Have you ever started to face sudden FPS drops and stuttering while playing a graphics-intensive game? What you were facing is likely thermal throttling.
Key Takeaways
- Thermal throttling is caused when a CPU/GPU starts overheating and drawing less power (thus reducing performance) to cool down.
- Every CPU and GPU starts thermal throttling at a specific temperature called TjMax or Maximum Junction Temperature. This varies from 85°C-105°C for CPUs and 90°C to 110°C for GPUs.
- The key signs of thermal throttling are drops in performance and stuttering. At the same time, CPU/GPU clock speeds and power consumption will be reduced.
- Thermal throttling is caused by many factors, including dust buildup on your components, drying thermal paste, and inadequate cooling in general.
Thermal Throttling (Or Dynamic Frequency Scaling)
Firstly, it’s important to note that the thermal throttling of the CPU and GPU are almost entirely similar processes; that is: both components lower their power consumption to lower heat production.
Thermal throttling occurs when your CPU/GPU starts producing more heat than it can dissipate, lowering the power it receives[1]. Lower power also means lower core clock speeds (also memory clock speed for GPUs). This usually occurs when running a graphics-intensive game or performing rendering workloads.
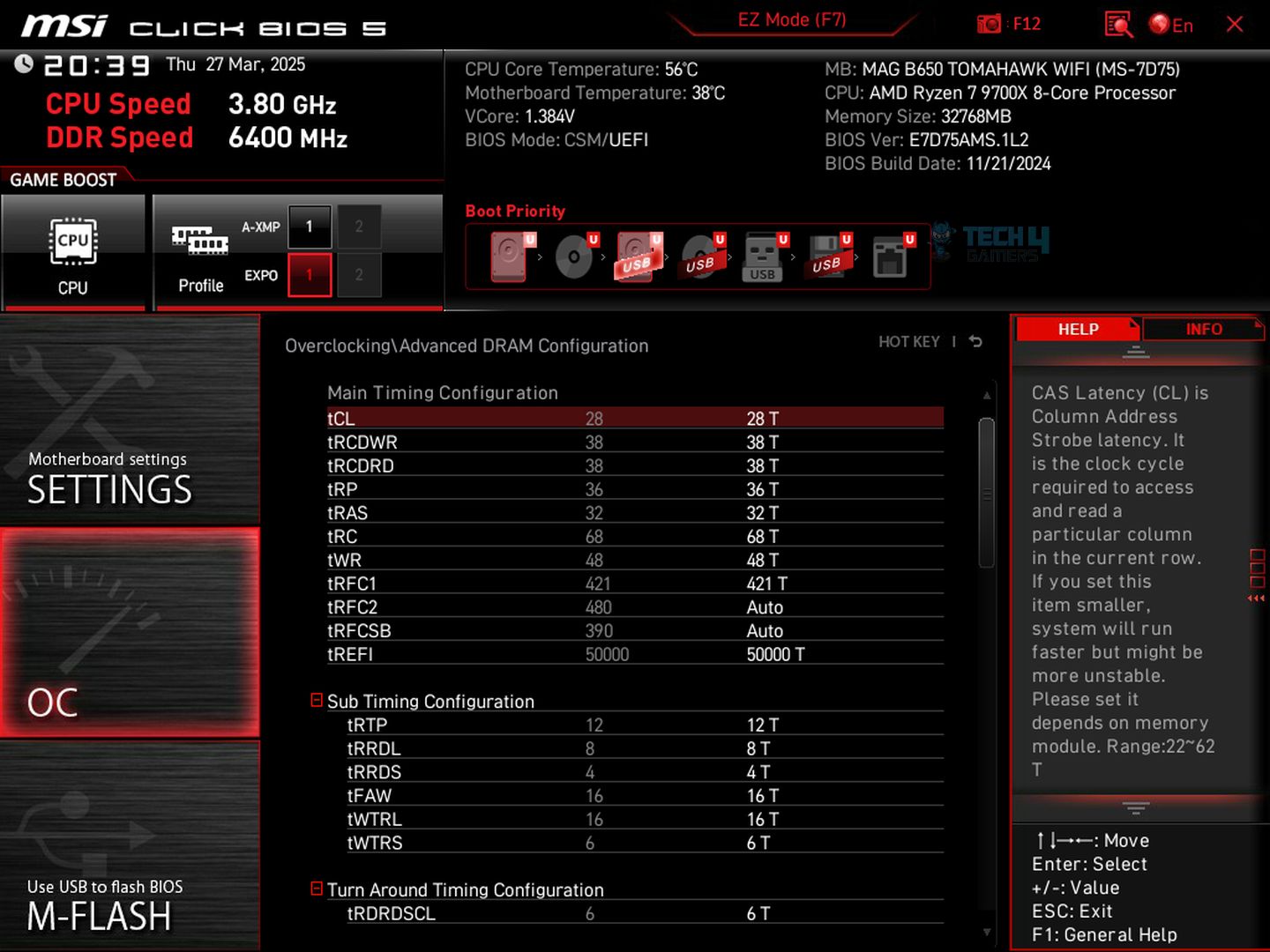
Thermal throttling also occurs with RAM, typically when the RAM is overclocked.
