It can be tough to get into computers for new enthusiasts, especially with all the new technologies that keep releasing one after another. Of course, one of the first hardware components a new enthusiast will try to understand is the CPU or processor. So, in the following article, we’ll explore the question, “what is a CPU?” in exquisite detail.
Key Takeaways
- The processor is also considered the PC’s brain due to its ability to handle data and execute instructions.
- Four major components within a processor are the Control Unit (CU), Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Registers, and Cache Memory.
- Four common CPUs are the Central Processing Unit (CPU), Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), Accelerated Processing Unit (APU), and Digital Signal Processing (DSP).
- Many things can affect a processor’s performance, including high temperatures, clock speeds, the number of cores, and cache size.
Importance Of The CPU
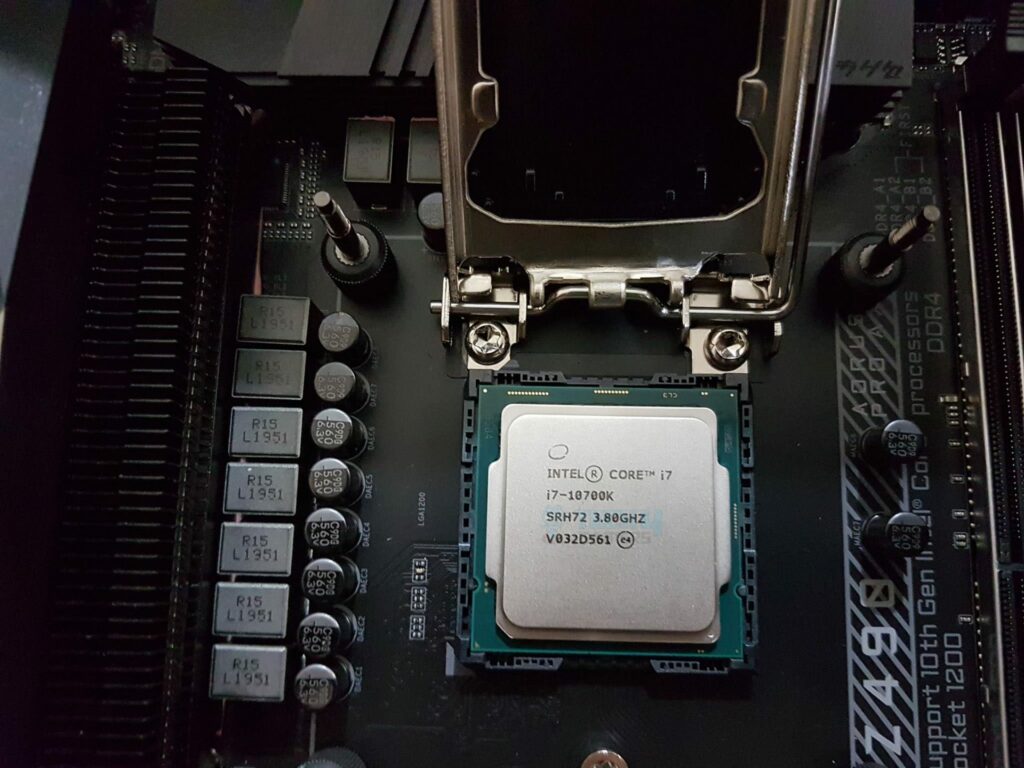

To explain, a processor is present in computers, smartwatches, electric cars, and most digital appliances. Also, a processor is made up of billions of microscopic transistors that are etched onto a computer chip[2]. However, it is important to note that a processor cannot work alone. It needs RAM to store temporary data, a motherboard to house itself, and a graphics card to render 3D frames.
The processor’s main function can be broken down into three key stages: fetching, decoding and executing. A processor fetches, or takes instructions stored temporarily within the RAM, decodes them to understand what they’re saying, and then executes the instructions using relevant computer parts[3]. Moreover, these things happen every second, and hundreds of instructions are passed at once.
Therefore, your computer wouldn’t even know what to do without a processor, similar to someone without a brain. Neither would your processor be useful without any of the other components. Well, most of them, at least.
Also Read: How To Lower Processor Temperature
Types Of Components In A CPU
When discussing processors, we must learn the different components present within one to understand its functions better. A processor has four main components; the Control Unit (CU), Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Registers, and Cache memory. Let’s discuss each briefly.
