Are you looking to buy an Intel CPU and have encountered the term “Hyper-Threading”? In this article, we’ll explain the unique technology found in Intel chips.
Key Takeaways
- Intel Hyper-Threading technology splits a core into two threads so that the core can perform more tasks in parallel.
- The technology is helpful for multithreaded tasks. Meanwhile, it provides no performance improvement in single-threaded tasks.
- It leads to higher power consumption and heat output. Also, CPUs with Hyper-Threading tend to cost more than those without it.
Intel Hyper-Threading
Hyper-Threading is the name of Intel’s Simultaneous Multithreading Technology (SMT) implementation. Hyper-Threading splits a core into two threads (rather than one) to process more workloads than the standalone thread can handle[1]. These threads are also called logical or virtual cores.
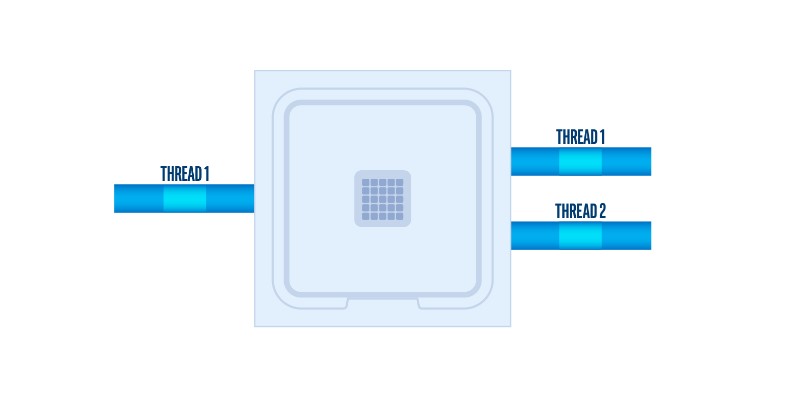
Each logical processor can function independently of the other in the same core to execute specific threads or instructions. More logical processors mean more work can be done in parallel[2]. Thus, the cores and the CPU can be better utilized to their full potential.
- Advantages: Hyper-Threading can benefit you depending on the workload. Multithreaded workloads benefit from Hyper-Threading and perform much better with it than without it[3]. It also speeds up multitasking.
- Disadvantages: Hyper-Threading has no significant drawbacks, as modern games and programs increasingly rely on multiple threads. However, CPUs with Hyper-Threading do use more power and generate more heat[4]. Furthermore, CPUs with Hyper-Threading cost more than those without Hyper-Threading.
Single-threaded tasks don’t benefit from Hyper-Threading. This is especially true for old games (earlier than 2010) that only need a single thread and benefit from high clock speeds instead.
In sporadic cases, Hyper-Threading can lead to a performance decrease [5](though you most likely won’t encounter such a case). This may occur because the core’s resources, such as cache, execution engine, and functional units, are shared between the two threads in a Hyper-Threaded core.
Hyper-Threaded Core Vs Dual-Cores
It should be remembered that a single core with Hyper-Threading does not equal two cores (without Hyper-Threading)[6]. Hyper-Threading does not replicate entire cores; it only doubles the instruction pipeline for a single core to utilize the core more efficiently.
It’s important to remember this general principle:
Hyper-Threaded Dual-Core CPU > Dual-Core CPU without Hyper-Threading > Hyper-Threaded Single-Core CPU > Single-Core CPU without Hyper-Threading
Thus, a single core with Hyper-Threading is better than the same core without Hyper-Threading. The same applies to dual-core CPUs.
Does My Intel CPU Have Hyper-Threading?
First, if you have a Rocket Lake (10th gen) or newer Intel CPU, your CPU has Hyper-Threading support unless it’s one of the Celeron chips[7]. For older CPUs, refer to the specs sheet for that particular CPU.

Hyperthreading support is one of the aspects to look out for when choosing an Intel CPU — read about how to select a CPU to know what other factors you should consider.
Should I Enable Hyper-Threading?
If your CPU supports Hyper-Threading, the feature will already be enabled by default[7]. And yes, you should keep Hyper-Threading enabled if you have already invested in a CPU with Hyper-Threading support. It can provide a substantial performance boost depending on your specific workload(s).
More resources by Tech4Gamers:
References:
- Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology. (n.d.). [Harvard.edu]. Retrieved from https://read.seas.harvard.edu/cs161/2022/pdf/intel-hyperthreading.pdf
- Multi-core processors and the future of parallelism in software. (n.d.). [Ryan Christopher Youngman] . Retrieved from https://scholarworks.lib.csusb.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=4193&context=etd-project
- Journals, E. (2016, February 7). MULTICORE PROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY ADVANTAGES AND CHALLENGES. Retrieved from https://www.academia.edu/21674512/MULTICORE_PROCESSOR_TECHNOLOGY_ADVANTAGES_AND_CHALLENGES
- Balancing Power Consumption in Multiprocessor Systems. (n.d.). [EuroSys]. Retrieved from https://os.itec.kit.edu/downloads/publ_2006_merkel-bellosa_balancing-power.pdf
- Multiprogramming Performance of the Pentium 4 with Hyper-Threading. (n.d.). [James R. Bulpin and Ian A. Pratt]. Retrieved from https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=b924b526a1dc655eb02c284349feeb819c840982
- Can Hyper-Threading Improve Gaming Performance? | Lenovo CA. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.lenovo.com/ca/en/glossary/what-is-hyperthreading/
- Here’s how Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology (Intel® HT Technology). (n.d.). What is hyper-threading? Retrieved from https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/gaming/resources/hyper-threading.html
Frequently Asked Questions
Intel Hyper-Threading divides each core into two threads to execute more instructions in parallel. It keeps the CPU cores from idling and utilizes them more efficiently.
Almost every modern game, especially graphics-intensive ones, can utilize Hyper-Threading to provide better performance. However, games older than 2010 generally won’t benefit from Hyper-Threading, and FPS will not be improved.
If you have an Intel CPU that supports Hyper-threading, you should keep it enabled as it can provide significant performance improvement, and its disadvantages are minimal.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads![What Is A Modular PSU? [Pros & Cons] Modular Bay](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/REVOLUTION-D.F.-2-1200W-Gold-Modular-Bay-218x150.jpg)
![Mouse Polling Rate [What, Why, & How]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/HOW-TO-4-218x150.jpg)
![PC Heatsink [What, How & Guide]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/HOW-TO-6-1-218x150.jpg)

![PSU ATX 3.0 Standard [Explained] Front Box](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Front-Box-218x150.jpg)