Intel 11th Generation
Rated: 6.5/10
Intel 12th Generation
Rated: 8/10
Pros And Cons
| CPU | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| 11th Generation | ✅ Lower price tag ✅ Cheaper supporting hardware | ❌Lower overall performance ❌Worse Power efficiency |
| 12th Generation | ✅ Better overall performance ✅ Choice to DDR4 or DDR5 RAM ✅ Improved [power efficiency | ❌Higher price |
- The 11th generation of Intel processors bring significant performance uplifts over their 12th gen counterparts, ranging from 10-20%.
- Because of its more complex processing nodes, the 12th gen processors consistently consume less power than the 11th gen ones, with thr exception of the 12900K which takes about the same amount of power.
- The price difference of the two generations still holds in late March 2024, with the processors being priced 18-35% apart depending on their place in the hierarchy.
- The 11th generation processors appeal to people looking for good entry-level processors, whereas the 12th generation gives more performance for more cash.
General Specifications
| Feature | 12th Generation | 11th Generation |
|---|---|---|
| Socket | LGA 1700 | LGA 1200 |
| Codename | Alder Lake | Rocket Lake |
| Architecture | Cyprus Cove | Hybrid Architecture |
| Max No. of Cores | Up to 8 Performance and Efficiency Cores each | Up to 8 Cores |
| L3 Cache | Up to 30 MB, shared | Up to 16 MB, shared |
| Integrated GPU | UHD 770, UHD 730, UHD 710 | UHD 750, UHD 730 |
| DMI Version | 4.0 (up to x8) | 3.0 (x8) |
| DMI Speed | 16 GT/s | 8 GT/s |
| PCI Express | 5 | 4 |
| Memory Support | DDR5, DDR4 | DDR4 |
| Thunderbolt | 4.0 Supported | 4.0 Supported |
| Max No. of SATA 6 GBPs Ports | 8 | 6 |
| Max No. of Displays | 4 | 3 |
