- The 13th-generation Intel Raptor Lake CPUs will have a high boost frequency of 6.0 GHz, more cores, improved connectivity, a redesigned core architecture, compatibility with PCIe 5.0 Drives, and more.
- Raptor Lake will work with existing motherboards to offer Alder Lake customers an upgrade path. However, the boards need a firmware update to be compatible.
- Core i9-13900K now has 24 cores at a maximum of 5.8 GHz thanks to the addition of eight efficient E-cores, eight more regular threads, and an additional 600 MHz of the turbo.
- The Core i7-13700K is the following variant, adding 400 MHz to the turbo speed and four more cores and threads.
The Intel 13th Gen Raptor Lake processors are set to challenge AMD’s Ryzen 7000 series. Despite AMD’s advancements, Intel aims to stay competitive with a new hybrid architecture and promised performance enhancements. Let us see what advancements they’ve made with this series.
Introduction to Intel 13th Gen Raptor Lake

The Intel Raptor Lake is an incremental improvement over the Alder Lake series, keeping all the core fundamentals the same while changing a few key aspects. The biggest change they’ve made is the higher performance core clock speeds, along with additional E-cores in most of their processors.
Processors Lineup

The 13000 series CPUs, such as the Core i9-13900K, Core i7-13700K, and Core i5-13600K, bring significant upgrades for content creators with more E-cores.
Intel’s flagship now matches AMD’s thread count with notable performance enhancements. The Core i9-13900K boasts 24 cores at up to 5.8 GHz, while the Core i7-13700K and Core i5-13600K also see improvements in core count and turbo speed. Overclocking remains a feature across the lineup of K series chips.
Supported Chipsets
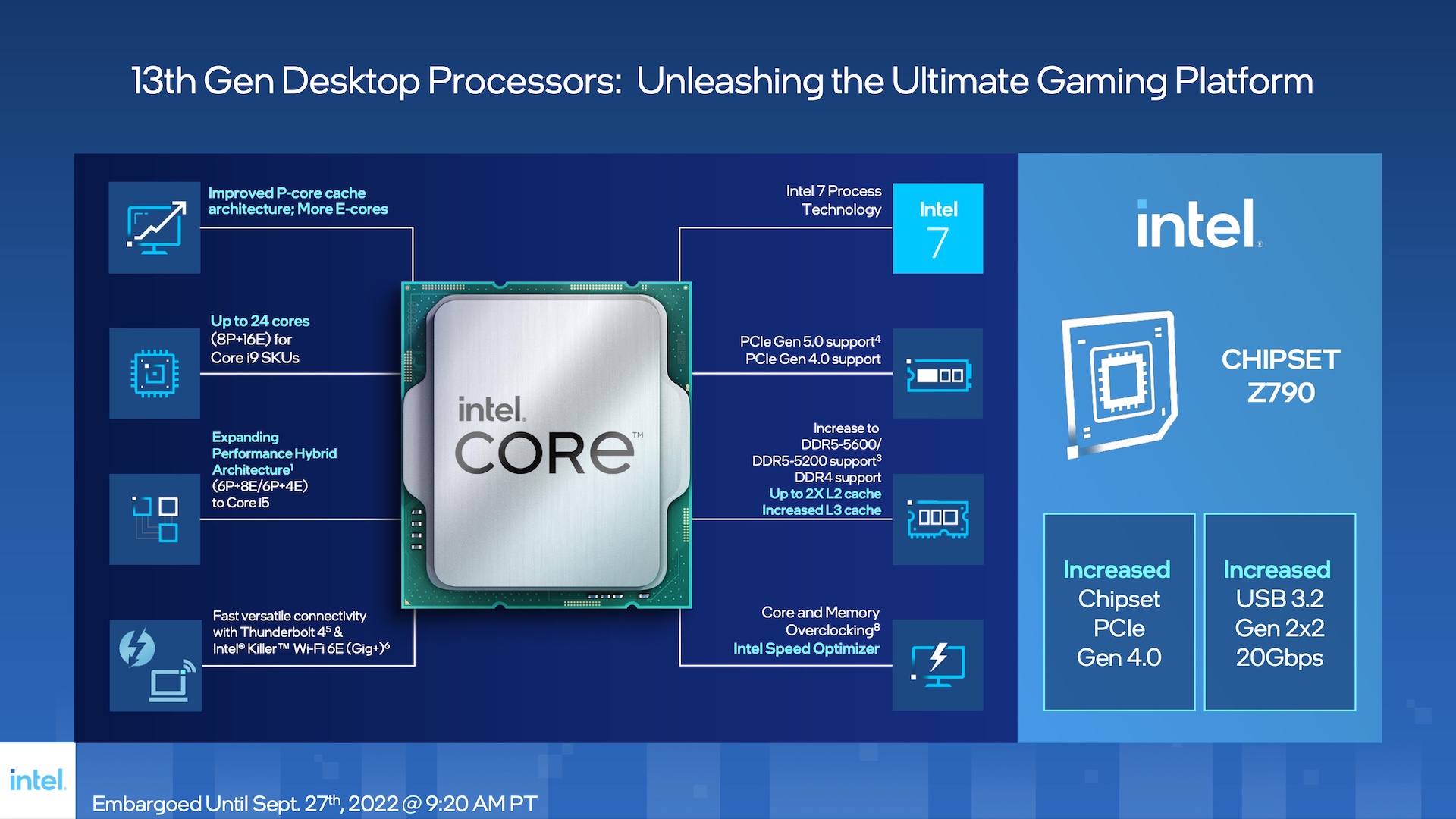
The 13th generation Intel processors, like “Raptor Lake,” continue the 10nm process node, offering little efficiency improvements. They’re compatible with existing motherboards, though firmware updates may be needed.
