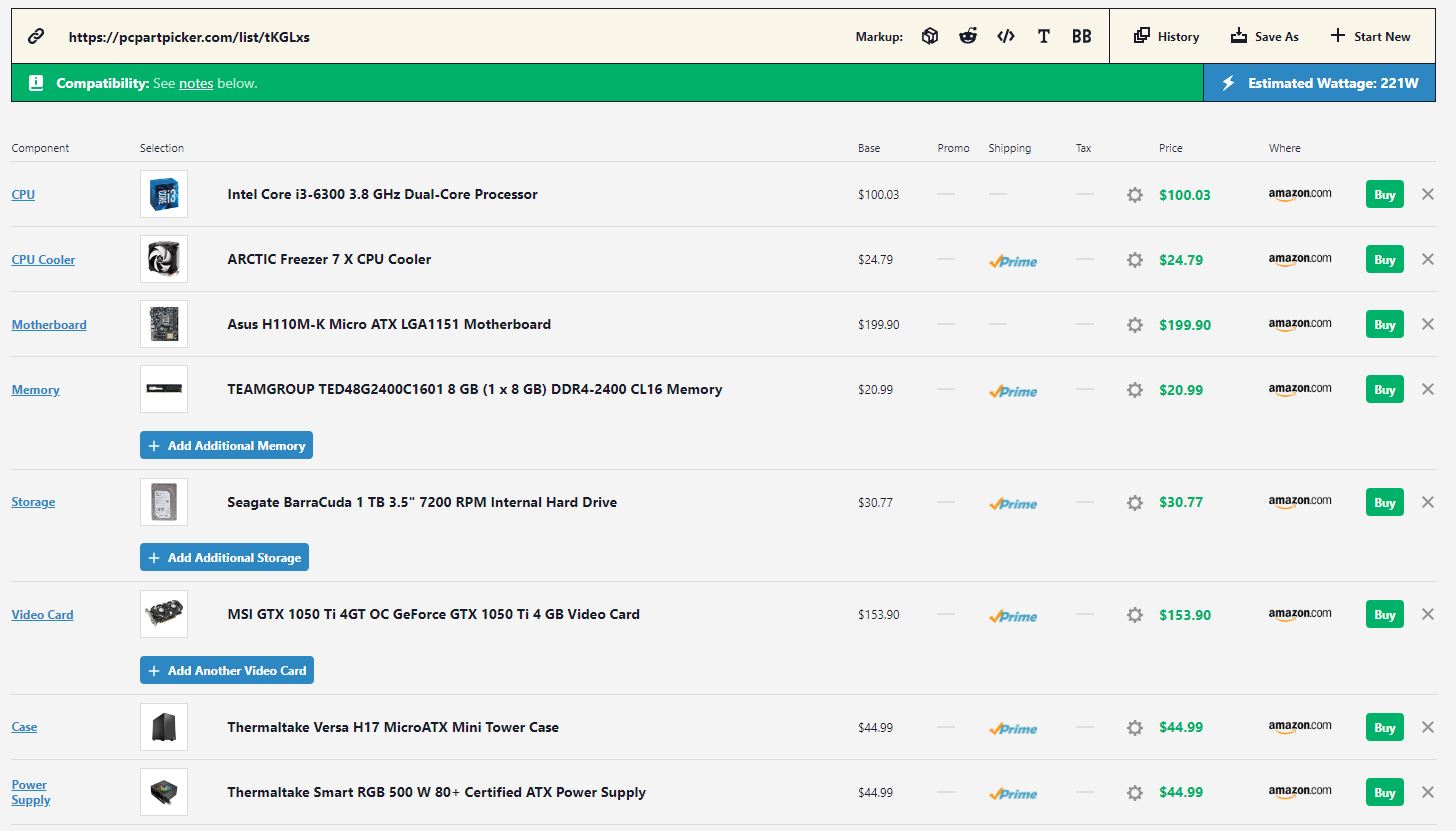
While looking at the following image, we see a reasonably low-end build, considering the currently available hardware. We use an NVIDIA graphics card to look at an Intel-oriented build.
- Be that as it may, we are going with the reasonably durable Intel Core i3-6300 for the processor. Also, the processor has a TDP ranking of 51W.[7] To complement the Intel Core i3-6300, we have the Asus H110M motherboard.