| Wi-Fi Support | Wi-Fi 6E | Wi-Fi 6/Wi-Fi 6E |
| Launch Date | 16th March, 2021 | 4th November, 2021 |
Intel’s 12th-generation CPUs, codenamed “Alder Lake,” dominate the PC gaming market, surpassing AMD chips and older Intel CPUs at similar prices. Today, we’ll compare Intel’s 12th gen vs 11th gen to gauge Alder Lake’s performance leap over the previous generation.
An Intro To Alder Lake
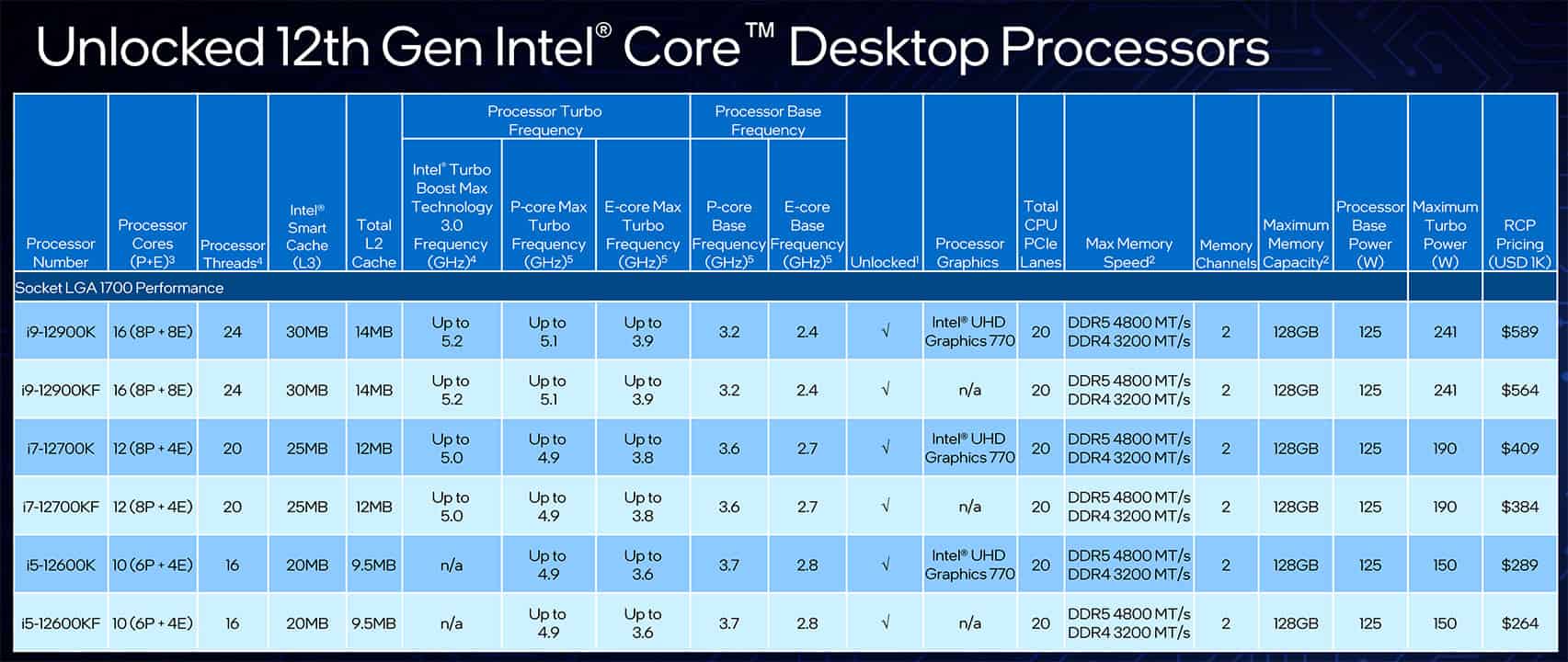
Alder Lake brings various chips to the table, including unlocked chips with the K series and KF series, locked chips with the 1200 series, and some power-efficient chips with the T series. For this comparison, we will focus on the K series of chips between the two generations, but if you want more information on the rest of the lineup, feel free to scroll through our extensive comparisons page.
Unlike Rocket Lake, Alder Lake brings new i3, Pentium, and Celeron chips. These lower-end CPUs offer various variants, distinguished by F or K suffixes. While they may not receive as much attention as higher-end options, it’s beneficial for consumers to have these choices from Intel. We will discuss the new features of these chips in detail below.
Supporting Chipsets
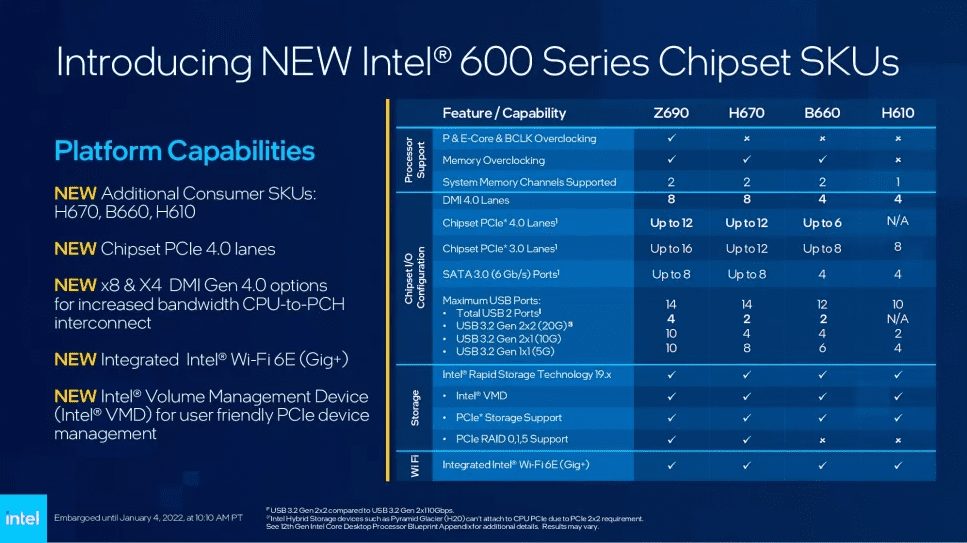
Like Rocket Lake, Intel introduces us to four new chipsets supporting the new Alder Lake CPUs at different price points. These are Z690, B660, and H670.
The main difference is that CPU overclocking is only supported on Z690, while H610 does not support overclocking of any type. H610 also supports only one memory channel. Furthermore, Z690 and H670 share the same 8 lanes of DMI 4.0, while the number of lanes is halved for B660 and H610.
Read our detailed guides if you want a Z690, H670, B660, or H610 motherboard.
