A VRM regulates the voltage supplied to the processor or GPU. It takes the incoming voltage from the power supply and converts it to a specific voltage level required by the processor or GPU. This ensures stable and consistent performance and helps to protect the processor or GPU from damage due to over or under-voltage conditions.

Key Takeaways
- VRMs regulate voltage coming from the PSU and maintain stable and consistent voltage levels.
- VRM components work together to regulate voltage output from the power supply to the processor or GPU by converting the incoming voltage, storing electrical energy, controlling the flow of electrical current, and dissipating heat to maintain stability.
- The number of power phases in a VRM affects the stability and control of the voltage output.
- When choosing a VRM for future-proofing, it is essential to consider factors such as power delivery capability, cooling, overclocking support, etc.
Importance Of VRMs
VRMs provide stable and efficient power delivery in computer systems, like to the CPU and RAM. A good VRM design can help reduce power loss and heat generation, improve power efficiency and stability, and prevent damage to the processor or GPU.[1] A poor VRM design, on the other hand, can result in power instability, reduced efficiency, and even permanent damage to the GPU or processor.
Understanding VRM Components
Users need to be considerate of multiple VRM components to grasp the idea behind its functionality. Below are some key components and VRM terminologies.[2]
- MOSFETs: A MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) is widely used in electronics for amplification and switching applications. It controls the flow of electrical current by acting as a switch, allowing or blocking the current flow depending on the voltage applied to its gate terminal.[3]
- Inductors: An inductor is a passive electronic component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. It is used in electrical circuits to store energy and regulate the flow of electric current.
- Capacitors: A capacitor is a passive electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It is used in electrical circuits to store energy and regulate the flow of electric charge. Capacitors are characterized by capacitance, which measures the amount of electrical energy stored per voltage unit.
- Controllers: A controller is a digital or analogue circuit that controls the operation of the VRM. It regulates the voltage output, manages the current flow, and communicates with other components in the system.
- Heat Sinks: VRMs can generate significant heat during operation, so heat sinks dissipate heat and cool the VRM components.
VRM Power Phases

VRM power phases refer to the number of separate power delivery channels used in a VRM to regulate the voltage supplied to a processor or GPU. Each power phase represents a particular channel for delivering power, allowing for greater control and stability of the voltage output.
In a single-phase VRM, all the power is delivered to the processor or GPU through a single channel.[4] This is sufficient for low-power applications but may need more strength for high-performance processors or GPUs.
In a multi-phase VRM, multiple power delivery channels are the optimal choice.[4] The number of power phases in a VRM can vary, but typical VRMs may have two, four, six, or even more phases.
Types Of VRM Designs
Multiphase VRMs are available in different designs,[4] some of which are as follows:
- 8-phase: An 8-phase VRM design is a type of voltage regulation module that uses eight separate power delivery channels to regulate the voltage supplied to a processor or GPU, dividing the voltage output across 8 phases for greater control and stability. The power delivered to the processor or GPU is divided into eight channels, each with its inductors and MOSFETs to regulate the voltage output.
- 12-phase: A 12-phase VRM design uses 12 separate power delivery channels to regulate the voltage supplied to a processor or GPU, dividing the voltage output across 12 phases for greater control and stability. It is more complex and expensive to implement than an 8-phase VRM and may not be suitable for lower-end systems.
- 16-phase: A 16-phase VRM design is a type of voltage regulation module that uses 16 separate power delivery channels to regulate the voltage supplied to a processor or GPU, dividing the voltage output across 16 phases for greater control and stability.
These are not the only multi-phase VRMs available, as high-end motherboards also come with 20-phase VRM and, further, for maximized performance.
VRM Cooling System
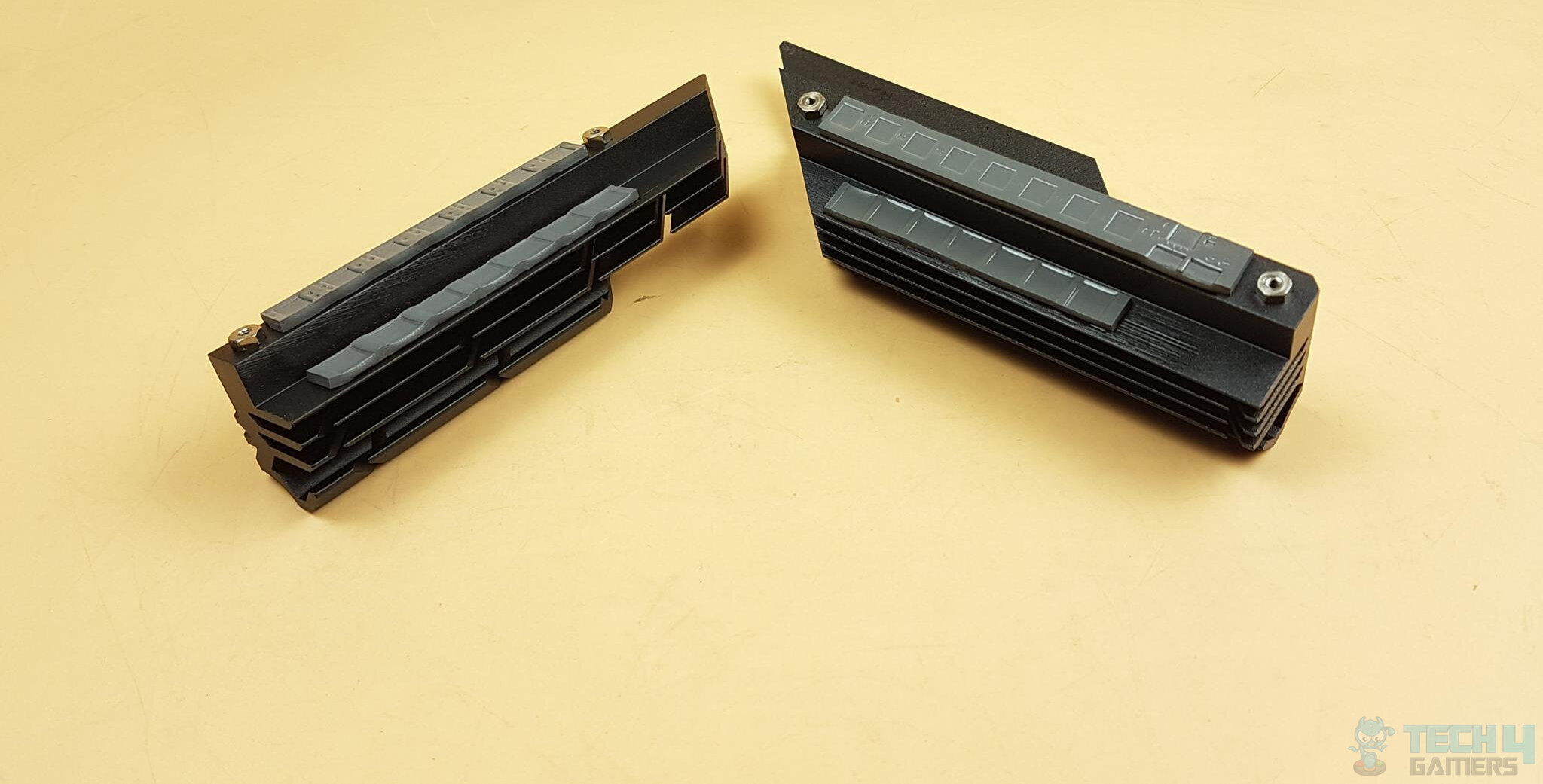

VRM cooling is an essential aspect of a voltage regulation module’s design [5] as it helps to dissipate heat generated by the VRM components during operation. To improve VRM cooling, many motherboard manufacturers use heatsinks, passive cooling devices that transfer heat from the VRM components to the surrounding air.
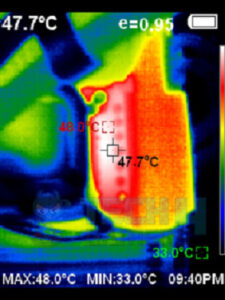
Heatsinks are typically made from materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum, and increase the surface area in contact with the air, promoting heat dissipation.[6]
VRM And Overclocking
A motherboard’s VRM design has a direct impact on its overclocking potential. Therefore, if you plan to overlock the build, consider the VRM structure.
Overclocking
Overclocking makes a computer component, such as a processor or graphics card, run more frequently than the manufacturer has designated.[7] This can be done by adjusting the component’s clock speed, voltage, or other parameters to increase performance. The procedure essentially helps you improve the processor’s performance for gaming, video editing, or scientific simulations.
How Does VRM Effect Overclocking?
When overclocking, the voltage requirements of the component increase, putting a significant strain on the VRM. Hence, you need a high-quality VRM to maintain the additional power requirements without issues.
The Impact Of VRM On Overclocking

The quality and design of the voltage regulation module can significantly impact the stability and performance of a processor or graphics card during overclocking.
- Power Phases: A higher number of power phases can provide better voltage regulation and improved stability during overclocking.
- Quality of Components: High-quality components, such as MOSFETs and inductors, can provide more stable and efficient power delivery during overclocking.
- Heat Dissipation: Overclocking generates more heat, which can cause the VRM to overheat and become unstable. A VRM with good heat dissipation capabilities, such as large heatsinks, can help mitigate this issue.
- Current Capability: The VRM must be capable of handling the increased current demand generated by overclocking. If the VRM cannot provide enough current, it may become unstable or cause permanent damage to the component.
Tips For Choosing A Motherboard Or Graphics Card With A High-Quality VRM
When choosing a motherboard or graphics card with a high-quality VRM, consider looking for VRM components from reputable brands. It would also help to check the number of power phases the VRM has. Additionally, you should consider looking for VRMs with high-quality capacitors and inductors and check reliable VRM cooling options, such as heatsinks or fan cooling.
While more phases mean a good VRM setup, you must consider X+Y specifications. The X shows the number of phases dedicated to your RAM or CPU, and Y means phases dedicated to other PC components. So, reading a 6+2 VRM setup means 6 VRMs for your CPU and 2 for your memory or other components.
Furthermore, reading reviews and researching the VRM specifications and design details can provide valuable insight into the VRM’s quality and performance.
Conclusion
To sum up, VRMs are crucial in regulating computer voltage and ensuring a consistent power supply to the processor or GPU. However, a VRM’s performance depends on several factors, including the number of power phases, components’ quality, and cooling solution.
More Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
- How To Turn Off Overclocking
- Can Motherboard Bottleneck Your PC? [CPU & GPU]
- How Long Does A Motherboard Last + Improve Lifespan
- Base & Boost Clock Speeds For CPU/GPU
References:
-
GeeksforGeeks. Voltage Regulator Module. Retrieved from https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/voltage-regulator-module/
-
Electricity Magnetism.org. Voltage regulator module (VRM). Retrieved from https://www.electricity-magnetism.org/voltage-regulator-module-vrm/
-
GeeksforGeeks. MOSFET – Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistor. Retrieved from https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/mosfet-metal-oxide-silicon-field-effect-transistor/
-
WikiChip. Voltage Regulator Module (VRM). Retrieved from https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/voltage_regulator_module#google_vignette
-
Bitcoin Forum. VRM Temperatures. Retrieved from https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=45367.0
-
Radian Technologies. What is a Heatsink? Retrieved from https://radianheatsinks.com/heatsink/
-
Lenovo. (n.d). What is Overclocking? Retrieved from Retrieved from https://www.lenovo.com/in/en/faqs/pc-life-faqs/what-is-overclocking/
Frequently Asked Questions
VRMs offer improved performance, efficiency, and stability compared to conventional voltage regulators, making them the preferred choice for high-performance computer systems.
One key emerging technology is digital VRMs, designed to use digital control circuits to regulate voltage output. These VRMs provide more precise voltage regulation and improved efficiency than traditional analog VRMs
VRMs with better heat dissipation capabilities can reduce the energy consumption of cooling systems, as they operate efficiently and reliably under high loads, reducing the energy required to cool the computer system. By reducing energy consumption and waste, VRMs can help lower computer systems’ carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
VRMs must handle high power levels and maintain stable voltage output, which requires sophisticated design techniques and high-quality components. They must be efficient, with low power loss and heat generation, to ensure the computer system’s overall efficiency is not impacted.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads
![PC Heatsink [What, How & Guide]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/HOW-TO-6-1-218x150.jpg)

![PSU Voltage Regulation [What, Why & How] Corsair SF1000L 12V Rail MOSFETs](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Corsair-SF100L-5-218x150.jpg)
![How Long Do Laptops Last? [Answered] How Long Do Laptops Last?](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/How-Long-Do-Laptops-Last-218x150.jpg)