- Looking at the graphics card, we’re going with the NVIDIA GTX 1050 Ti. By all means, the NVIDIA GTX 1050 Ti is an old GPU. However, running most triple-A title games at low settings is sufficient. So, if budget is a problem, the 1050 Ti is a great GPU. In any case, the 1050 Ti has a TDP of 75W.[8]
With all the other components within the PC, we have an estimated wattage of ~221W. So, buying a 400W or greater power supply should be the ideal choice.
Low-End AMD Gaming PC
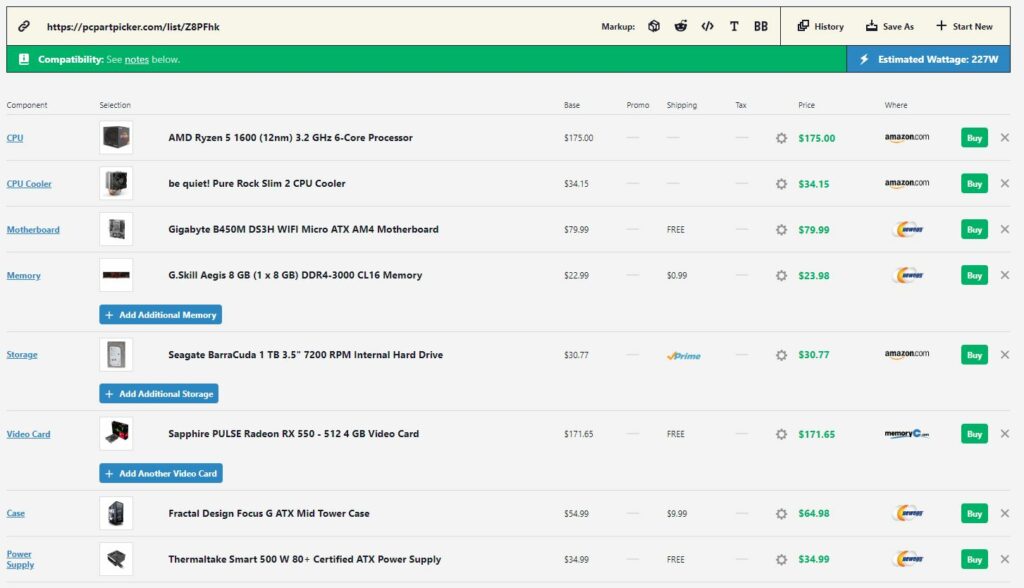
- Firstly, glancing towards the AMD Ryzen 5 1600, one can see that it’s a great processor with fantastic performance capabilities. Also, the 5 1600 barely requires a 65W TDP.[9] So, according to today’s standards, the 5 1600 has gotten old but provides adequate performance at lower prices.
- Secondly, moving toward the graphics card, we’re going with the AMD Radeon RX 550. It has a TDP requirement of barely 50W.[10] But, it’s important to note that the RX 550 holds no candles against the NVIDIA GTX 1050 Ti. So, if performance is an issue, you might want to go with the latter.
For an all-AMD low-end gaming PC, power usage averages around 227W, suggesting a 400-450W power supply is ample. Despite potential performance limitations, combinations like an AMD Ryzen 5 1600 and Radeon RX 550 offer value. Mixing AMD processors with NVIDIA GPUs can also yield improved results.
Mid-Range Gaming PC Power Usage
Moving to mid-range gaming PCs, power needs typically range from 500W to 700W. Let’s delve deeper into power requirements for both Intel and AMD builds in this category!
Mid-Range Intel Gaming PC
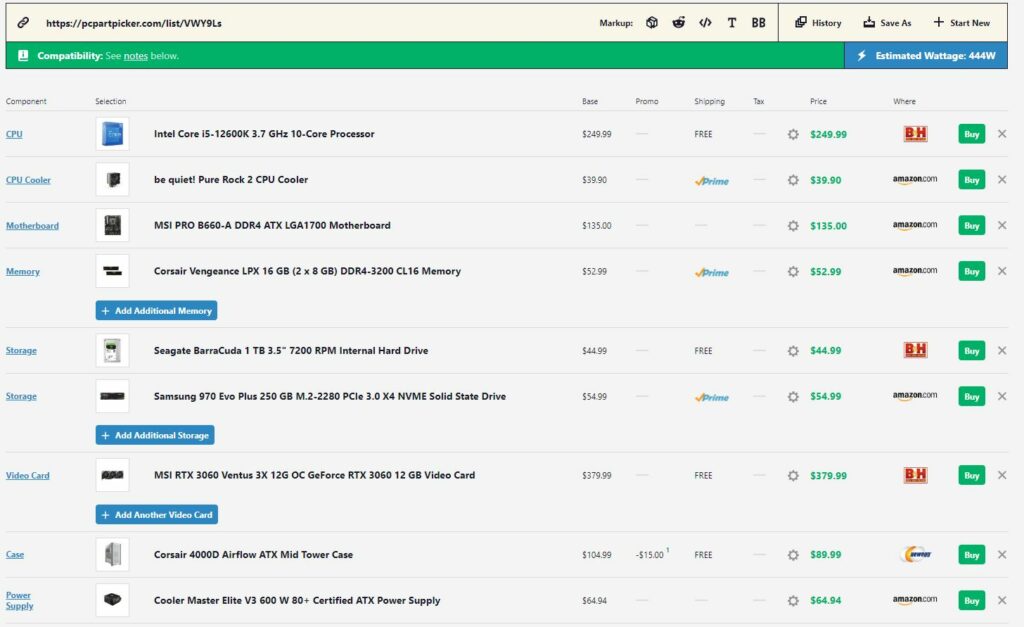
- By and large, looking at the processor, we’re using the Intel Core i5-12600K. Because of its low price and amazing performance, the i5 12600K offers superb value. Additionally, the i5-12600K has a 125W TDP requirement.[11] Also, the i5-12600K is future-proof, meaning it won’t become prolonged for at least a few more years.
- Subsequently, looking at the graphics card, we see that we have multiple options from NVIDIA. We’re using an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 GPU. Not only does the RTX 3060 offer a fantastic performance per dollar ratio, but it only has a 170W TDP.[12]
Consequently, the mid-range Intel build has an estimated wattage requirement of 444W. For that reason, a 600W power supply will prove to be helpful. However, you can opt for a higher-wattage power supply to help support your future builds.
Mid-Range AMD Gaming PC
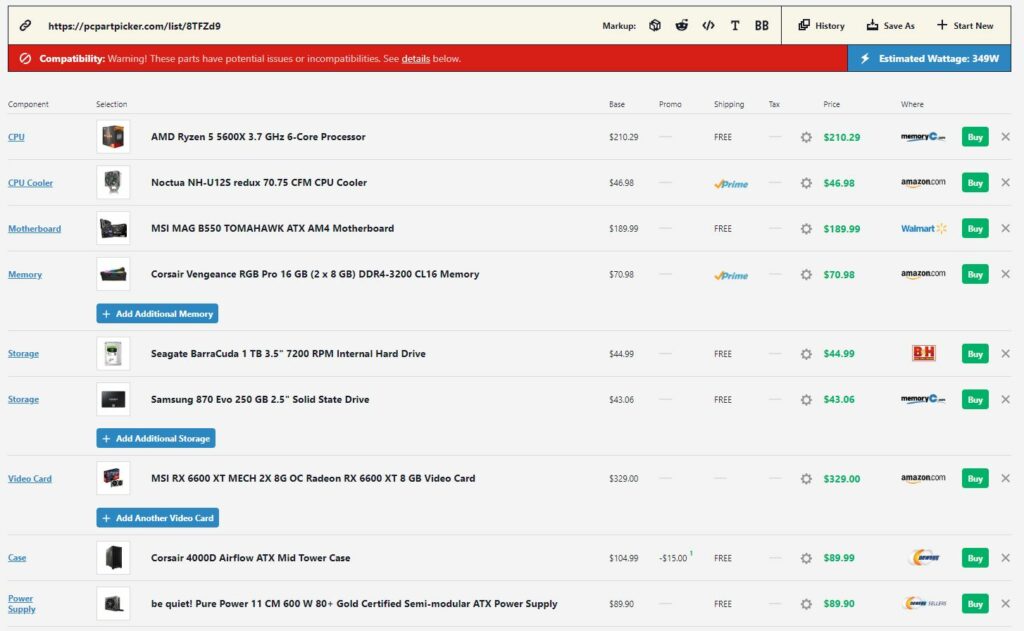
- The AMD Ryzen 5 5600X, despite being a generation old, remains an excellent mid-range processor choice. Its low 65W[13] power requirement offers significant power savings compared to its Intel counterpart.
- Secondly, looking at the graphics card, we’re using the AMD Radeon RX 6600 XT. Although, you can go with other options, such as the RX 580, RX 5700 XT, or even the RX 6600. Nonetheless, the AMD Radeon RX 6600 XT has a recommended power requirement of 160W.[14]
Be that as it may, the mid-range AMD build has an estimated power consumption of ~349W. Thus, a 600W power supply can run the PC without any problems. You can also mix and match Intel and AMD products to get a build of your liking. But for the most part, you need 600-700W power to run a mid-range gaming PC.
High-End Gaming PC Power Usage
High-end gaming PCs demand substantial power, typically ranging from 1,200 to 1,500W. These systems come at a premium cost, with PC parts currently more expensive than ever.
High-End Intel Gaming PC
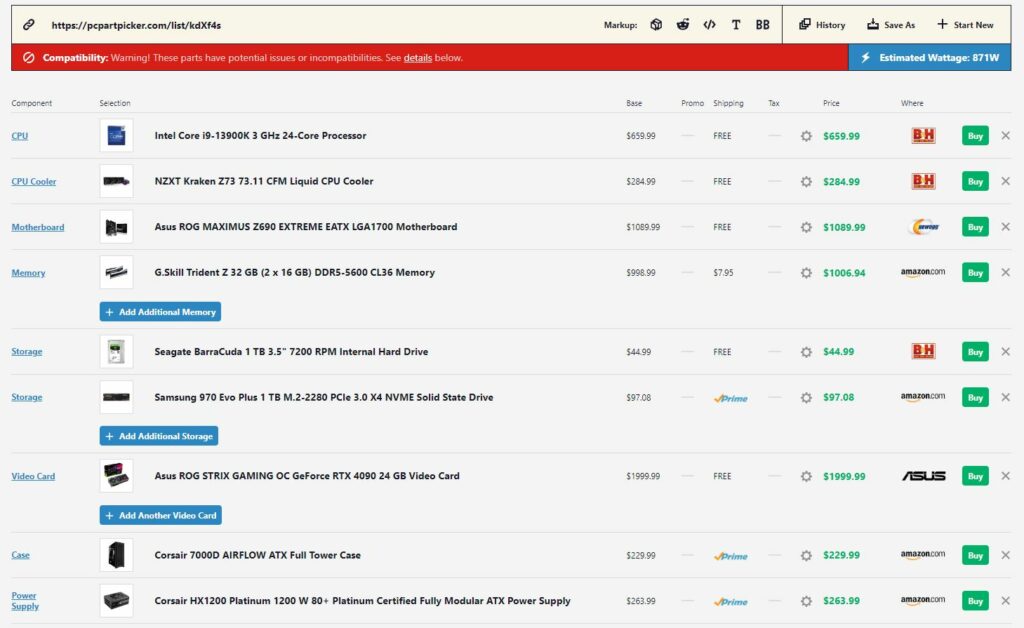
- In the high-end segment, the Intel i9-13900K is a flagship processor, matched only by AMD’s Ryzen 7900X. With exceptional performance comes higher power demands, reflected in the i9-13900K’s TDP range of 125-253W[15].
- Various GPU options are available for high-end builds, such as the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080, RTX 3090, RTX 3090 Ti, and RTX 4080. In this scenario, the 4090 is utilized. With an estimated power usage ranging from ~450W to 600W,[16] it’s noteworthy that this GPU is known to exceed 800 watts of power consumption at peak usage.
When all components are factored in, the estimated wattage typically reaches ~871W for a high-end Intel build. Hence, opting for a 1,200W power supply or higher is advisable, with a recommendation of 1,500W or greater if overclocking is planned. If done incorrectly, overclocking may risk damage to the GPU and other components and elevated temperatures, necessitating knowledge of how to lower GPU and CPU temperatures.
In conclusion, purchasing an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 is a better deal than buying the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4080. Also, in place of an Intel Core i9-13900K, consumers can go with the Intel Core i7-13700K or even the Intel Core i9-12900K. You can also check out our Intel Core i9-13900K vs Intel Core i9-12900K guide.