Hybrid Core Architecture
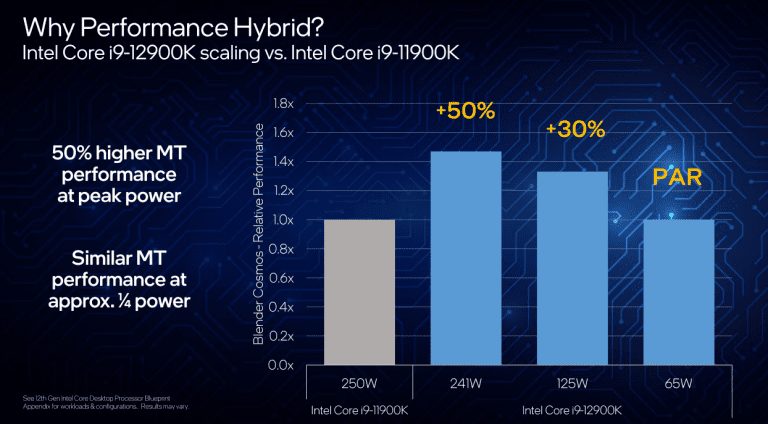
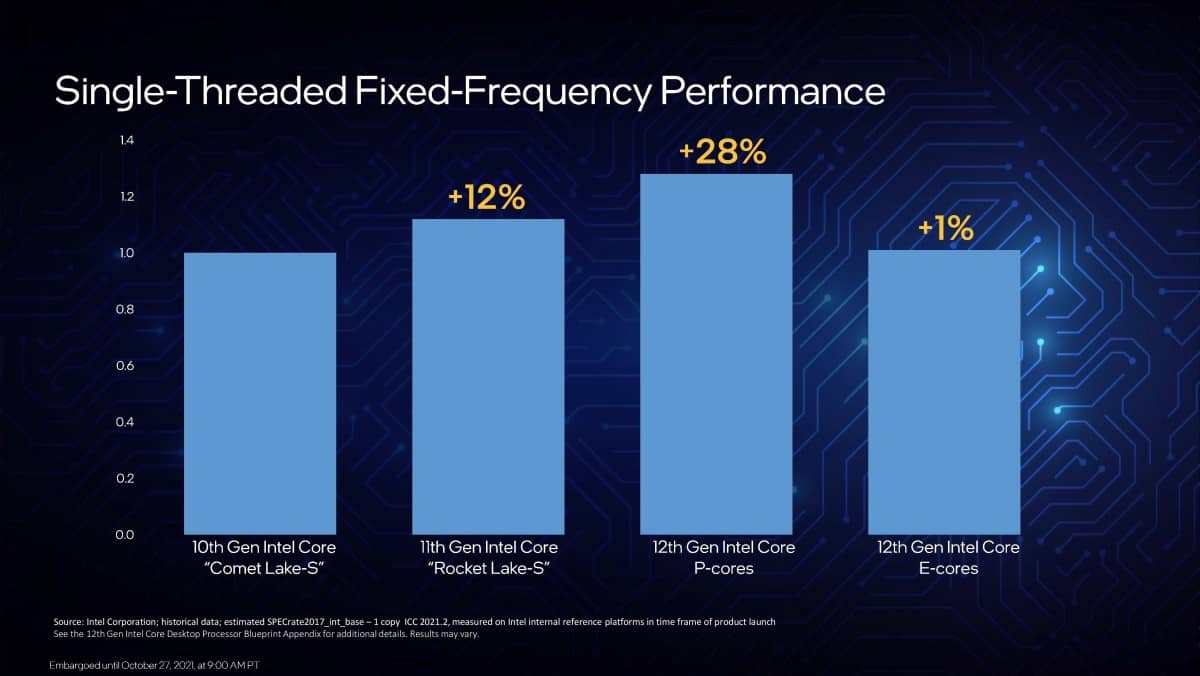
Intel’s 12th-generation CPUs introduce a hybrid core design. This architecture includes Performance (P) cores and Efficiency (E) cores, combining two different microarchitectures on a single CPU die.
Intel claims a significant increase in multi-threaded performance for the 12900K, maintaining power levels similar to the i9-11900K or achieving similar performance with a quarter of the power draw. Additionally, there’s a claimed 16% increase in single-threaded performance for Alder Lake P cores compared to Rocket Lake cores at the same frequency.
Integrated Graphics
Alder Lake CPUs feature integrated graphics, known as “Alder Lake GT1,” based on Intel’s Xe-LP microarchitecture. They come in three ranges: UHD 770, UHD 730, and UHD 710, with UHD 770 being the most powerful, showing an 8% improvement over Rocket Lake’s UHD 750 in older triple-A titles.
However, K or KF CPUs lack integrated graphics. Lower-end i3 and i5 chips have slightly weaker UHD 730 graphics, while Celeron and Pentium chips feature further downgraded UHD 710 graphics. Overall, the 12th Generation integrated graphics offer slightly better performance than the 11th Generation.
Multicore Enhancement

Intel’s K series Alder Lake CPUs come with Multicore Enhancement enabled by default. This feature allows the CPUs to run faster than their advertised stock speeds, provided your CPU cooling solution supports it. Unlike previous generations, this new addition sets the 12th Generation apart from the 11th.
DDR5 Support
PCIe 5.0
PCIe 5.0 doubles transfer speeds compared to PCIe 4.0, with each lane offering 4 GB/s, resulting in a bandwidth of up to 64 GB/s (16-lane configuration) and transfer speeds of up to 32 GT/s.
PCIe 5.0 also provides enough power to run high-end GPUs like the RTX 3090 without external power connectors, delivering up to around 600 watts of power through a PCIe 5.0 x16 slot.
A Reminder Of Rocket Lake
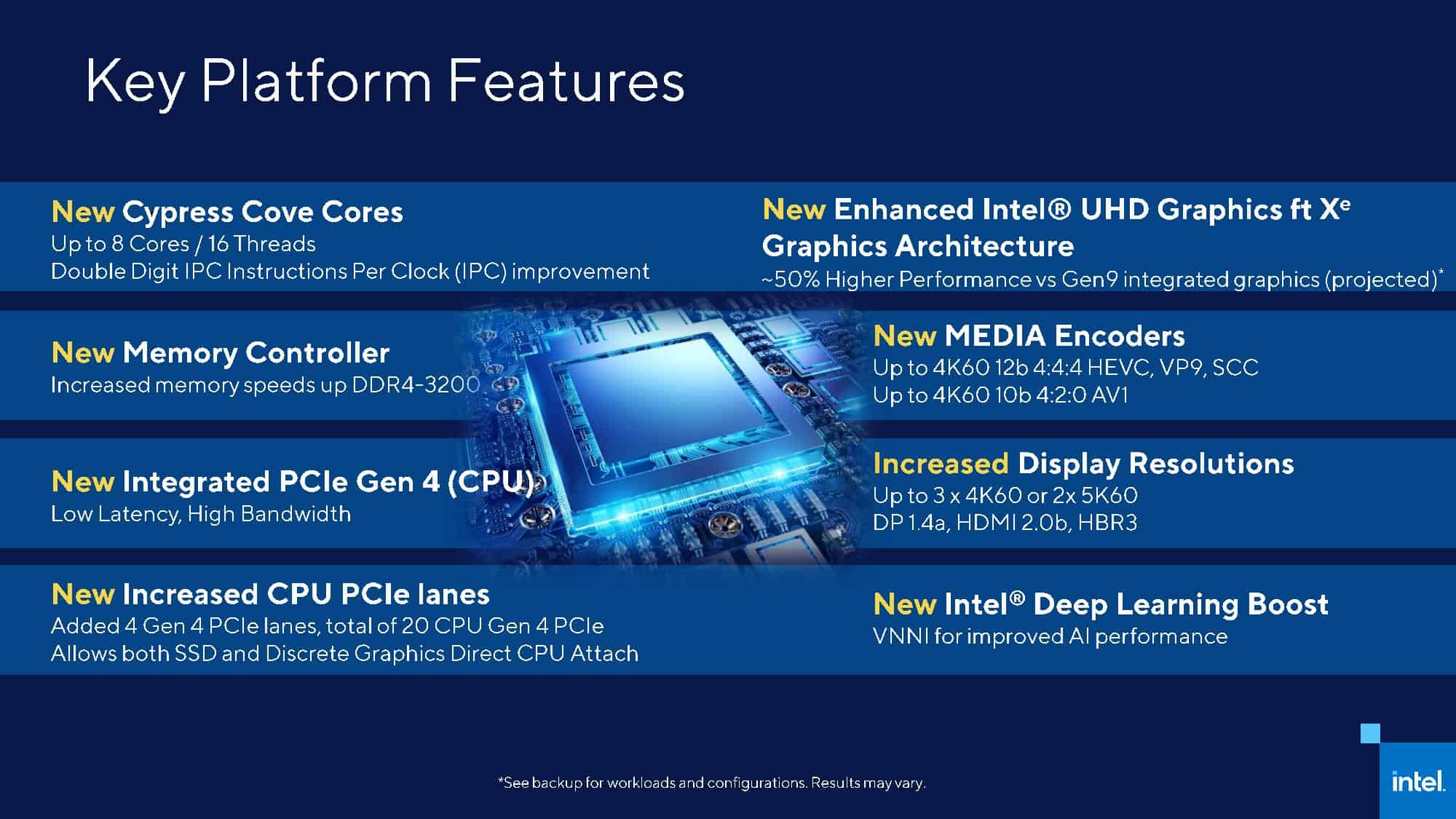
Rocket Lake is the codename of Intel’s 11th Generation CPU lineup, launched in March 2021. Unlike Alder Lake, Rocket Lake did not provide any major leaps in performance despite being based on the New Cypress Cove microarchitecture.