New 700-series boards will enhance connectivity, minimizing the need for replacements. Despite technological limitations, previous motherboards with LGA1700 sockets are somewhat future-proofed.
The 13th Gen maintains backward compatibility with Z690 and Z790 chipsets, ensuring consistent cooling support. Enhanced chipset capabilities include increased CPU throughput and additional PCIe lanes for faster peripheral access.
USB connectivity is also improved with more high-speed ports. Bundled systems featuring 13th Gen CPUs and Z790 chipsets will be available from October 20, 2022.
Architecture

Raptor Lake’s “Raptor Cove” P-cores and Gracemont E-cores feature significantly larger L2 cache and overhauled architectures. Each core cluster now has 6 MB of shared L3 cache, with two distinct 3 MB clusters.
Node enhancements enable E-cores to reach up to 4.30 GHz boost frequencies. Each cluster comprises four nodes, totaling 16 on the silicon. Enhanced cache utilization and prefetcher algorithms yield a claimed 41% multi-threaded performance boost.
Private L2 cache for E-cores has doubled to 2 MB, while cluster L3 cache has quadrupled to 4 MB, enabling 32 MB more L2 cache. Improved Thread Director middleware utilizes machine learning for better workload distribution across CPU cores.
Backward Compatibility
The 13th Gen Intel Core “Raptor Lake” CPUs and 700-series chipset share compatibility with the LGA1700 architecture, making them usable on existing 600-series chipset motherboards with a simple BIOS update.
Despite the short timeframe since Alder Lake’s release, motherboard manufacturers are already adapting. However, constant platform upgrades may deter some users from switching again. While Raptor Lake may be the last to use LGA Socket 1700, Alder Lake CPUs are compatible with 700-series chipsets.
Intel’s hardware improvements support its performance claims despite using the same manufacturing node as Alder Lake.
Memory Support
The Intel 13th Gen Raptor Lake supports DDR5 memory up to 5600 MHz, an increase from 4800 MHz in the previous generation. In comparison, DDR4 modules are still supported up to 3200 MHz, offering backward compatibility that AMD Ryzen 7000 lacks.
With DDR5 memory kits becoming more affordable, more Z790 motherboards may adopt DDR5. The platform supports XMP 3.0 for straightforward RAM overclocking, with initial compatibility up to 6600MT/sec and up to 7200MT/sec expected in Q4.
The memory controllers for DDR5 and DDR4 have been upgraded, enabling speeds up to DDR5-5600 or DDR5-4400, depending on the DIMM configuration.
Intel suggests enthusiasts can achieve P-core overclocks of up to 8.00 GHz with the latest Intel Extreme Tuner Utility, which maintains platform I/O consistency with Alder Lake and provides access to dual-channel DDR5 and DDR4 memory interfaces.
Performance
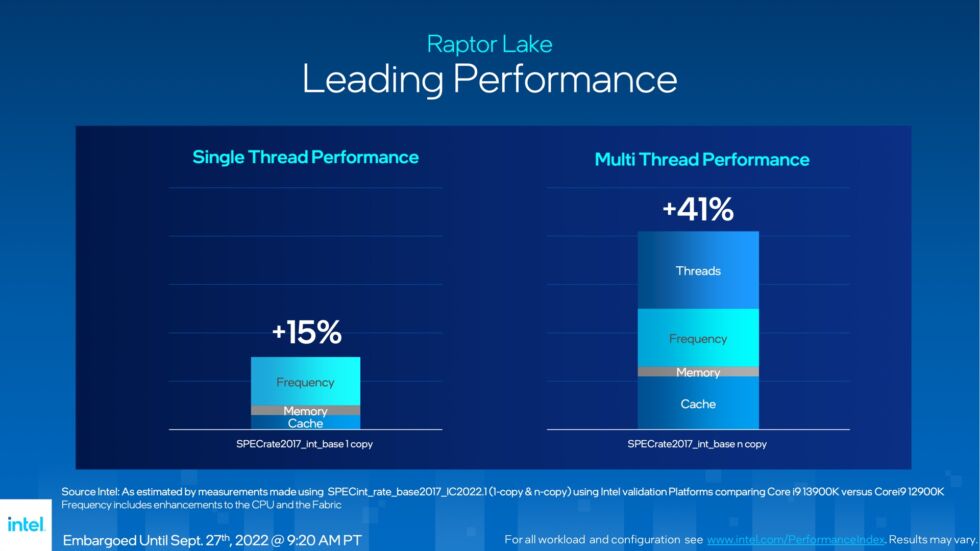
Intel’s Core i9-13900K boasts a 15% single-threaded and 41% multi-threaded performance improvement over its predecessor, the i9-12900K, positioning it as superior to AMD’s Ryzen 9 5950X and Ryzen 7 5800X3D in respective workloads.
The new “Raptor Cove” P-core offers a 600 MHz speed boost, improved power efficiency, and a larger 2 MB L2 cache. While some games show a 24% performance increase compared to the 12900K, results vary across titles.
AMD’s scheduled launch dates for their processors are also a factor to consider, as they could potentially affect CPU performance due to GPU bottlenecks.
Specifications
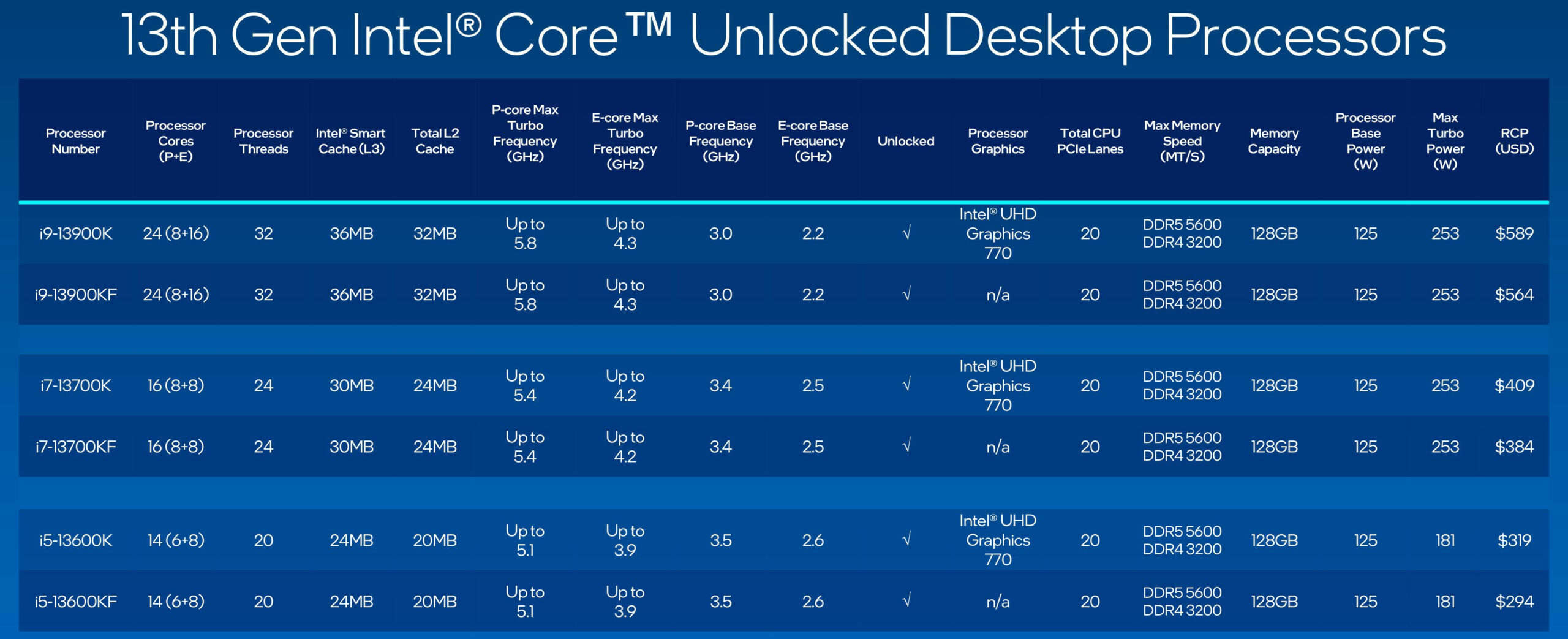
The Intel 13th Gen Raptor Lake lineup, comprising Core i9, i7, and select i5 models, features an 8+16 core configuration in the flagship Core i9-13900K, with eight additional E-cores compared to the previous generation.
Only these high-end processors will utilize the new 8+16 die design with increased cache space. The Core i7-13700K sees improvements, such as a 400 MHz boost in p-core clock speed to 5.4 GHz and an increase in maximum thermal power (MTP) to 253W.
Similarly, the Core i5-13600K boasts four extra e-cores, higher clock speeds, and a higher MTP of 181W. Intel has raised both p-core and e-core speeds across the lineup, while base clocks have decreased slightly to manage thermal design power (TDP) ratings.
Enhanced cache configurations benefit all three chips, with quadrupled L2 cache for e-core clusters and increased L2 cache for p-cores.
Thread Director
Intel’s Thread Director, crucial for core assignment, receives significant upgrades in Raptor Lake, promising a future-proof architecture. It enhances Windows scheduler efficiency, offering improved telemetry data for task allocation.
While initially introduced with 12th-Gen CPUs, it’s now more effective in the 13th Gen, adapting swiftly to varied workloads. Windows 11 is necessary for optimal utilization, as Thread Director isn’t supported in Windows 10.
Raptor Lake employs diverse core speeds tailored to voltage/frequency combinations, necessitating software awareness for workload optimization. Thread Director furnishes Windows 11 with low-level telemetry data for intelligent core scheduling, optimizing performance and efficiency invisibly to software.
Intel 13th Gen Raptor Lake Vs. Intel 12th Gen Alder Lake Gen
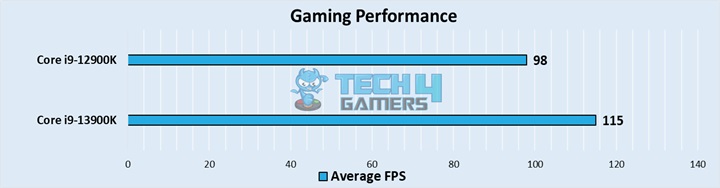
Intel emphasizes performance with Raptor Lake, suggesting significant boosts in multi-threaded tasks and up to 15% improvement in single-threaded tasks compared to Alder Lake. Gaming benefits depend on titles embracing hybrid core efficiency.
A 5% to 15% improvement is expected, which is more impactful for CPU-intensive programs than GPU-reliant ones. The L3 cache has increased to 36 MB, enhancing data access efficiency. The Ringbus interconnect enables seamless cache access with a maximum frequency of 5 GHz.
Intel 13th Gen Raptor Lake Vs. AMD Ryzen 7000 Series
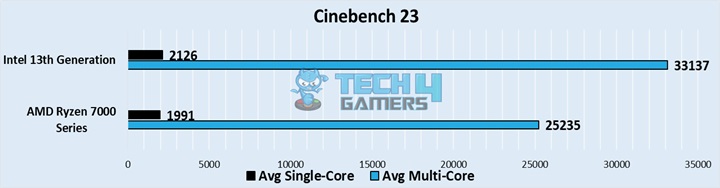
The 13th-generation processors take the lead in performance against the Ryzen 7000 series, at least in synthetic benchmarks. These differences might not reflect the performance these chips have in gaming tests. You can check out our comparisons of the two company’s competitors at the end of this article.
If you want to examine this comparison in more detail, we urge you to check out our Intel 13th gen vs AMD 7000 series comparison!
Intel 13th Gen Raptor Lake Price
| Processor | Launch MSRP | Current Price |
|---|---|---|
| Core i9 13900K | 💲589 | 💲474 |
| Core i7 13700K | 💲409 | 💲339 |
| Core i5 13600K | 💲289 | 💲268 |
| Core i3 13100F | 💲109 | 💲109 |
Since Intel released the 14th-gen processors, the 13th-gen processors have received a substantial price cut, reducing their prices to very reasonable amounts. Additionally, you can get these processors used for a further discount.
Final Thoughts
Despite the lack of innovation from Intel with these chips, they give solid performance for their price, especially now that they’ve fallen in value. The most iffy thing about these processors is their high power demands, which should not be a huge issue for most gamers.
For productivity, the 13th-generation processors are only beaten out by Intel’s successors and not by a lot. Both these reasons justify buying these processors in 2024.
Comparisons And Reviews
Since the debut of these chips, we at Tech4Gamers have been working hard to bring the best quality reviews and comparisons of the Intel 13th-gen processors and their supporting components. Check out the table below for further insights on these chips!
Bear in mind that this list of comparisons is in no way comprehensive of the contents of our websites, so feel free to search for a comparison if you are curious about the performance difference of any two processors.
Frequently Asked Questions
Intel’s upcoming Raptor Lake processors will support DDR4 and DDR5 memory. The 13th-generation CPUs may drive consumers toward DDR5 due to their significant boost in multi-core performance. Notably, Intel’s 13th Gen increases DDR5 capability to 5600.
On October 20, Intel released its 13th-gen Raptor Lake CPUs, with preorders for K-series models starting on October 13. These CPUs, including the Core i5-13600, i7-13700, and i9-13900, offer various options for users. The lineup consists of 22 desktop CPUs with unlocked K models and built-in graphics.
Intel’s 13th-gen Raptor Lake CPUs will support DDR4 RAM, providing compatibility for users looking to save money. DDR4 memory modules are confirmed to be supported up to 3200MHz.
Similar Articles
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads

