Keeping your PC operating under its thermal limit is crucial to prevent thermal throttling. There are various methods that are utilized for cooling. The most common method is using cooling fans. But, to choose a cooling fan that meets your requirements, you will need to have some knowledge about its parameters. One of these parameters is RPM, which I will discuss in this article.
Also Read: What Are CPU Coolers?
Key Takeaways
- RPM or Revolutions Per Minute is the measure of the rotational speed of a rotating object, usually a fan.
- Fans with higher rotational speeds can provide more cooling, but they will also make more noise.
- There are various methods of regulating fan speeds, such as BIOS settings, software utilities, fan controllers, or PWM techniques.
What Is RPM?

RPM is used to measure the speed of cooling fans[1] in a PC case or on components like the CPU and GPU. Fan RPM indicates how many revolutions the fan makes in a minute[2]. This measurement is important because it affects how much air the fan can move, affecting the cooling performance of the component it’s attached to. Higher RPM fans tend to move more air but can be noisier[3].
Also read: CPU Cooler Buying Guide
What Is A Good Fan RPM?
The appropriate fan RPM depends on several factors, including the fan size, intended use, and the desired balance between performance and noise. Let’s discuss good fan speeds for different fan sizes and their impact:
120mm Fans

120mm fans are usually used in medium-sized gaming rigs with adequate space[4]. The main advantage these fans offer over 140mm fans is their size. However, due to smaller blade sizes, 120mm fans need to operate at high rotational speeds to achieve performance similar to their 140mm counterparts.
Hence, while giving the same performance, the 120mm fans will sound more than the fans with larger blades. Generally, a rotational speed of 750-1000 RPM is considered good for 120mm fans.
140mm Fans

Coming to the 140mm fans, they benefit from their larger blade size[5]. As a result, they can offer good performance at comparatively low rotational speeds. However, due to their large size, they cannot be used in compact and small form factor builds. On the brighter side, you can get good performance at low RPMs from these fans, minimizing the noise levels[6].
However, if you operate a 140mm fan at a rotational speed similar to a 120mm fan, the larger one will sound more but also give better performance. A speed range of 600-800 RPM is considered good for the 140mm fans.
Check out:
Impact Of Performance On Noise Level
When choosing fan speed, it’s essential to consider the trade-off between performance (cooling efficiency) and noise levels[7]. Higher RPM fans generally provide better cooling performance because they can move more air, but they tend to generate more noise as a result. On the other hand, lower RPM fans are quieter but might not provide the same level of cooling performance, especially in high-demand situations.
The best choice of fan speed depends on your specific needs and preferences. However, if noise is a top priority and your system is not heavily overclocked or subjected to extreme loads, opt for fans with lower RPMs. Otherwise, if you’re building a high-performance system or plan to overclock, you might need fans with higher RPMs to ensure efficient cooling, but this might come at the cost of increased noise.
How To Change RPM?
Changing fan RPM for cooling fans in a PC depends on several factors, including the type of fans you have and the hardware and software tools available to you[8]. Here are the general steps you can take:
Method 1: BIOS/UEFI Settings
Many motherboards allow you to control fan speeds directly from the BIOS or UEFI settings[9]. Here’s how you can do it:
Step 1: Restart your computer and access the BIOS/UEFI settings by pressing a specific key (often Delete, F2, F10, or F12) during the boot process. The specific key varies depending on your motherboard manufacturer.
Step 2: Look for a section related to hardware monitoring, fan controls, or something similar.
Step 3: Depending on your motherboard, you might find options to set fan profiles (e.g., Quiet, Standard, Performance) or manually adjust fan curves based on temperature thresholds.
Method 2: Software Tools
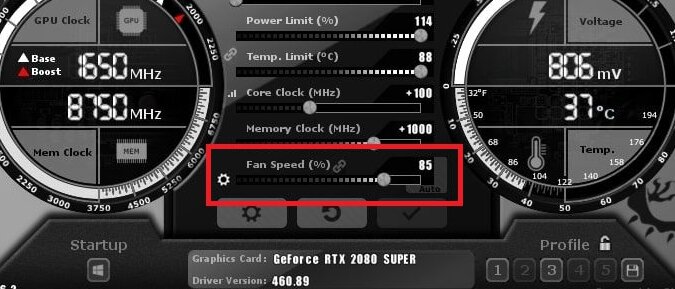
Some motherboards come with software utilities that allow you to control fan speeds from within the operating system. Additionally, there are third-party software tools that can help you achieve this as well. A couple of popular options are:
- SpeedFan: A widely used third-party software that provides detailed control over fan speeds and temperature monitoring. It works with a wide range of motherboards.
- MSI Afterburner: While primarily known for GPU overclocking, this utility can also control certain system fans on MSI motherboards.
Also Read: Can Overclocking Damage The GPU?
Method 3: Fan Controllers

Some cases or aftermarket accessories come with hardware fan controllers. These can be knobs, buttons, or even digital displays that allow you to manually adjust fan speeds without accessing the BIOS or using software tools.
Method 4: PWM Or Voltage Control

Most modern fans use one of two control methods: PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) or voltage control[10]. PWM fans are controlled by adjusting the power they receive in rapid pulses, while voltage-controlled fans have their speed regulated by altering the voltage supplied to them. PWM control is more precise and allows for finer adjustments.
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
References:
- Good RPM For CPU Fan. Retrieved from https://softwareg.com.au/blogs/computer-hardware/good-rpm-for-cpu-fan
- Chapter 1 – Recommendations Based on Fan Evaluations. Retrieved from https://afs.ca.uky.edu/poultry/chapter-1-recommendations-based-fan-evaluations
- Noise Control in PCs – Reduction of Noise in PCs. Retrieved from https://www.nonoise.org/resource/pcnoise/poweroid/poweroid.htm
- Computer fan – a guide to sizes and types. Retrieved from https://www.akyga.com/news-list/86-computer-fan-a-guide-to-sizes-and-types.html
- 120mm Vs 140mm Fans: Comparing Efficiency and Performance. Retrieved from https://gadgetmates.com/120mm-vs-140mm-fans
- Kia Javadi.(2024).Best 140mm Radiator Fan: Top Choices For Superior Cooling Performance. Retrieved from https://gadgetmates.com/best-140mm-radiator-fan
- Improving Fan System Performance – A Sourcebook for Industry. Retrieved from https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy03osti/29166.pdf
- Lenovo. How does a computer fan work? Retrieved from https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/glossary/fan/?orgRef=https%253A%252F%252Fwww.google.com%252F
- DellPoweredge-R710-OwnersManual.pdf. Retrieved from https://www.coloradosos.gov/pubs/elections/VotingSystems/DVSDemocracySuite513/documentation/DellPoweredge-R710-OwnersManual.pdf
- CPU cooling using PWM interfaced peltier unit. Retrieved from https://www.academia.edu/35424263/CPU_cooling_using_PWM_interfaced_peltier_unit
FAQs
It stands for “Revolutions Per Minute.” It is the measure of the rotational speed of a rotating object, usually a fan.
A high RPM fan provides more cooling at the expense of more noise.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads![When Xbox Is Off, Turn Off Storage [Feature Explained] When Xbox Is Off, Turn Off Storage](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/When-Xbox-Is-Off-Turn-Off-Storage-1.jpg)
![PSU ATX 3.0 Standard [Explained] Front Box](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Front-Box-218x150.jpg)

![What Are DIMM Slots? [Which One To Use First?]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/HOW-TO-10-218x150.jpg)
![What Is FPI In Radiators? [Clearly Explained]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/HOW-TO-8-218x150.jpg)