Cypress Cove
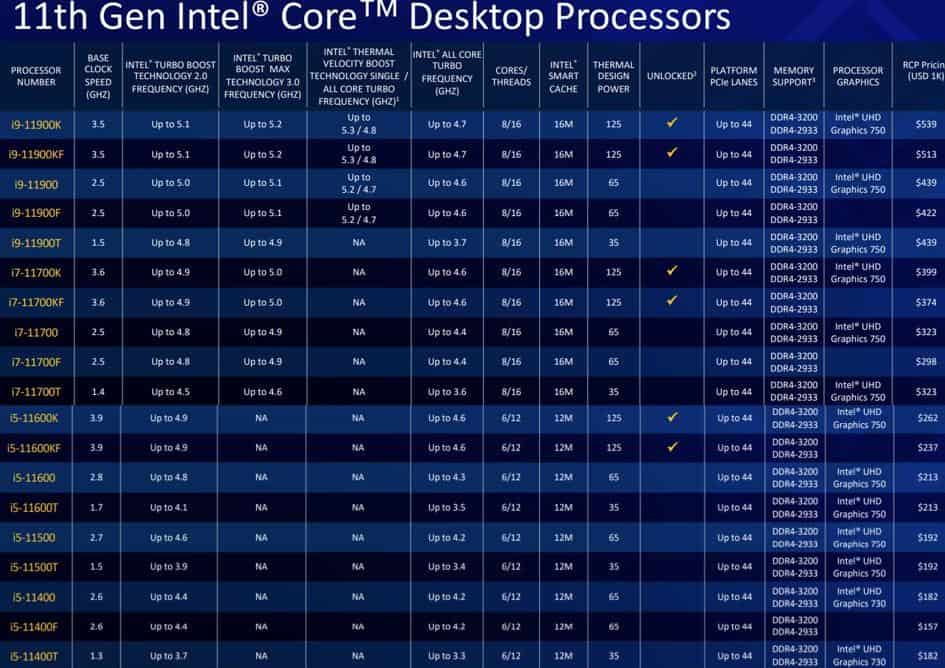
Cypress Cove is a variant of Intel’s mobile microarchitecture, Sunny Cove, based on a 10nm manufacturing process. However, Cypress Cove has been backported to the 14nm manufacturing process used in previous Skylake generations.
With a microarchitecture originally designated for a 10nm node, Intel had to reduce the number of maximum cores and was limited to up to 8. The 11900K features 8 cores and 16 threads, while the 10900K features 10 and 20 threads.
Supporting Chipset
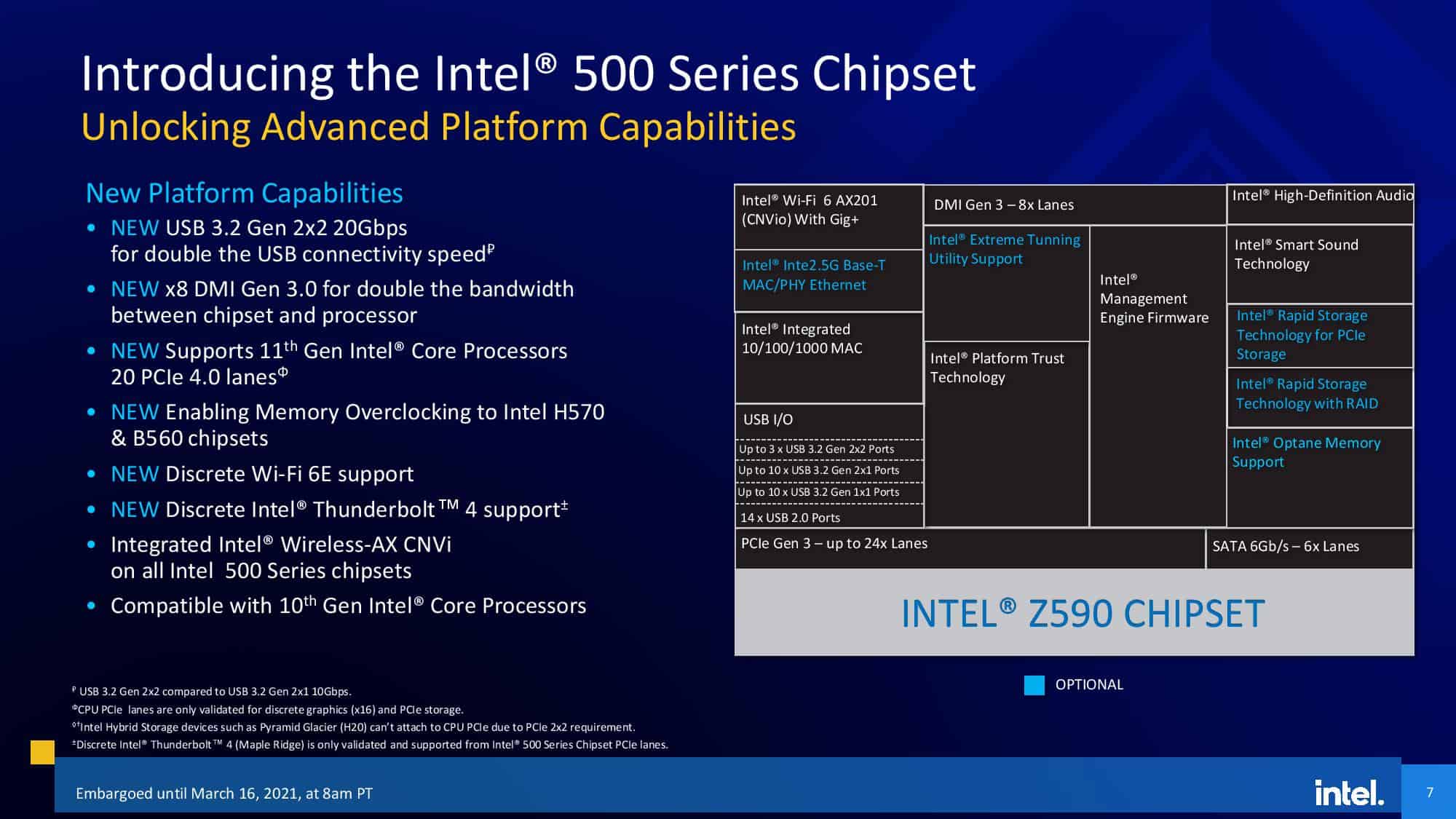
The Intel 500 series chipsets follow the same pattern as that of the 600 series, introducing us to four chipsets that support the 11th Generation CPUs: Z590, H570, B560, and H510. These motherboards will also support Intel’s 10th Generation (Comet Lake) chips, based on the same socket LGA 1200.
This chipset brought notable improvements like USB 3.2 20Gbps support, DMI 3.0 x8 with doubled bandwidth (16 GT/s), and Wi-Fi 6E and Thunderbolt 4. While Wi-Fi 6E and Thunderbolt 4 were not widely adopted initially, some 600 series motherboards lacked them.
Memory overclocking expanded to the cheaper H570 and B560 chipsets, previously only supported on the “Z” chipsets.
Gaming Benchmarks – 1080p
All the jibber jabber aside, the real meat of this comparison lies in the real-world performance of these chips. To test this, we compared the best that the 12th and 11th gen of Intel processors could offer with the 12900K and the 11900K.
Test Bench
- Operating System: Windows 11
- Graphics Card: Radeon RX 6900 XT
- Memory: T-Force NightHawk RGB DDR4 3200MHz
- CPU Cooler: Corsair iCue H115i Elite Capellix
- SSD: XPG GAMMIX S70 BLADE 2TB NVMe
- Power Supply: ENERMAX REVOLUTION D.F. X 1050W
Age of Empires IV
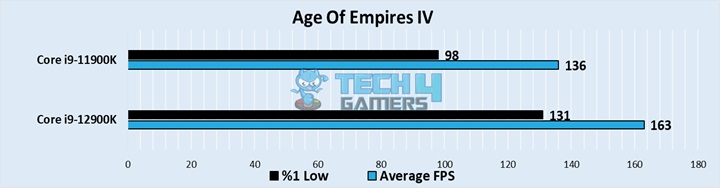
- The average framerates showed quite a difference, with the 12900K getting an average of 163 FPS, while the 11900K was quite a bit behind with an average of 136 FPS.
- Our testing showed an even bigger difference in the the 1% lows, with the 12900K hovering around 131 FPS, while the 11900K struggled to push 98 FPS.
Borderlands 3
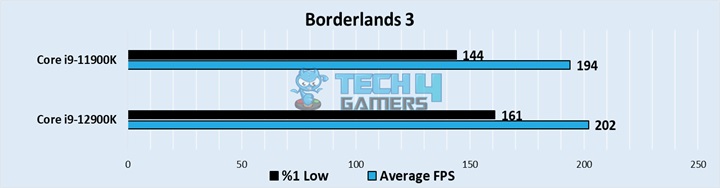
- The averages were evened out in this game, with the 12900K reaching around 202 FPS, while the 11900K had an average framerate of 194 FPS.
- The lows still showed a noticeable difference, with the Alder Lake processor hopping to 161 FPS for its lows, whereas the 11900K hovered around 144 FPS.
F1 2021
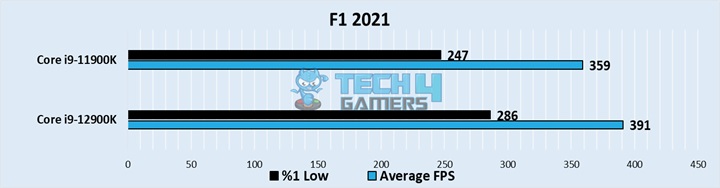
- The difference persisted in this game, with the best from Alder Lake staying close to 391 FPS, whereas the 11900K flew closer to 359 FPS on average.
- The lows once again showed the age of the older processor, with the 11900K sailing close to 247 FPS, whereas the 12th-generation processor held around 286 FPS.
Rainbow Six Siege
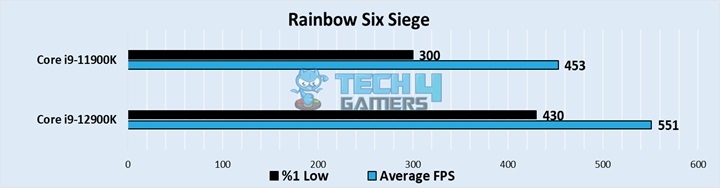
- A CPU-limited game like RSS showed the lead of the 12900K, with averages of around 551 FPS, whereas the 11900K had a framerate closer to 453 FPS.
- The lows were close to 300 FPS on the older chip, while the 12900K hovered around 430 FPS for its minimum framerates, amounting to an astonishing difference.
Overall Gaming Performance
| Featured | Core i9 12900K | Core i9 11900K |
|---|---|---|
| Average FPS | 327 📈 | 285 📈 |
| %1 lows | 252 📉 | 197 📉 |
| Winner: Core i9 12900K | ||
We saw an average of 14% advantage for the newer chip, though it was more exaggerated in some games than others like the ones tested above. The improvement Intel made with their 12th generation chips was definitely substantial, making the 11th generation look outdated in many games.
Productivity Benchmarks
Some people might be looking into these chips because of their performance in productivity software, which is why we’ve rounded up a possie of tests to show how these CPUs measure up against one another. We will, once again, look at the high-end of both generations for our testing.
Cinebench R23
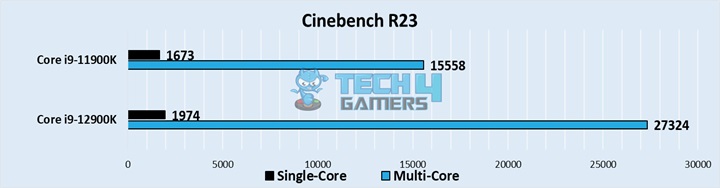
- The 12900K showed a massive 76% increase in performance over its last-gen counterpart in our Cinebench multi-core test thanks to its plethora of extra cores.
- The difference was a more timid 18% in our single-core test, though most productivity applications do not depend on this metric.
Blender
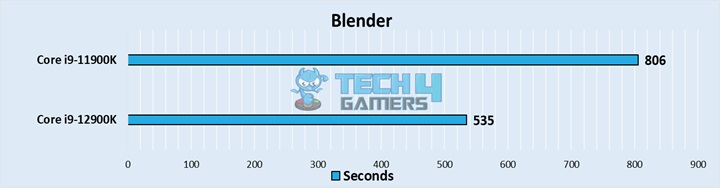
- In the blender open data, the 11900K was around 50% slower than the 12900K, taking over 13 minutes to complete the render, while the 12900K managed to complete it in a little over 9 minutes.
Corona 1.3
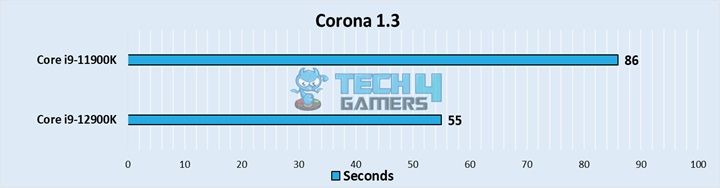
- Finally, the Corona benchmark took around 56% more time on the 11900K, putting the final nail in the coffin of the highest-end 11th-gen consumer processor.
Power Draw
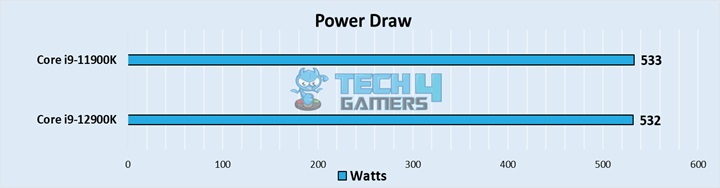
Going by the rest of the comparison, the 12900K took about the same amount of power as the 11900K whilst performing significantly better in most of our testing. This came as a wonderous achievement for the power efficiency of Intel chips, something that has sadly not seen much improvement since.
Price And Value
| CPU | Launch MSRP | Current Price |
|---|---|---|
| Core i9 12900K | 💲589 | 💲311 |
| Core i9 11900K | 💲539 | 💲230 |
| Core i7 12700K | 💲409 | 💲225 |
| Core i7 11700K | 💲399 | 💲185 |
| Core i5 12600K | 💲289 | 💲172 |
| Core i5 11700K | 💲262 | 💲145 |
Across the whole lineup, the 11th gen processors are significantly cheaper than its 12th gen counterparts. This difference ranges from 35% on the highest end to 18.6% on the lowest end. This skews our one sided debate into a bit more complexity with the 11th gen processors potentially giving better value.
Our Recommendation
11th Generation: The older processors are beginning to age in terms of performance, but they make up for it when it comes to value. If you find a good deal, you can buy a 11900K instead of the 12700K which might either be cheaper, or give you better framerates in the games you play.
12th Generation: The performance of these processors in certainly much better than the older counterparts, but their price is also that much higher. You get the added benefit of better power efficiency with these processors, which might lead to some savings in your power bill over time.
Overall, the decision between the 11th gen vs 12th gen of Intel processors depends on your prefrences and budget, but we would recommend going with the more recent processors because of their benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
No, since the 12th Generation lineup is designed for a new LGA 1700 socket, you have no option but to buy one of the 600 series chipset boards to run an Alder Lake CPU.
Yes. Intel’s 12th Generation CPUs give much better price-to-performance ratios, as well as DDR5, and PCIe 5.0 support. Thunderbolt 4 and Wi-Fi 6E are also more common on 12th Generation Motherboards.
Intel’s 12th Generation (Alder Lake) comes with a new Hybrid Architecture design with DMI 4.0 providing improved I/O connectivity. There is also DDR5 and PCIe 5.0 support.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Comparisons Expert]
Abdemanaf is a skilled creative writer who has been honing his craft since 2011. While initially working in different fields, he found a passion for technology and has been exploring the tech world since early 2015. Over the years, he has developed an in-depth knowledge of the latest tech trends and product offerings by various companies.
Abdemanaf’s writing reflects his analytical mindset and ability to think critically. He has a knack for breaking down complex technical information into easily digestible pieces, making his articles engaging and accessible to readers from all backgrounds. In February 2022, he joined Tech4Gamers as a blog and product comparison writer, where he has been able to hone his skills further.
As a writer, Abdemanaf is dedicated to staying up-to-date with the latest technological advancements and trends, enabling him to provide readers with the most relevant and accurate information. He is always eager to learn more and is constantly seeking new challenges to improve his skills.
Get In Touch: manaf@tech4gamers.com



![RTX 2080 Ti vs RTX 3090 Ti [8 Games Tested]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/RTX-3090-Ti-Vs-RTX-2080-Ti.jpg)



![RX 5700 XT Vs RTX 2070 Super [We Tested 8 Games]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/GPU-Comparison-Template-NEW-1-218x150.jpg)
Feedback By: