I bet you’ve come across the term “chipset” when picking out components for your gaming or professional build. But did you know that choosing the wrong or incompatible chipset can bottleneck your PC’s major components? Yup, that’s right! The chipset sets the ultimate performance limit for your performance beast. That’s why it’s super important to grasp the concept of chipsets and make a smart, well-informed decision when selecting one for your build. Without further ado, let’s dive into the technicalities of the chipset.
Key Takeaways
- Chipsets are a collection of ICs that establish communication between various components on the motherboard e.g., CPU and RAM.
- You can easily look up your chipset details using “CPU-Z”, a third-party tool specifically for exploring system specs.
- Chipset drivers are the software that communicates between the chipset and the operating system.
What Is Chipset In Motherboard?
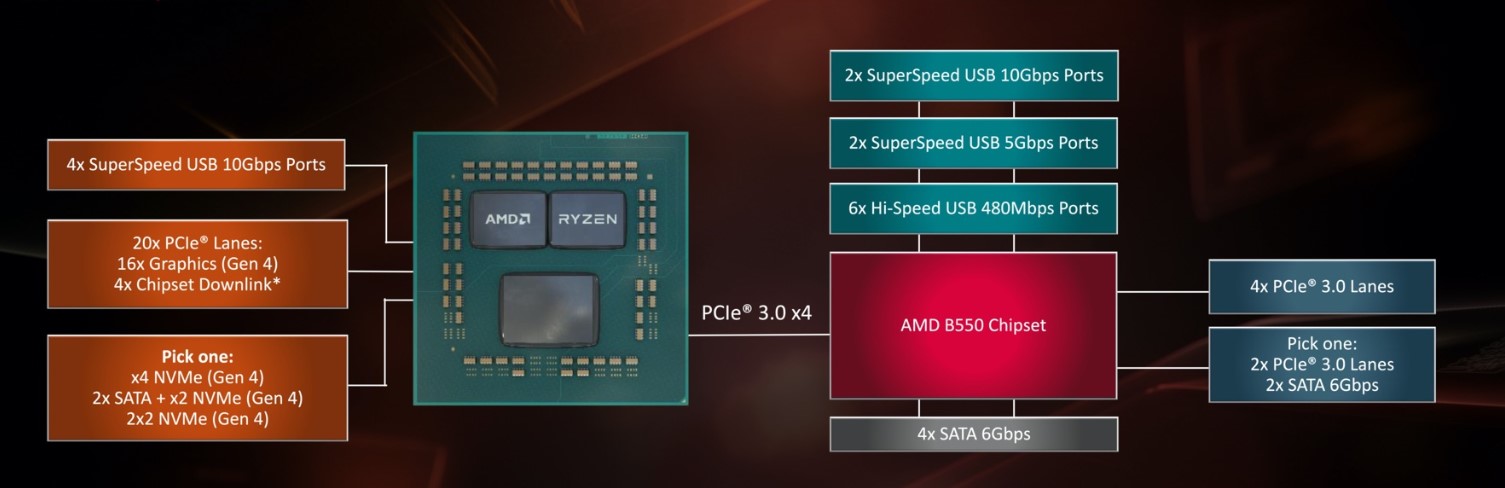
A chipset is a bunch of Integrated Circuits (ICs) on the motherboard that perform various tasks. The primary purpose of the chipset is to ensure communication between various components on the motherboard[1]. You can think of the chipset as the central nervous system of the motherboard that manages data flow and supervises the interactions between processors, storage, memory, GPU, and other peripherals.
Moving onto the construction, the chipset can be divided into two parts[2]: Southbridge and Northbridge. Northbridge takes care of high-speed interactions[3] that are between processors and components like memory and graphics card. While the southbridge handles lower-speed interactions like the interactions between CPU and USB ports, SATA ports, and audio jacks[4].
Latest Intel and AMD Chipsets Breakdown
Undoubtedly, Intel and AMD have been two leading giants in the PC industry for decades. Both offer various pros and cons in their products while serving a mutual aim of optimizing the user experience. Let’s take a brief look at the latest chipsets and their supported processors offered by these two giants.
| Chipset Series | Chipset | Supported Processors |
|---|---|---|
| Intel 700 Series Desktop Chipset | Z790, W790, B760, H770 | Intel's 12th and 13th Gen |
| Intel 600 Series Desktop Chipset | Z690, Q670E, Q670, R680E, W680, B660, H610, H610E, H670 | Intel's 12th and 13th Gen |
| AMD Socket AM5 Chipset | X670E, X670, B650E, B650, A620 | AMD Ryzen 7000 Series |
How Do I Find My Motherboard Chipset?