At What Temperature Does Thermal Throttling Start To Occur?
The temperature at which thermal throttling occurs is called TjMax (or maximum junction temperature). It’s also called maximum operating temperature[2]. The value varies with different CPUs and GPUs. This temperature is generally between 100°C-105°C for Intel CPUs and 85°C-95°C for AMD’s Ryzen CPUs. Meanwhile, for graphics cards (Nvidia and AMD), the temperature varies from 90 °C to 110 °C.
Also Read: GPU Idle Temperature
For laptop CPUs and GPUs, the maximum junction temperature limit is typically less than their desktop counterparts. This is because they usually have less efficient cooling and less room to dissipate the heat.
To find the TjMax rating of your CPU/GPU, refer to the specs sheet on the manufacturer’s website. You might also be interested in learning about the CPU temperature while gaming.
What Are The Signs Of Thermal Throttling?
There are two key signs of thermal throttling. Note that both these signs are correlated to each other. If you’re facing FPS drops or low FPS in general, but your CPU/GPU temperatures and clock speeds are normal, you’re not facing thermal throttling.
Performance Drop
Thermal throttling protects your hardware from critical damage but comes at a cost. When thermal throttling occurs, your CPU and GPU are forced to reduce performance because they receive less power[3]. As a result, you’ll face sudden FPS drops in games with stuttering and potential crashes.
The impact on performance depends on workload and CPU cooler quality. In extreme cases, games may crash, graphics distort, or the system shut down for protection. Rendering speed can dramatically slow, potentially leading to PC shutdowns.
High Temperatures (Plus Lower Power Consumption And Clock Speeds)
The heading is self-explanatory; you’re likely facing thermal throttling if you see:
- Temperature is close to or exceeding TjMax value.
- Decreasing power consumption.
- A drop in core clock (and memory clocks for GPUs) frequencies.
High temperatures mean your CPU/GPU fans will start spinning at maximum RPM, so expect noise from your fans too[4]. Learn more about how to lower GPU temperature and CPU temperature.
To keep an eye on these figures, you’ll have to turn on in-game monitoring of these particular figures. You can do that by using MSI Afterburner.
How To Keep An Eye Out For Thermal Throttling
You can watch out for thermal throttling in advance by monitoring your CPU/GPU temperatures. If the temperature hits 80°C and keeps gradually increasing, you will eventually face thermal throttling.
Is Thermal Throttling Bad For Your CPU/GPU?
Thermal throttling in itself is not a bad thing, as it’s simply a mechanism to protect your CPU and GPU from damage.
However, thermal throttling indicates your CPU/GPU is running too hot. And even though your CPU/GPU can run perfectly fine below the TjMax, temperatures near the thermal throttling limit generally indicate something is wrong. Optimally, your CPU and GPU should run under 80°C, even at 100% load.
If your CPU/GPU is thermal throttling, you should look to pinpoint the problem causing high temperatures and fix it. Continually running your CPU/GPU after it hits the maximum junction temperature can shorten its lifespan[5].
How To Prevent Thermal Throttling
A variety of reasons can cause thermal throttling. These include but are not limited to dried-out thermal paste, dust buildup inside your case, and an inadequate cooling solution[6]. Here are a few fixes that might fix your thermal throttling problem:
Remove Excess Dust From Your Case
Even if you have a triple-fan GPU or a beefy CPU liquid cooler, dust will prevent it from running optimally and cause thermal throttling. Use a compressed air can or an air blower to eliminate excess dust inside your PC case and target all the fans. We also have a detailed guide on how to clean your PC without compressed air.

Reapply Thermal Paste
Good-quality thermal paste can last up to 5-7 years, so if you recently applied thermal paste, this step won’t help you. To reapply it, you’ll need to learn how to properly remove it first.
The dried thermal paste on the GPU is a common issue, especially with older GPUs or those bought used. Replacing the thermal paste, although more complex than on the CPU, is a good idea after a few years of use. Proceed carefully when doing so.
Reverse Any Overclocking Changes
If you have overclocked your CPU (manual overclocking or Intel Turbo Boost) or your GPU and are dealing with thermal throttling, turning off overclocking will likely help[7].
Get A Better Cooler (For CPUs)
You may be facing CPU thermal throttling simply if your present cooler is inadequate to cool your CPU. This might especially be the case if you have a high-end CPU (such as an Intel Core i7 or an AMD Ryzen 7) and the ambient temperature in your room gets too high in the summer.

Install Case Fans / Improve Airflow
You should ensure optimal airflow inside your case. For this, you should have at least two fans inside your case—one for intake and one for exhaust. Ideally, two fans in the front for intake and one in the back for exhaust is enough for most mid-to-high range systems.
Undervolting Your CPU/GPU
Undervolting is somewhat of an extreme measure and should only be done as a last resort. It lessens the amount of voltage (and consequently heat) received by your CPU or GPU[8]. Undervolting requires trial and error to find a stable value. In any case, decrease the voltage in small increments and test it out. Once you fail, return to the value you set before that.
Ensuring Your PC Is Running In An Air-Conditioned Room
You should use your PC in an air-conditioned room if you live in a warm climate where temperatures can shoot too high for comfort (35°C or higher).
A Larger Case (For GPUs)
Final Thoughts
Thermal throttling may seem daunting when it initially occurs, but it’s a very important measure to protect your CPU and GPU from damage. It is simply a sign of overheating, so you should turn your attention and follow the steps I’ve mentioned to try and lower those temperatures.
Related Helpful Articles By Tech4Gamers:
References:
- Karen Stealey (2023). What is thermal throttling and how does it impact gaming?. Retrieved from https://insights.samsung.com/2022/08/23/what-is-thermal-throttling-and-how-does-it-impact-gaming/
- Information about Temperature for Intel® Processors. Retrieved from https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/support/articles/000005597/processors.html
- Karen Stealey. What is thermal throttling and how does it impact gaming. Retrieved from https://insights.samsung.com/2022/08/23/what-is-thermal-throttling-and-how-does-it-impact-gaming/
- Identifying High temperatures, Heat, Thermal Concerns, Fan Noise on Dell Laptops. Retrieved from https://www.dell.com/support/kbdoc/en-us/000130447/identifying-high-temperature-heat-thermal-concerns-fan-noise-on-dell-notebook-systems
- Customer concern–Does running the CPU at high temperatures for extended periods of time impact its quality and lifespan. Retrieved from https://www.dell.com/support/kbdoc/en-in/000212668/customer-s-concern-running-the-cpu-at-high-temperatures
- Explained: Thermal Throttling, Why It Happens and How To Prevent It. Retrieved from https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/gadgets-news/explained-thermal-throttling-why-it-happens-and-how-to-prevent-it/articleshow/96969669.cms
- How To Reverse Overclocking CPU. Retrieved from https://softwareg.com.au/blogs/computer-hardware/how-to-reverse-overclocking-cpu
- Luigi Oppido. How to Undervolt a GPU to Lower Temps and Reduce Power Usage. Retrieved from https://www.wikihow.com/Undervolt-Gpu
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. Thermal throttling reduces FPS in games as the CPU/GPU starts drawing less power and lowers its clock speeds.
Thermal throttling does not damage your CPU or GPU – it protects them. However, if you continue to run your CPU/GPU at such high temperatures, then there’s a possibility of damage.
Depending on the root cause, you can try different things to fix thermal throttling. These include cleaning your components of dust, reapplying thermal paste, and upgrading your cooling solution.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


![AMD EXPO [Features & How You Can Enable It]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/CORSAIR-VENGEANCE-RGB-DDR5-RAM-32GB-2x16GB-6000MHz-CL30-AMD-EXPO-RGB-Lighting-3-218x150.jpg)
![Intel XMP [What, Why, & How] XMP Profile](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/XMP-Profile-218x150.jpg)