Do different clock speeds like base clock speed, boost clock speed, and overclock speed often confuse you? Do not worry; we are here to explain these clock speeds in detail. At the end of this article, you will fully understand how these clock speeds are related and how they impact the performance of your PC.
- Base clock speed is the default speed at which your CPU runs, while boost clock speed is the temporarily higher speed when the load is heavy.
- Boost clock speed can be limited by VRM, cooling system, silicon quality, and the number of cores boosted simultaneously.
- Intel Turbo Boost and AMD Precision Drive are two features installed in Intel and AMD CPUs, respectively, that allow them to increase their clock speed depending on the workload dynamically.
What Is Base Clock Speed?
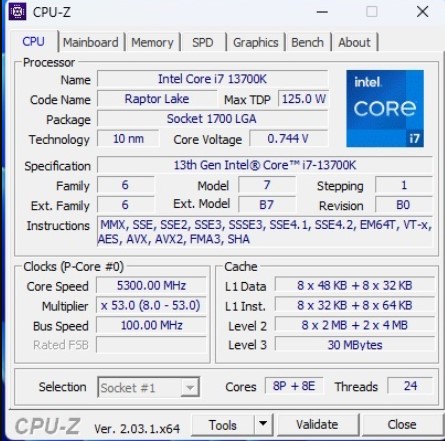
The base clock speed is the speed or frequency at which your CPU or GPU generally operates without any performance boost[1]. Usually, base clock speed is the default clock speed at which all the CPU and GPU devices operate. It is also your device’s lowest clock speed unless it supports underclocking. If your CPU has a base clock of 4.0 GHz, it will always run at this clock speed normally.
What Is Boost Clock Speed?
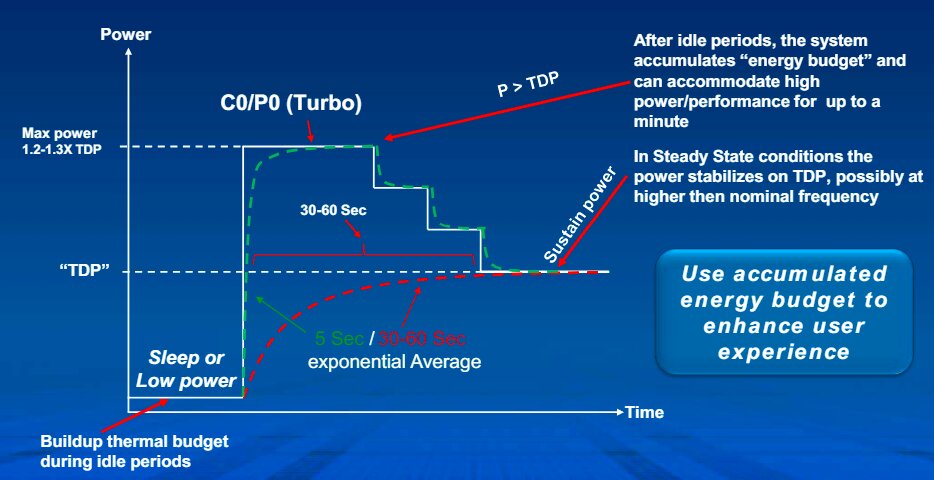
Another common clock speed you often hear in CPU or GPU discussions is the boost clock speed. The boost clock speed is the temporary high speed at which your CPU or GPU operates when it is under heavy load[2].
The good thing is you do not have to overclock your CPU or GPU to make it work at boost clock speed. The CPU or GPU automatically operates at the boost clock speed when the workload rises above a certain threshold. The clock speed eventually returns to the base clock speed when the workload declines.[3]
How Does Base Clock Speed Impact Performance?
Most of the time, your CPU or GPU will operate at the base clock speed. So, it is a crucial factor when deciding the performance of your PC. Devices with higher clock speeds tend to be faster as they can execute more instructions in less time[4]. If your GPU has a higher base clock speed, it will render heavy graphics in less time, resulting in a performance boost.
Boost Clock Speed vs Overclock Speed
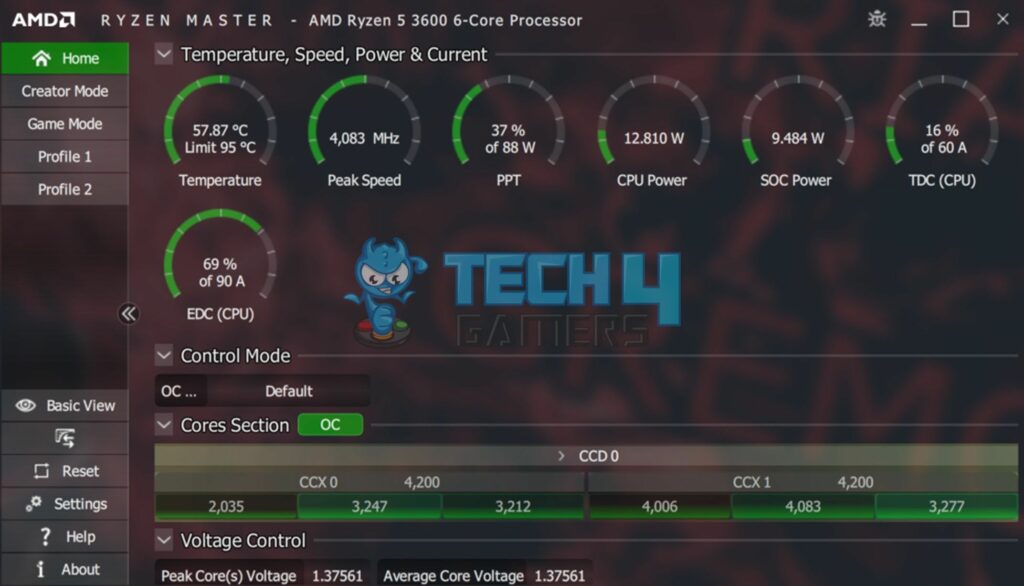
Boost clock speed is the built-in tendency of a CPU or GPU to operate at higher frequencies automatically. Meanwhile, the overclock speed refers to the higher clock speed achieved by manually overclocking the CPU or GPU. You do not have to overclock your CPU to operate at boost clock speed. However, to use it at overclocked speed, overclocking is required.
Overclocking has specific risks associated with it that can lead to damaging your component[5]. On the other hand, boosting clock speed is entirely safe[1]. It does not require you to temper your piece’s default operating conditions. Additionally, overclock speeds are higher than the boost clock speeds, which can lead to performance gain, but it is not risk-free.
What Are the Factors That Impact Boost Clock Speed?
While boost clock speed is a built-in feature, it does not necessarily mean it has no limitations. Various factors impact the boost clock speed. Some of them are discussed here:
- VRM of the Motherboard: VRM is the power-delivery unit that regulates and delivers power to all the components on the motherboard. To ensure a smooth experience with boost clock speed, you should ensure that the VRM on your motherboard can provide uninterrupted power to your CPU or GPU while operating it at boost clock speed. If your VRM is not capable enough, your device might be unable to work at boost clock speed.
- Cooling Solution: Keeping your CPU or GPU at optimal temperatures is necessary for a smooth experience. If the cooling solutions in your PC are not adequate, the CPU or GPU may be forced to operate at reduced clock speeds to avoid overheating.
- Silicon Lottery: This refers to the natural variation in silicon quality among CPUs and GPUs. Some chips can operate at higher clock speeds with lower voltage and better stability than others, which results in different real-life boost clock speeds for chips with identical specifications due to manufacturing variations[6]. However, quality control measures from Intel and AMD minimize the impact of this variation on clock speeds.
- Number of Boosted Cores: The boost clock speed in a multi-core CPU depends on the number of simultaneously boosted cores. Boost clock speeds are typically higher for fewer cores, allowing the CPU to devote more power to each core[7]. However, if too many cores are being boosted simultaneously, it can cause the CPU to overheat and reduce its boost clock speed.
Intel Turbo Boost
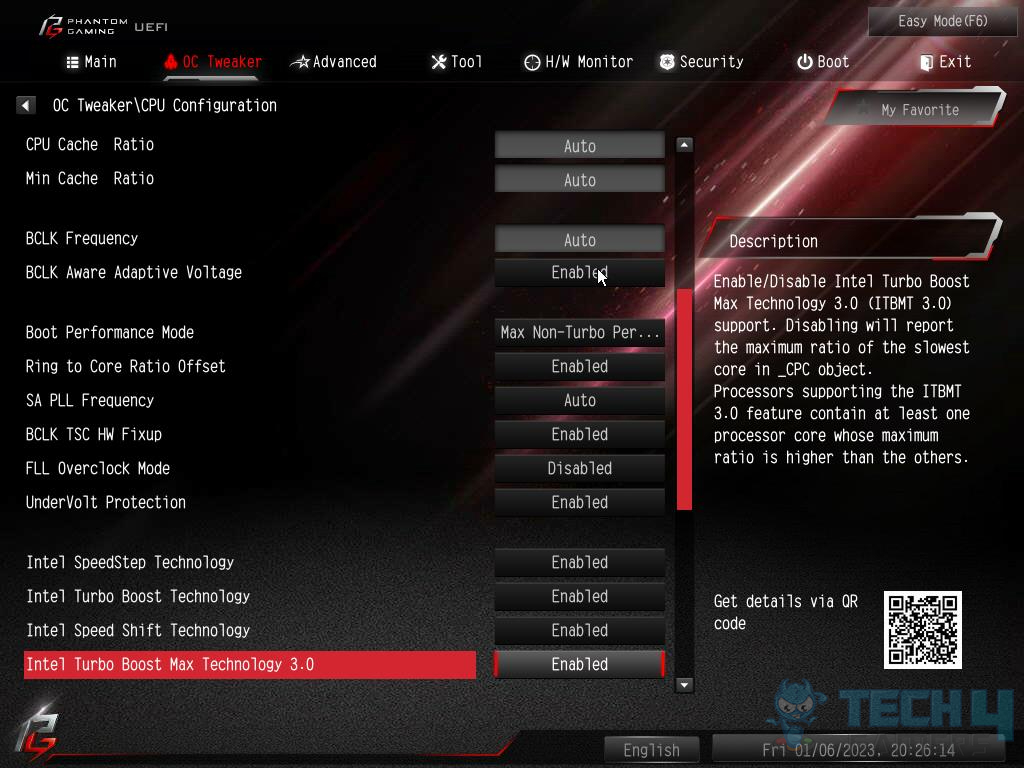
If you are an Intel user, chances are you already benefit from the Intel Turbo Boost technology. Intel Turbo Boost technology is built into Intel CPUs, allowing them to increase their clock speed when additional dynamic performance is needed. Typically, Turbo Boost is limited to a specific duration, after which the CPU will return to its base clock speed.
It works by monitoring the workload and adjusting the clock speed accordingly, up to a maximum boost clock speed. Unlike overclocking, Intel Turbo Boost is a safe and reliable way to increase performance without risking damage to the CPU.
AMD Precision Boost Overdrive
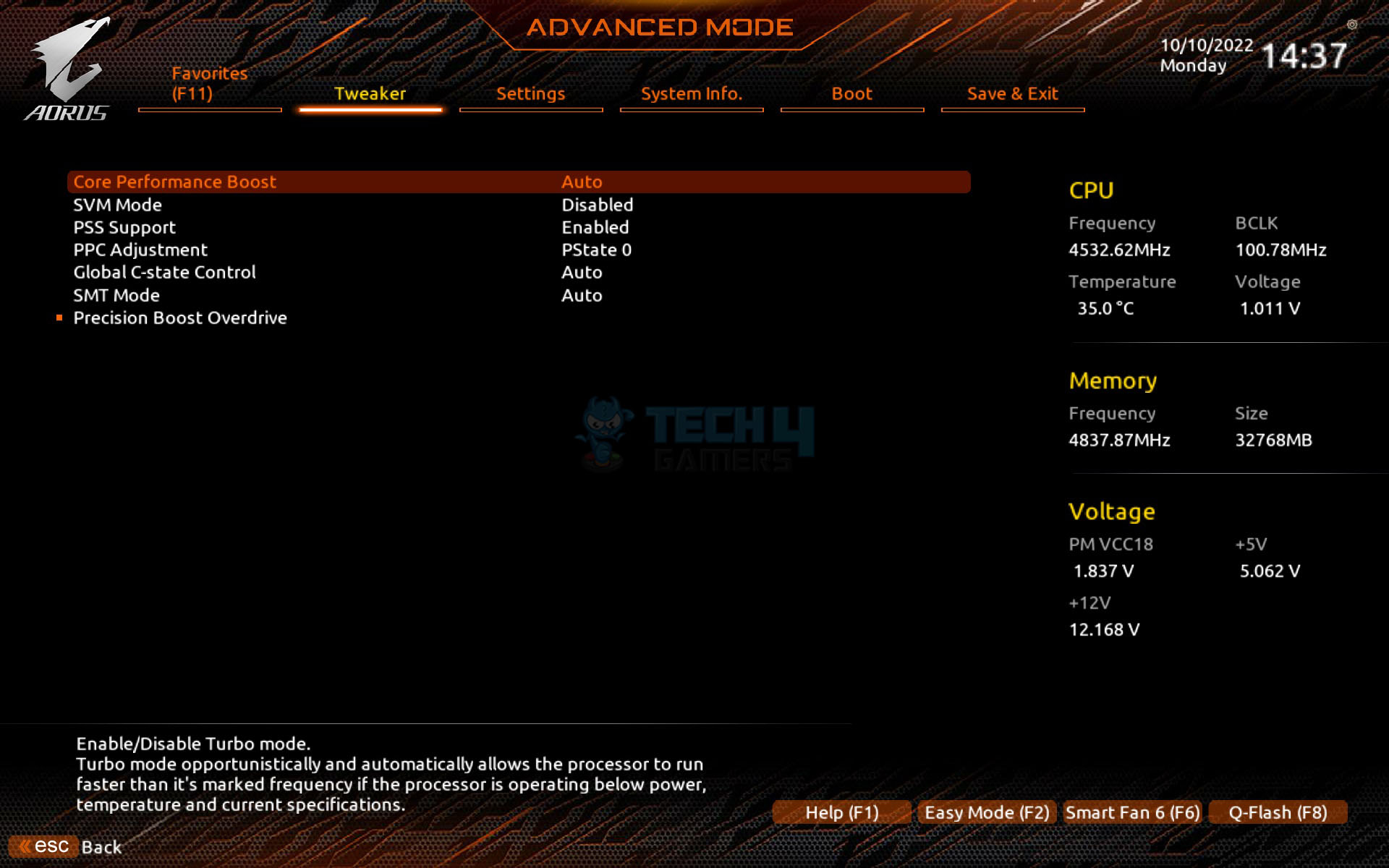
AMD Precision Boost Overdrive is a technology similar to the Intel Turbo Boost, built into AMD CPUs, allowing them to adjust their clock speed based on the workload dynamically. Unlike Intel Turbo Boost, it also allows for manual overclocking to provide additional performance by increasing power consumption and voltage. However, like overclocking, it can reduce the lifespan of the CPU and void the warranty if done incorrectly.
Conclusion
In summary, base clock speed represents the default operating frequency of your CPU or GPU, while boost clock speed denotes the higher frequency automatically engaged under heavy loads. Unlike manual overclocking, boost clock speed is an automated feature that enhances performance without user intervention.
However, it’s subject to certain limitations such as VRM capability, cooling efficiency, silicon quality, and the number of cores boosted simultaneously. Both Intel Turbo Boost and AMD Precision Boost Overdrive offer similar functionalities, but AMD’s feature supports overclocking, distinguishing it from Intel’s counterpart.
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
- Best GPU Overclocking Software
- How To Turn Off Overclocking
- Does Overclocking RAM Increase FPS?
- PC Building Simulator Overclocking
- How to Disable GPU Overclocking
References:
- Intel. (n.d). CPU Speed: What Is CPU Clock Speed?. Retrieved from: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/gaming/resources/cpu-clock-speed.html
- Lenovo. (n.d). AMD Ryzen for Gaming. Retrieved from https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/glossary/amd-ryzen-for-gaming/?orgRef=https%253A%252F%252Fwww.google.com%252F
- Rotem, E., et al. (2011). Sandy Bridge Power Delivery and Thermal Management. Retrieved from: https://old.hotchips.org/wp-content/uploads/hc_archives/hc23/HC23.19.9-Desktop-CPUs/HC23.19.921.SandyBridge_Power_10-Rotem-Intel.pdf
- Hewlett-Packard. (2018, December 18). What is Processor Speed? Retrieved from https://www.hp.com/us-en/shop/tech-takes/what-is-processor-speed
- Avast Software. (n.d). How to Overclock Your CPU. Retrieved from: https://www.avast.com/c-how-to-overclock-cpu#:~:text=Overclocking%20can%20cause%20your%20device,it%20could%20cause%20data%20corruption.
- Singh, N., et al. (2006, September). Impact of Process Variations on Integrated Circuits. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD ’06). Retrieved from: https://scholarworks.umass.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1455&context=theses
- Shilov, A. (2021, March 16). Overclocking with Intel Rocket Lake: Four Core i9-11900K Binned and Analyzed. AnandTech. https://www.anandtech.com/show/16857/overclocking-with-intel-rocket-lake-four-core-i911900k-binned-and-analyzed/7
FAQs
No, boost clock speed is a built-in feature that does not require overclocking manually.
Yes, boost clock speed is an entirely safe built-in feature, unlike overclocking.
No, the CPU or GPU automatically operates at the boost clock when subjected to a heavy load. When the workload intensity declines, it automatically switches back to the base clock speed.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com



![Intel XMP [What, Why, & How] XMP Profile](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/XMP-Profile-218x150.jpg)

![What Is VRM? [Definition, Types & Importance] What is VRM](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/What-is-VRM-218x150.jpg)
![Is A Laptop Considered A PC? [Explained] Is Laptop a PC](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Is-Laptop-a-PC-218x150.jpg)