Control Unit
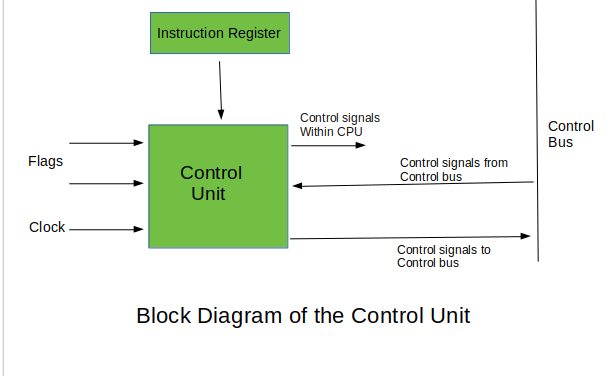
In brief, the Control Unit or CU is a processor’s circuitry that helps direct instructions. As stated above, a processor fetches, decodes, and executes instructions. A CU’s responsibility is to handle the execution of the instructions by utilizing proper computer parts[4].
So, the CU instructs the memory, input, output devices, and logic units on what to do about a program’s instructions. All processors and graphics cards use control units to handle execution.
Of course, the Control Unit has other uses and responsibilities, but understanding its core duties is sufficient. For example, the CU understands commands and instructions, coordinates data flow in and out of a processor, and more[5].
Also Read: How To Fix NVIDIA User Account Is Locked
Arithmetic Logic Unit
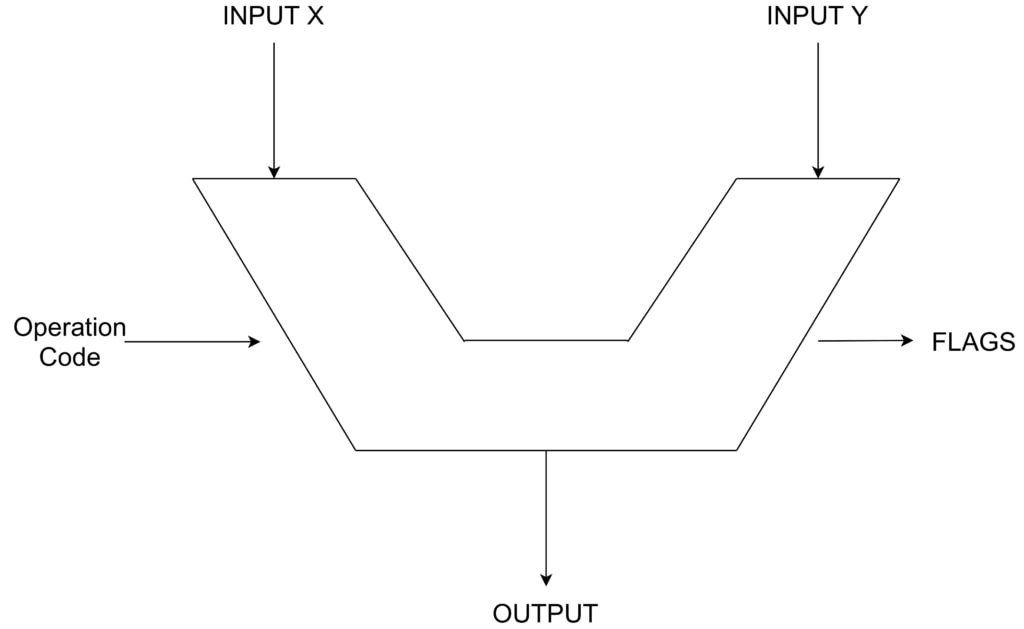
An Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is a part of the processor that helps carry out arithmetic and logic operations[6]. Out of the three stages of a processor’s function, the ALU manages the decoding.
So, all of the instructions from the RAM go to the ALU and are decoded for the computer to understand. The ALU later transfers these instructions to the Control Unit (CU), which executes the instructions.
Furthermore, the ALU is divided into two parts within some processors. These parts are the Arithmetic Unit (AU) and the Logic Unit (LU)[7]. However, the AU and LU functions are similar to the ALU.
Moreover, the ALU typically has access to the computer’s memory, RAM, and input/output devices. Input and output instructions come through electrical signals called “bus,” which the ALU handles[8]. For example, an input signal arrives through the bus, the ALU decodes the signal and processes it towards the output through another bus.
So, without the ALU, you wouldn’t be able to see any of the functions you perform on the computer daily.