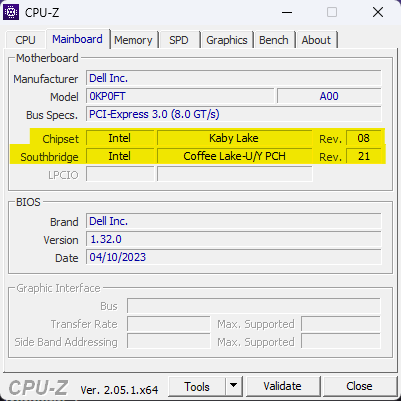
While there are many ways to check your system specs, including the motherboard chipset, my favorite is checking using “CPU-Z“. It is a light and easily available tool that can help you explore your PC specs[5]. Once you are done installing CPU-Z, just run it and go to the “mainboard” tab there, and you will see something like the following:
What Are Chipset Drivers?
Like any other drivers, Chipset drivers are software that facilitates communication between the chipset and the operating system[6]. Chipset drivers are specific to the chipset manufacturer e.g., Intel or AMD. Incompatible drivers can lead to rapid and repetitive system crashes and can even cause component damage in some cases[7]. Let’s briefly take a look at the primary purpose of chipset drivers.
- System Stability: Chipset drivers help ensure the motherboard’s stability and smooth operation by regularly providing necessary updates, bug fixes, and patches. They can even address compatibility issues, improve system performance, and resolve relevant problems.
- Hardware Support: Chipset drivers enable the proper recognition and functionality of various hardware components connected to the motherboard. This includes features such as USB ports, SATA controllers, audio devices, network interfaces, and more. Without the appropriate chipset drivers, some devices may not work correctly or may not be recognized by the operating system.
- Performance Optimization: Chipset drivers often include optimizations and enhancements that can improve system performance. These optimizations may involve memory management, power management, or enhanced data transfer speeds for storage devices or expansion slots.
- Feature Activation: Chipset drivers may also enable specific features and capabilities of the chipset and motherboard. For example, they can unlock overclocking options, RAID functionality, or support for advanced technologies like Intel Optane Memory or AMD StoreMI.
Final Thoughts
In a nutshell, Chipsets are an important part of a PC’s architecture. A chipset is a group of ICs that facilitate communication between onboard components (e.g., RAM, graphics card, USB ports) and CPU along with performing various specific tasks. You can easily check your chipset information by using any third-party tool like CPU-Z.
Furthermore, chipset drivers play a crucial role in building communication links between the operating system and the chipset. Incompatible drivers can lead to instability and not being able to detect several devices. On the other hand, the right chipset drivers can easily address the chipset problems. It is important to regularly keep updating the chipset drivers.
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
References:
- Motherboard. Retrieved from https://www2.hawaii.edu/~cyee/HTML/motherboard.htm
- Difference between North bridge and South bridge. Retrieved from https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-north-bridge-and-south-bridge/
- What is the northbridge. Lenovo. Retrieved from https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/glossary/northbridge/
- What is the southbridge. Lenovo. Retrieved from https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/glossary/southbridge/
- What is CPU-Z. Retrieved from https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/glossary/what-is-cpu-z/?orgRef=https%253A%252F%252Fwww.google.com%252F
- David Janowsky. Device Drivers and Interfaces. Retrieved from https://sites.tufts.edu/eeseniordesignhandbook/files/2020/05/Janowsky_RedOrange-Tech_Note.pdf
- Recurrent crashing drivers “Not compatible”. AMD Community. Retrieved from https://community.amd.com/t5/drivers-software/recurrent-crashing-drivers-quot-not-compatible-quot/td-p/638360
No, the chipset is not a CPU. Chipset provides a platform for communication between all the components on the motherboard, including the CPU. On the other hand, the CPU is the central processing unit of the system which handles different operations and processes. Chipsets can be divided into two main types i.e., northbridge and southbridge chipsets. Northbridge handles the high-speed communication e.g., communication with RAM, and GPU. Whereas Southbridge takes care of low-speed communication e.g., communication between USB ports and SATA ports. Chipset is given its name because it is a bunch of chips and ICs. That’s why it is called a set of chips or chipset. FAQs
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads