As the brain on the system, it is the CPU‘s responsibility to calculate and execute instructions. However, the speed at which it performs said calculations depends on various crucial factors, and the CPU clock speed is one of them. In this article, we will take you through various aspects of clock speed that will help you decide while choosing a CPU.
Key Takeaways
- CPU clock speed is the number of computation cycles a CPU can execute in one second. It is written in GHz most of the time. The greater the clock speed, the faster the CPU executes instructions.
- Turbo Frequency allows modern CPUs to operate temporarily at clock speeds higher than their base clock speed.
- You can adjust the CPU’s clock speed by adjusting the CPU’s multiplier or base clock frequency through BIOS/UEFI settings.
- A good clock speed for gaming lies between 3.5 GHz to 4.0 GHz, while clock speeds above this are considered excellent.
What is CPU Clock Speed?

Measured in Hertz (Hz), the CPU clock speed, or clock rate or frequency, refers to the number of cycles a CPU can execute per second[1]. For example, if your processor has a clock speed of 4.0 GHz (Gigahertz), then it means it can execute 4 billion computation cycles in just a second.
A CPU’s clock speed is determined by an integrated oscillator, which generates electrical pulses that synchronize the data flow within the CPU. Each pulse represents a single cycle of processing[2]. The CPU’s clock speed is higher when the pulses are faster. Therefore, a higher clock speed can execute more instructions in less time, leading to better performance[3].
What is Turbo Frequency?
Turbo Frequency, or Turbo Boost, allows modern CPUs to operate temporarily at clock speeds higher than their base clock speeds. It is an automatic overclocking feature that kicks in when the CPU is under heavy load and needs to perform at maximum performance[4].
For instance, a CPU with a 3.0 GHz base clock and a Turbo Frequency of 4.5 GHz can temporarily boost to 4.5 GHz under heavy loads, reverting to base speed when the workload decreases. Turbo Frequency adjusts based on temperature, power, and workload, but not all CPUs have this feature[5]. Check your CPU’s specs to know its capabilities.
How To Adjust CPU Clock Speed?
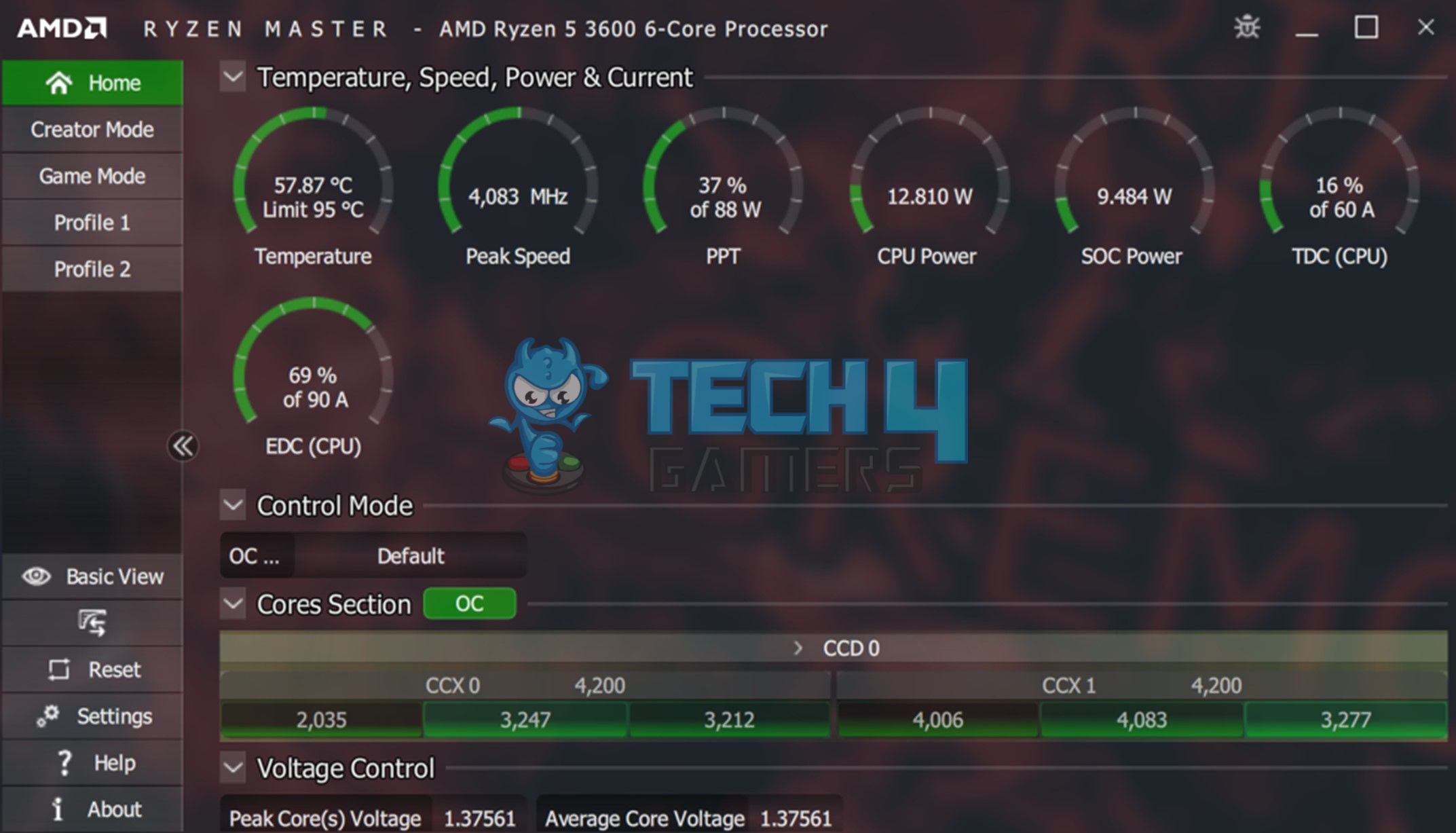
While it is generally not recommended for you to interfere with the default CPU clock speed, some CPUs allow users to increase the CPU clock speed through overclocking.
Overclocking increases the CPU’s clock speed beyond its rated speed, typically by adjusting the CPU multiplier or base clock frequency in the computer’s BIOS or UEFI settings[6]. Overclocking can result in higher CPU performance, but it also generates more heat and may require additional cooling solutions to prevent overheating.
Overclocking also has certain risks, such as voiding the CPU’s warranty, stability issues, data loss, or permanent CPU damage[7]. Thoroughly research overclocking’s risks and limitations before adjusting the CPU clock speed.
How Does CPU Clock Speed Impact Performance?
CPU clock speed is a critical factor that impacts the performance of a CPU. A higher clock speed allows a CPU to execute more instructions quickly, which results in faster performance[8]. This is particularly noticeable in single-threaded tasks, meaning they rely on a single CPU core to perform the calculations.
Also Read: CPU Threads
Remember, the CPU’s true capabilities aren’t solely determined by clock speed. Factors like cache capacity, architecture, and core count also play crucial roles in performance. Simply having a high clock speed doesn’t guarantee the best performance; optimizing all relevant factors is key.
What is a Good CPU Clock Speed for Gaming?
Typically, a good CPU clock speed for modern games is around 3.5 GHz to 4.0 GHz, and people consider 5.0 GHz excellent[9]. However, it’s important to note that CPU clock speed does not solely determine gaming performance. Factors such as game requirements, GPU performance, RAM speed, and storage speed also play a significant role in deciding the quality of gameplay.
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
- Base & Boost Clock Speeds For CPU/GPU
- How to fix Fan Speed
- How To Choose A CPU?
- CPU Threads
- CPU Cores
References:
- ARCHIVED: What is a computer’s clock speed. Retrieved from https://kb.iu.edu/d/aekt#:~:text=The%20unit%20of%20measurement%20called,)%20or%20gigahertz%20(GHz).
- ITE 115 Introduction to Computer Applications and Concepts. Retrieved from https://courses.lumenlearning.com/sanjacinto-computerapps/chapter/reading-the-central-processing-unit/
- What is clock speed. Retrieved from https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/glossary/what-is-clock-speed/?orgRef=https%253A%252F%252Fwww.google.com%252F
- Turbo Boost Technology (TBT) – Intel. Retrieved from https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/intel/turbo_boost_technology
- How do you use Intel® Turbo Boost Technology to speed up your processor? We’ll explain how it works. Retrieved from https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/gaming/resources/turbo-boost.html
- Sviat Soldatenkov (2 Jan 2024).What Is Overclocking a CPU? Explained in Detail. Retrieved from https://www.auslogics.com/en/articles/what-is-overclocking-a-cpu-explained-in-detail/
- Is It Okay To Overclock CPU. Retrieved from https://ms.codes/en-gb/blogs/computer-hardware/is-it-okay-to-overclock-cpu
- Clock speed. StudySmarter. Retrieved from https://www.studysmarter.co.uk/explanations/computer-science/computer-organisation-and-architecture/clock-speed/
- Sophie Sirois (December 18, 2018).What is Processor Speed and Why Does It Matter?. Retrieved from https://www.hp.com/us-en/shop/tech-takes/what-is-processor-speed
FAQs
While experts generally do not recommend it, you can manually increase the clock speed of some CPUs through careful overclocking.
CPU performance depends on multiple factors, including clock speed, architecture, cores, cache size, and memory speed, so higher clock speed alone does not guarantee optimal performance; a well-balanced system with optimized components is crucial for achieving the best overall performance.
Overclocking can improve CPU performance but can also lead to increased heat, potential stability issues, data loss, and voiding of warranty, requiring additional cooling and careful consideration of risks and limitations.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads
![Mouse Polling Rate [What, Why, & How]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/HOW-TO-4-218x150.jpg)
![Is A Laptop Considered A PC? [Explained] Is Laptop a PC](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Is-Laptop-a-PC-218x150.jpg)
![Can Motherboard Bottleneck Your PC? [CPU & GPU] Can Motherboard Bottleneck Your PC](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Can-Motherboard-Bottleneck-Your-PC-218x150.jpg)