Also Read: PS Vita Could Not Connect To The PC
Registers
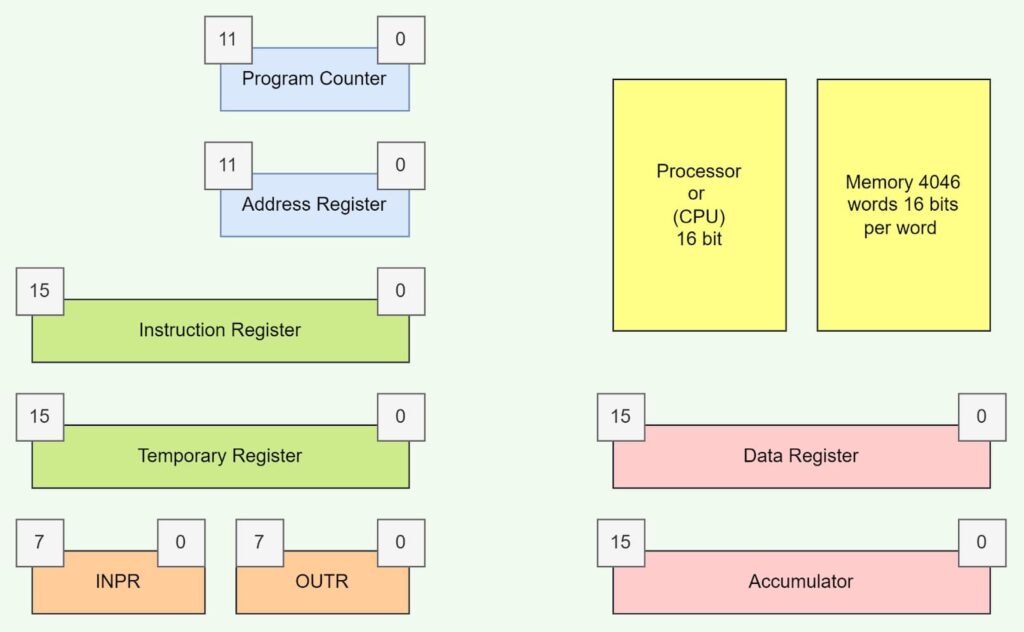
Registers are computer memory that quickly accepts, stores, and transfers data and instructions to the ALU and CU. Of the three key stages of a processor’s functions, registers are in charge of fetching data and instructions[9]. Registers can hold instructions, storage addresses, or any other type of data that the processor needs immediately[10].
Computers require registers to manipulate data and hold storage addresses. Registers holding a memory location are used to calculate the address of the next storage address that the processor will use. The task is initiated once the previous instruction is executed.
Also, there are many types of registers, such as the Data Register, Address Register, Input Register, Output Register, Accumulator, Instruction Register, and many more[11].
Therefore, without registers, a processor wouldn’t know where to find information, and simple tasks would take much longer to complete.
Also Read: How to Enable TPM 2.0
Cache Memory
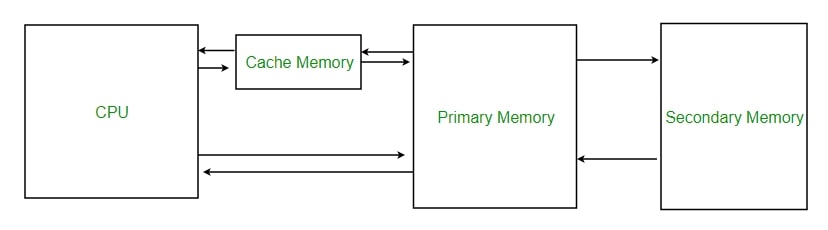
Cache memory is extremely fast in a processor that synchronizes with high-speed processors[12]. Unlike slower registers, the cache memory can fetch and transfer more instructions and data per second. So, of the three key stages of a processor’s functions, the cache memory handles the fetching as a substitute for registers.
While the cache memory is faster, it is much more expensive than the more economical registers. Therefore, today’s processors utilize the cache memory and processor registers at once.
Moreover, the cache memory acts as a cushion between the RAM and the processor, as it immediately holds available data when the processor requires it. The cache is a smaller and faster type of memory that stores data duplicates from frequently visited storage addresses. There are different cache types, but the main three are the L1, L2, and L3 Cache.
Also Read: How To Overclock RAM
Types Of CPUs
After discussing the components within a processor, it’s important to know the types of processors. While there are many types, the main four are Central Processing Units (CPUs), Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), Accelerated Processing Units (APUs), and Digital Signal Processing (DSP).
Central Processing Unit

As stated above, the Central Processing Unit, or processor, is a computer’s brain. It is one of the most important components within a computer, which processes instructions from a program or application and performs relevant calculations.
The Central Processing Unit comprises billions of transistors etched onto a small computer chip. You can find processors in almost all digital appliances today, whether smartwatches, phones, electric vehicles, or anything else.
However, it’s important to note that a processor cannot work alone within a computer. It needs RAM to store instructions, a motherboard to house itself, and a graphics card to render 3D images and videos.