High-End AMD Gaming PC
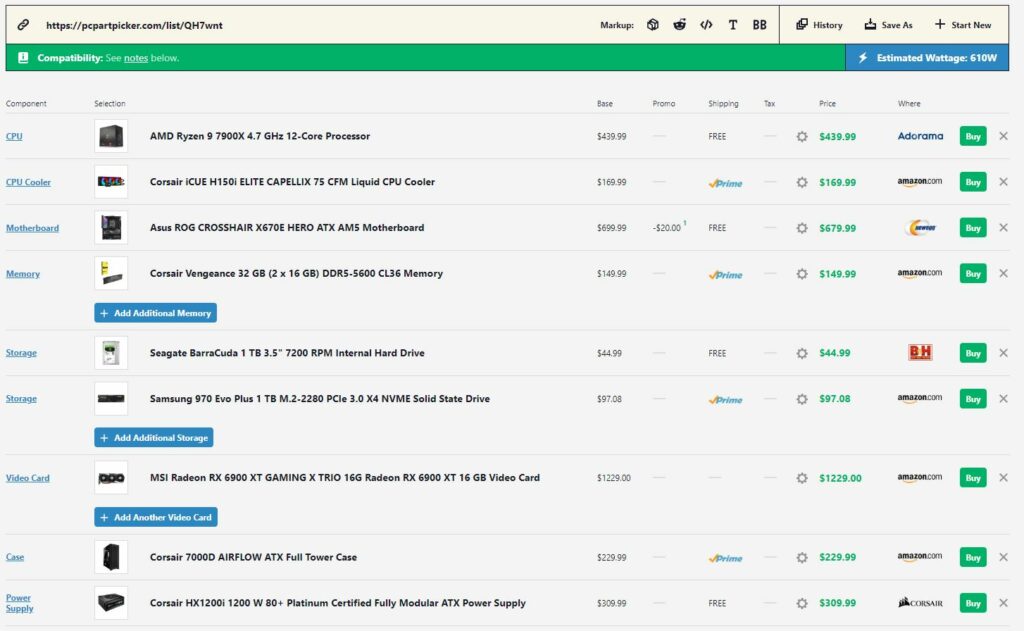
- Firstly, regarding the processor, we have the AMD Ryzen 9 7900X, which is the company’s flagship processor. However, other options, such as the Ryzen 7 5800X3D Vs the Ryzen 7 7700X, are also present. Furthermore, the AMD Ryzen 9 7900X has a TDP of 170W.[17]
- Secondly, we’re using the AMD Radeon RX 6900 XT. In contrast with the processors, few AMD GPU segment options exist. For that reason, the only other high-end AMD option, for now, is the AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT. In any case, the AMD Radeon RX 6900 XT has a company TDP of 300W.[18]
Effects Of Insufficient Power On A PC
When your computer’s power supply unit is insufficient to meet its power requirements, you’ll notice the problems associated with inadequate power for your PC components.
If you find yourself in this situation without a way to upgrade your power supply, here are the things that you can expect to happen, as well as the best course of action you can take:
- Avoiding Upgrades: If your PSU is on its last legs, prioritize upgrading it before any other component. Neglecting this could risk damaging current and future components, as faulty power supplies commonly cause system failures.
- Revert Any Overclocking: Overclocking involves pushing components beyond their intended limits for increased performance, which strains the power supply. If your PSU is failing, it’s best to undo any overclocking, regardless of scale, to relieve stress on the system.
- Crashes: If your system crashes under heavy load, it likely indicates an inadequate power supply not meeting the system’s required TDP, potentially leading to GPU crashes. Insufficient power can cause crashes during heightened PC activity, including:
-
- Inserting a thumb drive.
- Opening your optical drive.
- Performing heavy workloads like gaming or productivity.
- Loading medium to large-sized files, especially on hard drives.
- Make your fans ramp up in any way.
- PSU Failure: Constant low power to your components can mess up their working and cause a short circuit, frying your computer. So, if you detect burning components or smell smoke from your PC, promptly unplug it and address any fires. Then, test components individually or seek professional assistance. Salvage usable parts and ensure your PC has sufficient power to prevent future issues.
Final Words
In conclusion, low-end builds require anywhere between 300-400W of power. On the other hand, mid-range builds require an average of 500-600W of power. Consequently, high-end builds require 1,200-1,500W of power. So, on average, if you mix and match components from all builds, the overall gaming PC power usage is between 400-700W- power.
More Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
- How To Fix AIO CPU Fan Not Working
- Replace GPU Fans [All Steps Guide]
- RGB Fusion 2.0 Not Detecting GPU [FIXED]
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 Vs. AMD Radeon RX 6900 XT
- Single-Rail Vs. Multi-Rail PSU
- EVGA Vs. Corsair PSU
- Best Gaming PC Build Under $1500 In 2023
- Build a Gaming PC In 2023
- Best Gaming PC Build Under $2000 [Top Rated]
- Build A White Gaming PC in 2023
- How Much Does It Cost to Ship A PC?
- How long Do Gaming PCs last?
References:
-
3DCenter.org. Lounch-Analyse nVidia GeForce RTX 3060. Retrieved from http://www.3dcenter.org/artikel/launch-analyse-nvidia-geforce-rtx-3060
-
AMD. AMD Radeon RX 6600 XT Graphics Card. Retrieved from https://www.amd.com/en/products/graphics/amd-radeon-rx-6600-xt
-
LDLC. AMD Ryzen 5 3600 (3.6 GHz / 4.2 GHz). Retrieved from AMD Ryzen 5 3600 (3.6 GHz / 4.2 GHz) – Processor – LDLC | Holy Moley
-
Intel. Intel Core i5-11600K Processor. Retrieved from https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/212275/intel-core-i5-11600k-processor-12m-cache-up-to-4-90-ghz.html
-
AMD. AMD Ryzen 9 7900X Desktop Processor. Retrieved from https://www.amd.com/en/products/processors/desktops/ryzen/amd-ryzen-9-7900x.html
-
Intel. Intel Core i9-13900K Processor. Retrieved from https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/sku/230496/intel-core-i913900k-processor-36m-cache-up-to-5-80-ghz/specifications.html
-
Intel. Intel Core i3-6300 Processor. Retrieved from https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/sku/90731/intel-core-i36300-processor-4m-cache-3-80-ghz/specifications.html
-
nVIDIA. GeForce GTX 1050 Ti Specifications. Retrieved from https://www.nvidia.com/en-gb/geforce/graphics-cards/geforce-gtx-1050-ti/specifications/
-
B & H. AMD Ryzen 5 1600 3.2 GHz Six-Core AM4 Processor. Retrieved from AMD Ryzen 5 1600 3.2 GHz Six-Core AM4 Processor YD1600BBAEBOX (bhphotovideo.com)
-
AMD. Radeon RX 550 Drivers & Support. Retrieved from https://www.amd.com/en/support/downloads/drivers.html/graphics/radeon-600-500-400/radeon-rx-500-series/radeon-rx-550.html
-
Intel. Intel Core i5-12600K Processor. Retrieved from https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/134589/intel-core-i5-12600k-processor-20m-cache-up-to-4-90-ghz.html
-
MSI. GeForce RTX™ 3060 GAMING X 12G. Retrieved from MSI GeForce RTX 3060 GAMING X 12G
-
AMD. AMD Ryzen 5 5600X Desktop Processors. Retrieved from https://www.amd.com/en/products/processors/desktops/ryzen/amd-ryzen-5-5600x.html
-
AMD. AMD Radeon RX 6600 XT Graphics Card. Retrieved from https://www.amd.com/en/products/graphics/amd-radeon-rx-6600-xt
-
Intel. Intel Core i9-13900K Processor. Retrieved from https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/sku/230496/intel-core-i913900k-processor-36m-cache-up-to-5-80-ghz/specifications.html
-
HLTV. RTX 4090 TDP. Retrieved from https://www.hltv.org/forums/threads/2573136/rtx-4090-tdp
-
AMD. AMD Ryzen 9 7900X Desktop Processor. Retrieved from https://www.amd.com/en/products/processors/desktops/ryzen/amd-ryzen-9-7900x.html
-
AMD. AMD Radeon RX 6900 XT Graphics. Retrieved from https://www.amd.com/en/products/graphics/amd-radeon-rx-6900-xt
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads
![What Is A Modular PSU? [Pros & Cons] Modular Bay](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/REVOLUTION-D.F.-2-1200W-Gold-Modular-Bay-218x150.jpg)

![What Is RPM In PC Fans? [All Explained]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/HOW-TO-2-1-218x150.jpg)
![Intel XMP [What, Why, & How] XMP Profile](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/XMP-Profile-218x150.jpg)