When talking about processors, consumers tend to compare different processors to find out which is better. If you want to buy one, read through our Intel i5-13600K Vs Intel i9-12900K comparison article!
Graphics Processing Unit

While it sounds difficult to be true, a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a type of Central Processing Unit. Although we use the GPU and graphics card terms interchangeably, they hold a subtle difference. To explain, a graphics card is an add-in board that holds the GPU, just like how a motherboard contains the processor[13].
So, the GPU is responsible for providing the computer with 3D images and video. Furthermore, there are two basic types of GPUs: integrated and discrete[14]. Integrated GPUs are found within processors, which can provide basic images. However, most integrated GPUs aren’t useful for gaming or high-end rendering.
On the other hand, discrete GPUs are standalone graphics cards produced by certain manufacturers. For the most part, NVIDIA and AMD produce most of the discrete graphics cards used by the average joe. However, Intel recently joined in the race, making it the third biggest company to produce discrete graphics cards.
In any case, these discrete GPUs are mounted on their circuit board and are typically attached to a PCIe Lane. If you’re interested in buying, check out our AMD Radeon RX 7900 XTX Vs NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 Ti comparison article!
Accelerated Processing Unit

Accelerated Processing Units (APU) are a type of CPU specifically produced by AMD. An APU is a mixture of a Central Processing Unit and a Graphics Processing Unit[15]. Unlike an average processor, APUs combine both to garner more performance and eliminate the distance between components. You can think of an APU as a pencil with an eraser at the back.
In most computers, the processor and graphics card are attached separately. While there aren’t any problems with that, data transfer speeds become significantly faster if we can eliminate the distance between both. That is exactly what AMD has achieved with its innovative APUs.
Using an APU has many advantages, such as lower power usage, affordability, more performance, and less required space[16]. However, the technology must improve until it matches the highest-end processors’ standards and discrete graphics cards.
Also Read: AMD vs Intel For Video Editing
Digital Signal Processing
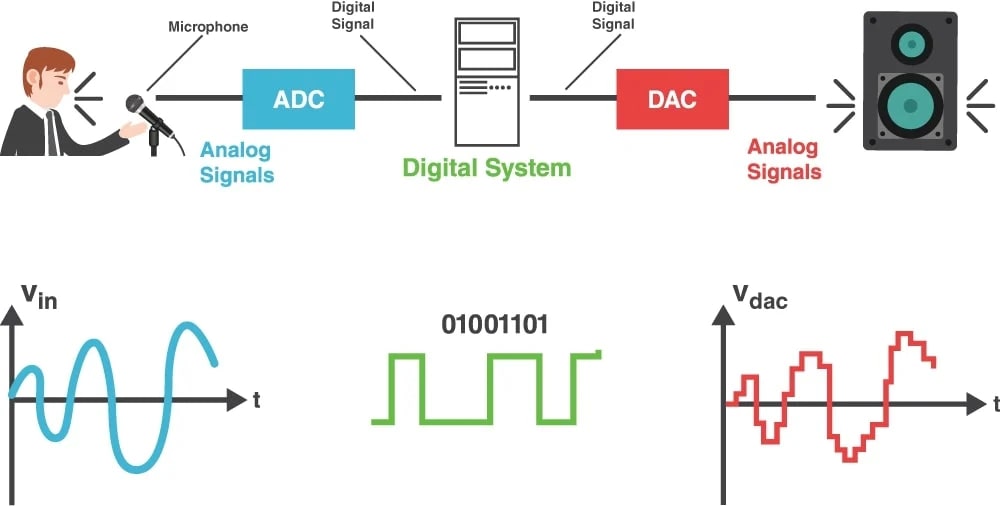
The last type of CPU is called Digital Signal Processing (DSP). As the name suggests, DSPs mainly handle real-world signals such as voice, temperature, video, and others and then mathematically manipulate them[17].
As the above image iterates, DSPs use analog signals as input, mathematically manipulate the signals, and send analog signals. So, we see a person speaking on a mic; after quick manipulation, the sound is processed through a speaker.
Similar technology is used when we talk with Google’s Alexa or Microsoft’s Cortana AI. We speak in the mic, the DSP manipulates our voice, and then we receive an output. Although, with AI, there are other steps involved as well.
A DSP does these tasks in one of two ways: digitally or through an Analog-to-Digital converter. While Analog-to-Digital conversion is the conventional method, digitally converting signals is significantly faster.
Thus, concluding, Digital Signal Processing has become an integral part of our lives as we continue to progress. Although DSPs are progressing, they are nowhere near as advanced as other Central Processing Units.
Also Read: How To Use Headset Mic On PC With One/Two Jacks?
What Is CPU Clock Speed?
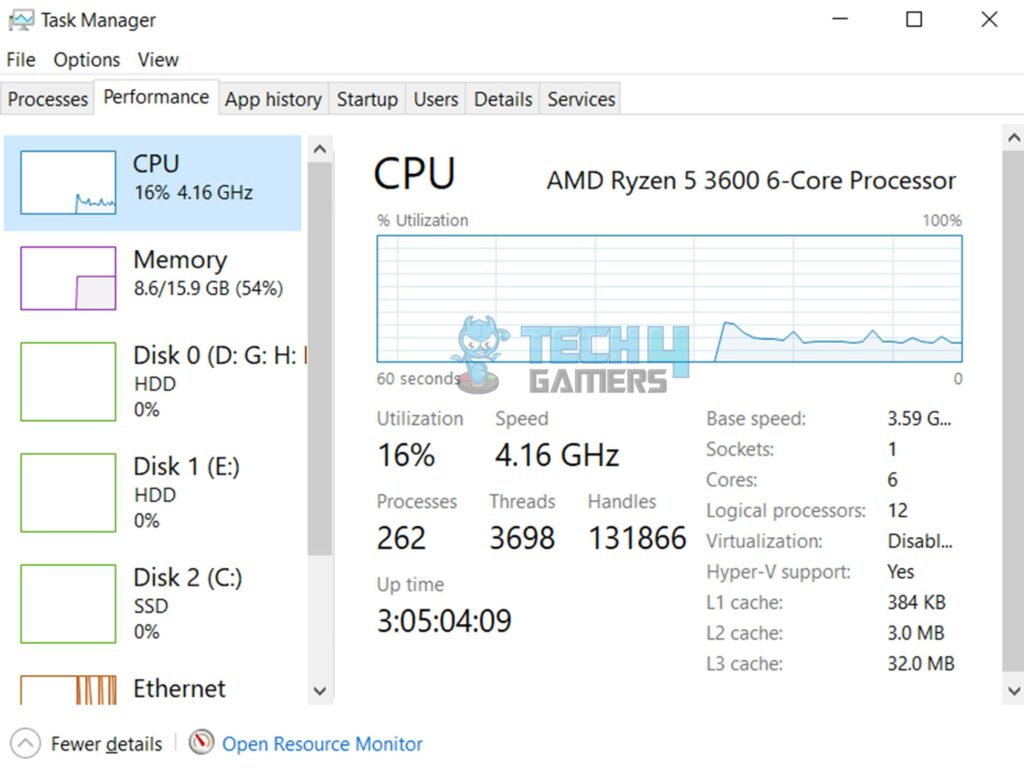
Furthermore, billions of transistors within the processor open and close during each cycle. The higher the processor’s clock speed, the better it performs in most tasks. Gaming, for example, requires higher clock speeds and better Instructions Per Clock (IPC) to get more performance.
However, clock speeds and IPC aren’t the only factors in a processor’s performance. The number of cores and total bus speed also affect a processor’s performance[19]. Moreover, cores handle unconventional and more time-consuming tasks, unlike the clock speed. Meanwhile, the bus speed represents how fast the PC can communicate with its peripherals and other input/output devices.
As processors progress, we now see multiple baselines for clock speeds. We have a low “base” clock speed and a faster “turbo” clock speed. Also, we can overclock processors to increase the clock speed beyond what the manufacturer allows. Although, if you’re trying to overclock your processor, you must stay careful, or you can damage the CPU.
While safe overclocking won’t damage your processor, it might reduce the overall lifespan. If you’re interested in overclocking, read through our article explaining overclocking! You will also need to turn it off, so look at how to turn off overclocking.
Difference Between MHz And GHz
As both terms are similar, there isn’t a big difference between MegaHertz (MHz) and GigaHertz (GHz). One MHz equals one million cycles, whereas one GHz equals one billion cycles. So, a processor with a clock speed of 4.2GHz means a clock speed of 4,200MHz or a cumulative of 4.2 billion cycles per second.
Other than that, GHz is also used outside computers, whereas MHz is confined to computing only. For example, we use GHz to study electromagnetic spectrums in radio transmissions.
Also, we usually use MHz when referring to graphics cards, while we handle CPUs in GHz. However, both terms can be used for both components, as graphics cards’ clock speeds go beyond 2,000MHz with some of the latest editions.
Factors Affecting CPU Performance
After going through the types of processors and clock speeds, we must learn the factors that affect a processor’s performance. While there are many factors, our focus shall remain on the following: the number of cores, clock speed, cache size, and extreme temperatures.
Number Of Cores
Cores are one of the most important features of a processor. Gamers often buy processors based on how many cores the processor has and how fast it runs. Each core is designed to fetch, decode and execute functions. So, having more cores equals more instructions getting executed every second[20].
However, having a lot of cores isn’t the correct solution to increasing the performance of a processor. Due to the cores’ constant communication, a processor needs better IPC.
Moreover, every program on your computer has a string of data called “threads.” A processor with a single core can only process one thread simultaneously, so it will keep changing threads, slowing it down. Therefore, manufacturers have created processors with multiple cores and more threads which assist in delivering greater performance.
So, a processor excelling in cores may not be as fast as an optimized processor with an adequate IPC. Thus we see the Intel 12th gen processors outperforming AMD’s Ryzen 5000 series processors. If you’re interested to find out which is better, read our comparison between the Intel Core i9-12900K Vs AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D processors.
Clock Speed
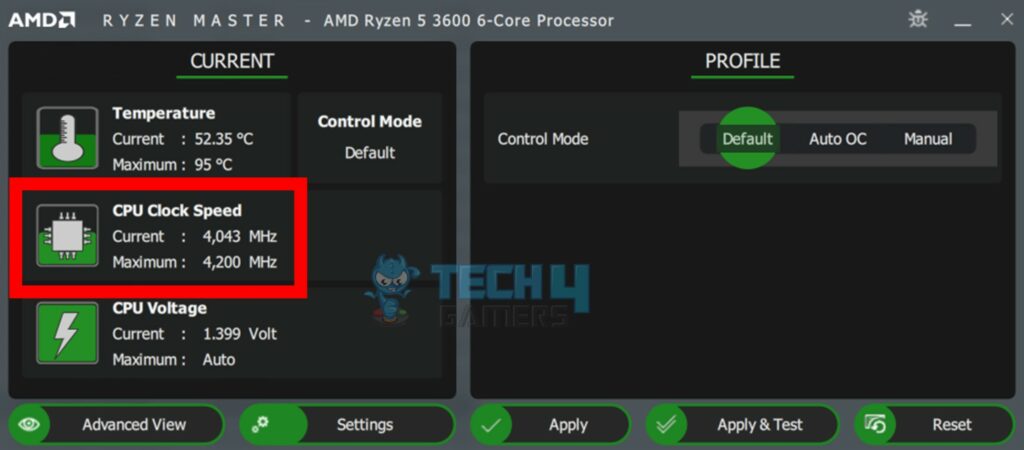
The faster the clock speed of a processor, the more instructions it can execute and the greater performance it can provide[21]. However, a ridiculous clock speed isn’t the only thing required to improve a processor’s performance. Of course, while necessary, other components, such as the number of cores and IPC performance, matter too.
Moreover, if your processor has a slower clock speed, you can overclock most AMD processors to a certain degree. Although, if you own an Intel processor, only “K” variant processors are overclockable.
So, you can increase your performance if needed without getting an upgrade. But be mindful of decreasing the lifespan of your processor if you overclock excessively.
Also Read: Ryzen 9 5950X Vs Intel i9-10900K
Cache Size
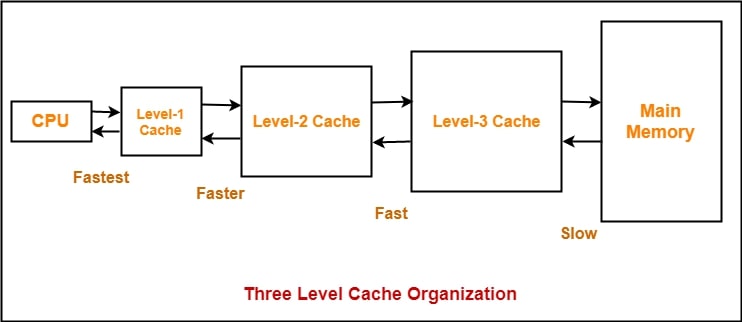
The third factor affecting a processor’s performance is its cache size. As stated above, the cache is a faster yet more expensive substitute for processor registers. Also, processors don’t have a lot of caches, so they still take help from registers.
All processors have three types of cache, L1, L2, and L3 cache[22]. To explain, the L1 cache is the smallest but the fastest type of cache in a processor. The L1 cache has the data that a processor will most likely use to complete certain tasks. Each processor has its amount of L1 cache. For example, the high-end Intel Core i9-13900K has 80KB of L1 cache per core, which doesn’t even equal 2MB.
The L2 cache, however, is slower but exists in larger quantities. Although the L2 cache might be slower than the L1 cache, it’s still faster than the computer RAM. For instance, the AMD Ryzen 5 5600X has 384KB of L1 cache but 3MB of L2 cache. Moreover, while we calculate the L1 cache in Kilobytes (KB), we measure the L2 cache in Megabytes (MB).
Lastly, the L3 cache is the slowest in the highest quantities. Most games thrive the most with L3 cache, which is why AMD has opted to move along with its 3D V-Cache technology that increases the amount of L3 cache a processor has. The AMD Ryzen 7-5800X has 32MB of L3 cache. On the other hand, the AMD Ryzen 7-5800X3D has 96MB of L3 cache.
Therefore, the memory cache plays an important role in a processor’s performance, along with clock speeds and core count. But it’s important to note that high amounts of cache don’t equate to greater productive performance of a CPU.
Also Read: Intel Core i9-12900K Vs AMD Ryzen 7-5800X3D.
High Temperatures
The last factor affecting a computer’s performance is high temperatures. To explain, lower temperatures are better for a computer as each component is designed to stay under a certain temperature. Furthermore, if you’re overclocking, you won’t be able to cross a certain threshold with higher temperatures.
For that reason, having proper cooling in your system is necessary to ensure that your processor can perform as intended. Also, if you don’t take care of the temperatures of your processor and other components, you risk reducing their lifespan.
Moreover, most processors have a temperature cap of 95°C to 105°C. So, if your processor starts getting close to those temperatures, it will become slower and slower to continue running. The only exception to these temperatures is AMD’s latest Ryzen 7000 series processors that average 90°C without losing performance.
Therefore, it’s important to keep a check on the temperatures of your components. You must read our article on how to lower CPU temperature to learn more! While at it, you might as well go through a few best budget coolers for your PC.
CPU Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of a processor, or its lithography, is another important aspect to look into before buying one. When researching processors, you will often find numbers such as “14nm”, “10nm,” or “7nm”. These numbers indicate the size of a processor chip.
As we already know, processors are made of billions of tiny transistors etched onto a computer chip. These chips are made of silicon, and the transistors take power to open and close every second[23]. So, the smaller the silicon chip is, the more efficient it is. Therefore, manufacturers try to shrink their processor chips in almost every generation.
Following “Moore’s Law,” an old observation states that the number of transistors should double yearly while the costs are cut to half[24]. However, CPU manufacturers have had a difficult time lately keeping that observation in check. Mainly Intel has been lacking in its lithography, with its latest Intel 13th gen processors following a 10nm process node.
Except for AMD utilizing the latest 7nm process node manufactured by TSMC, Intel stayed at the 14nm process node for a long time. Moreover, Intel introduced new lithographies, such as the 14nm+. Only in 2019, after a long period of no advancements in the process nodes, did we see Intel introduce its latest 10nm process, which is being used today.
All-in-all, smaller process nodes don’t directly equate to greater performance. For example, AMD’s Ryzen 7000 series processors, which utilize TSMC’s 7nm node, can barely stand their ground with Intel’s 13th gen processors utilizing a 10nm process node.
In conclusion, while a processor’s lithography impacts performance, manufacturers might use it as a gimmick. So, it would be best if you glanced through all the other processor specifications before going through with a purchase.
Impact Of Lithography On CPU Performance
While lithography does not directly impact a processor’s performance, it indirectly affects a lot. For example, a processor with an advanced process node is more likely to experience lower temperatures during heavy workloads. Due to that, the processor can showcase its boost clock speeds for longer.
However, a processor with an older process node might get hotter easily, slowing its performance. Moreover, the smaller the process node, the more transistors manufacturers can add to the processor. In addition, smaller process nodes require lower power, so the TDP of processors remains manageable for longer.
Although through these points, Intel’s processors slightly go against the concept of lithography. We see that the latest Intel processors utilize the 10nm process node, but the temperatures are on-par with AMD’s 7nm processors. Also, many AMD processors have higher temperatures than Intel processors.
In conclusion, lithography does impact a processor’s performance, but there are more variables. Therefore, when researching a processor, you must take into account all the features the processor showcases.
Also Read: Intel Core i5-10400F Vs AMD Ryzen 5-3600
Conclusion
To conclude and answer the question, “what is a CPU?” we understand a processor is one of the most important components of a PC. Furthermore, a processor is considered the PC’s brain because of its ability to handle data and execute tasks.
While there are more things to understand regarding processors, the basics cover the types, characteristics, features, impacts on performance, and understanding of a processor’s lithography.
To conclude, if you’re looking to buy a processor, you should look for the number of cores, clock speeds, cache amount, and IPC performance. Other than that, knowing its process node and performance-per-dollar are other must-know points.
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
- How To Choose A CPU? [Things To Know]
- CPU Cores
- CPU Threads
- CPU Clock Speed
- CPU Temperature While Gaming
References:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU). Khan Academy. Retrieved from https://www.khanacademy.org/computing/computers-and-internet
- Billions of Transistors Make Up a Processor. A New Video Shows How They are Made. Retrieved from https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/newsroom/news/billions-transistors-make-processor-new-video-shows-how-they-made.html#gs.7vf5z6
- How Computers Work: The CPU and Memory. Retrieved from https://homepage.cs.uri.edu/faculty/wolfe/book/Readings/Reading04.htm
- Introduction of Control Unit and its Design. Retrieved from https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/introduction-of-control-unit-and-its-design/
- Control Unit. Byjus. Retrieved from https://byjus.com/gate/control-unit-notes/
- Arithmetic Logic Unit | ALU Definition, Function & Operation. Retrieved from https://study.com/academy/lesson/arithmetic-logic-unit-alu-definition-design-function.html
- ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit). Byjus. Retrieved from https://byjus.com/gate/alu-notes/
- What is ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit). Retrieved from https://www.javatpoint.com/what-is-alu
- Which memory is used as a part of the processor. Retrieved from https://testbook.com/question-answer/which-memory-is-used-as-part-of-the-processor–625291541ce23ce52e3280c3
- Jessica Hopkins (2023). What is a Register in a CPU and How Does it Work. Retrieved from https://www.totalphase.com/blog/2023/05/what-is-register-in-cpu-how-does-it-work/
- Types of Register in Computer Organization. Retrieved from https://www.javatpoint.com/types-of-register-in-computer-organization
- Difference between Cache Memory and Register. Retrieved from https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-cache-memory-and-register/
- What is a GPU? Retrieved from https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/gpu
- What Is a GPU? Graphics Processing Units Defined. Retrieved from https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/docs/processors/what-is-a-gpu.html
- Daniel Horowitz (October 17, 2021). APU vs CPU: Which is Best for You. Retrieved from https://www.hp.com/us-en/shop/tech-takes/apu-vs-cpu-which-is-best
- Malcolm Archibald (October 2022). What is an APU? Is it the right chip for you. Retrieved from https://blog.acer.com/en/discussion/324/what-is-an-apu-is-it-the-right-chip-for-you
- A Beginner’s Guide to Digital Signal Processing (DSP). Retrieved from https://www.analog.com/en/lp/001/beginners-guide-to-dsp.html
- Common Measurement Of CPU Speed. Retrieved from https://ms.codes/blogs/computer-hardware/common-measurement-of-cpu-speed
- What is the impact of the number of cores on processor performance. Retrieved from https://www.linkedin.com/advice/0/what-impact-number-cores-processor-performance-ssnae
- Christopher Trick (Jul 18, 2022). How Many Cores are Enough. Retrieved from https://www.trentonsystems.com/en-us/resource-hub/blog/how-many-cores-are-enough
- Clock Speed: CPU Technique & Impact | StudySmarter. Retrieved from https://www.studysmarter.co.uk/explanations/computer-science/computer-organisation-and-architecture/clock-speed
- What kind of data does L1, L2, L3 cache hold. Retrieved from https://cs.stackexchange.com/questions/152591/what-kind-of-data-does-l1-l2-l3-cache-hold
- Computer Hardware. Stanford University. Retrieved from https://web.stanford.edu/class/cs101/hardware-1.html
- Carla Tardi. What Is Moore’s Law and Is It Still True. Retrieved from https://www.investopedia.com/terms/m/mooreslaw.asp
Frequently Asked Questions
A dual-core processor has a total of two cores, whereas a quad-core processor has a total of four cores. However, technology has developed, and we see processors with as many as 24 cores.
There isn’t a single answer to this question. Intel and AMD processors excel in certain situations, so depending on your use case scenario, you should opt for one. Of course, consumers often also decide based on the performance-per-dollar value of a processor, which is another way to test which processor is better.
A GPU is also considered a Central Processing Unit. While the processor handles data and executes instructions, a GPU renders 3D images and videos.
You must compare at least two processors within the same environment in any number of games and applications. Depending on the price and performance difference between both processors, you can find out which has better value.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble. Currently speaking, Ali’s about to complete his Bachelor’s in Business Administration from Bahria University Karachi Campus.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


![AMD EXPO [Features & How You Can Enable It]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/CORSAIR-VENGEANCE-RGB-DDR5-RAM-32GB-2x16GB-6000MHz-CL30-AMD-EXPO-RGB-Lighting-3-218x150.jpg)
![Intel XMP [What, Why, & How] XMP Profile](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/XMP-Profile-218x150.jpg)
Feedback By: