LGA Sockets
Rated: 7/10
PGA Sockets
Rated: 8.5/10
Pros And Cons
| CPU | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| LGA Sockets | ✅ Robust CPU ✅ Easy Installation | ❌ Subpar Motherboard Compatibility |
| PGA Sockets | ✅ Durable Motherboard ✅ Supports Intel Processors | ❌ Less Space Efficient |
- Over the last decade, AMD and Intel have been the two market leaders in CPUs. Customers constantly argue about which side has superior technology in their products.
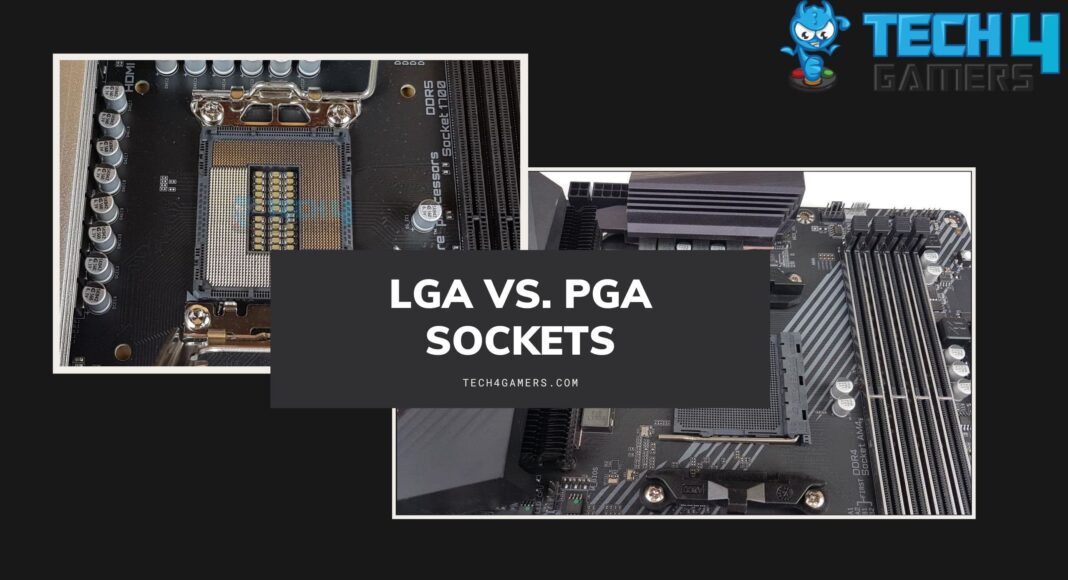
- LGA vs PGA Sockets are complete opposites of one another. LGA is a CPU socket with pins. In contrast, PGA arranges the Processor’s pins to fit correctly into a socket with correspondingly positioned slots.
- Breaking a CPU’s pins may be more costly than breaking the motherboard’s. A CPU may cost twice as much as a motherboard or even more.
- The many reasons that Intel shifted to LGA was how less risky it is to harm the CPU physically on LGA sockets. There are no fragile pins, as the CPU is often one of the more expensive components we cannot take any risks.
Architecture Differences
- Socket Type: Starting, we see that the LGA (Land Grid Array) sockets have pins on the motherboard, while PGA (Pin Grid Array) sockets have pins on the processor. Intel CPUs utilize LGA sockets, while AMD CPUs use PGA sockets.
- Exceptions and Transitions: Recent AMD Ryzen series have shifted towards LGA sockets, though there are exceptions like the AMD Threadripper. Previous Intel CPUs used PGA sockets, but recent generations have shifted to LGA sockets.
- Durability and Risks: Moving on, we observe that the PGA sockets tend to be more prone to damage compared to LGA sockets. LGA sockets offer a lower risk of damage, with pins located on the motherboard rather than the CPU.
- Efficiency and Installation: LGA pins are narrower than PGA pins, providing more efficiency in space usage. Conversely, PGA sockets are easier to install compared to LGA sockets, but breaking CPU pins can be costlier than damaging the motherboard.
- Decision Factors: Choosing between a less durable motherboard or CPU, our preference leans towards the less durable motherboard. Intel historically used LGA sockets while AMD stuck with PGA until recent shifts in socket choices.
- Considerations for PC Building: Users getting into PC building may find Intel systems appealing due to performance and widespread adoption, but AMD’s competitiveness prompts consideration for Ryzen components.
It has been a long debate among PC enthusiasts on which CPU socket is the best. Therefore we at Tech4gamers will provide you with an in-depth analysis of LGA vs PGA Sockets. Since CPU sockets have minimal impact on performance, they are seldom mentioned. Moreover, it provides a standard shape for all processors of a particular generation.
Land Grid Array (LGA)
The acronym “LGA” means “Land Grid Array.” It is fully compatible with Intel chipsets. All Intel motherboards and CPUs use numbered sockets. Typically, Integrated circuits come in LGA, a surface-mounting packaging standard. In contrast to PGA, it relies on contact pins mostly on the motherboard socket rather than the chip itself.
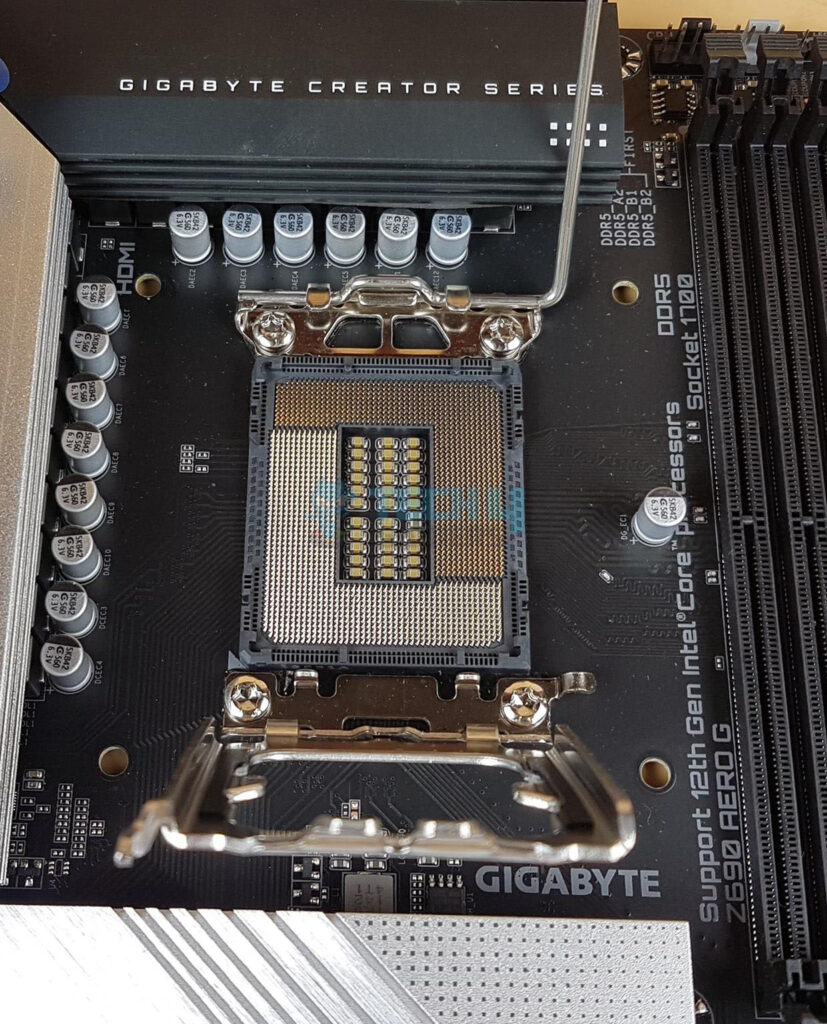

LGA CPUs connect to the motherboard via metal pads, offering excellent density and consistent connectivity, but repairing a broken pin can be challenging, often requiring the replacement of the entire CPU socket.
LGA Socket’s flexible pin layout accommodates future CPU upgrades without risking damage to CPU pins, as they are located on the motherboard. Even if mishandled, the CPU remains unharmed.
Intel’s LGA Sockets Compatibility
When it comes to LGA sockets, the CPU’s pads make contact with pins on the motherboard for data and power transmission. We installed the LGA CPU easily by lifting the lever, sliding the CPU into place, and lowering the lever to secure it.
Intel’s LGA naming convention indicates the number of connections on the CPU and motherboard, like LGA 1151 or LGA 1700. Despite the intricate installation process, LGA sockets reduce the risk of damaging expensive CPUs compared to PGA sockets.
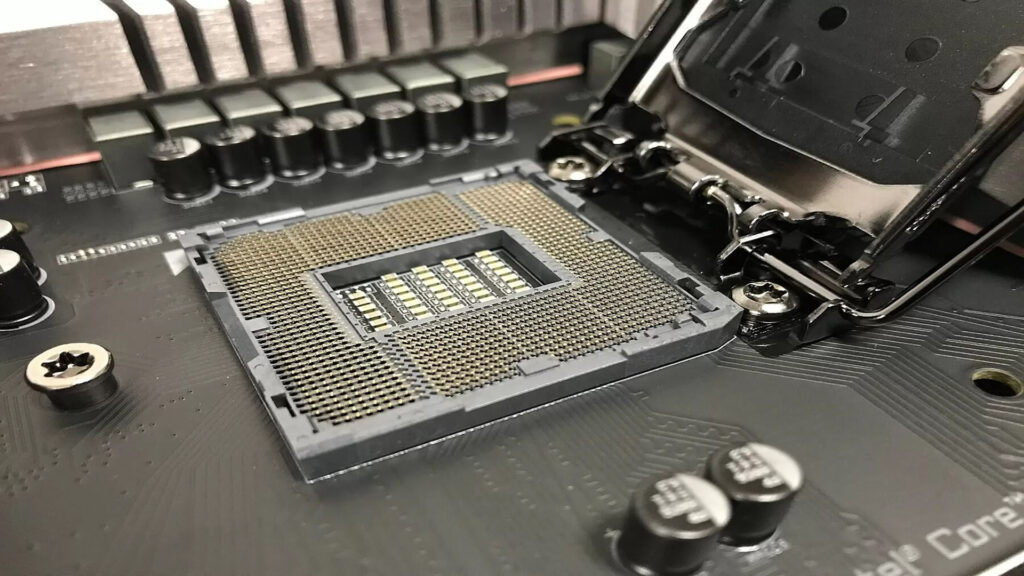
The LGA design transfers sensitive components to the motherboard, minimizing the risk of damage to the CPU. Though the installation process may be complex, the secure placement of the CPU in the Socket simplifies aftermarket cooler installation.
Pin Grid Array (PGA)
Conversely, we observed that the AMD chips now exclusively use the Pin Grid Array (PGA) format, while the new Ryzen processors have moved away from it. Unlike LGA, PGA sockets have contact pins on the processor chip itself.
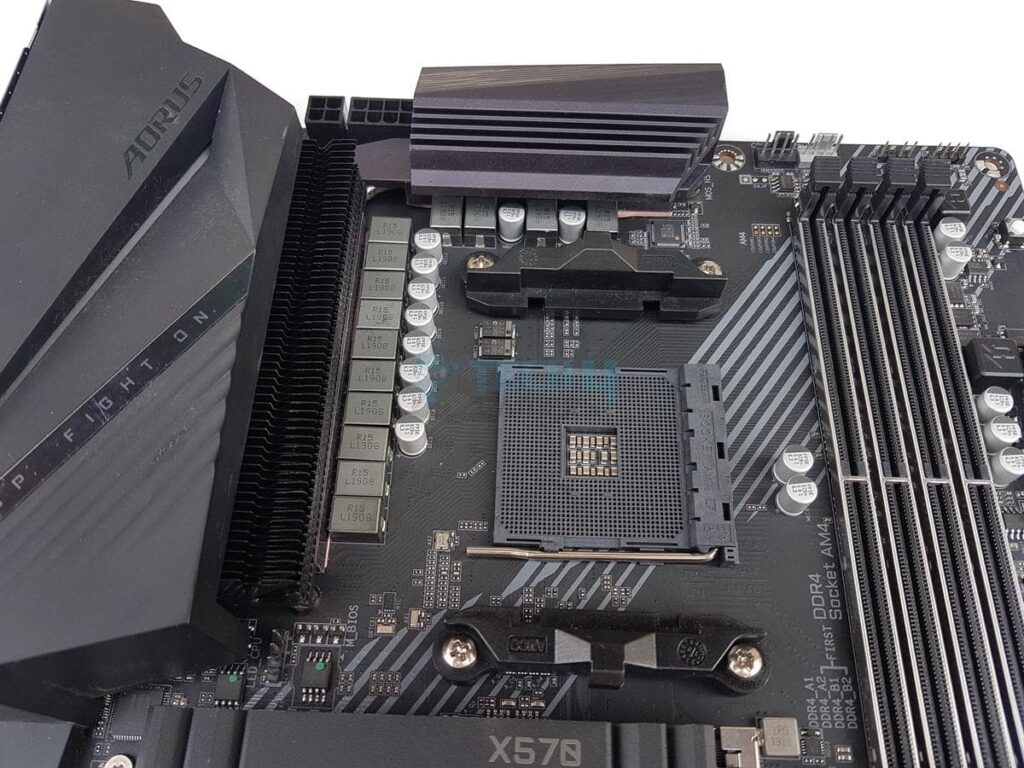

Although PGA sockets offer easy installation, misalignment or pin bending can lead to permanent CPU damage, a common criticism of AMD’s PGA architecture. However, the motherboard remains unharmed, ensuring secure CPU attachment.
Despite their durability and straightforward installation, PGA sockets pose risks, as a single broken pin can render the entire CPU useless, potentially increasing overall costs compared to replacing an LGA motherboard socket.
AMD’s PGA Socket Compatibility
In our analysis of AMD’s CPU sockets, they historically favored PGA designs like AM3, FM2, and AM4, identifiable by their pin counts. Installation of PGA CPUs involves careful alignment and zero insertion force, but mishandling can still damage CPU pins.
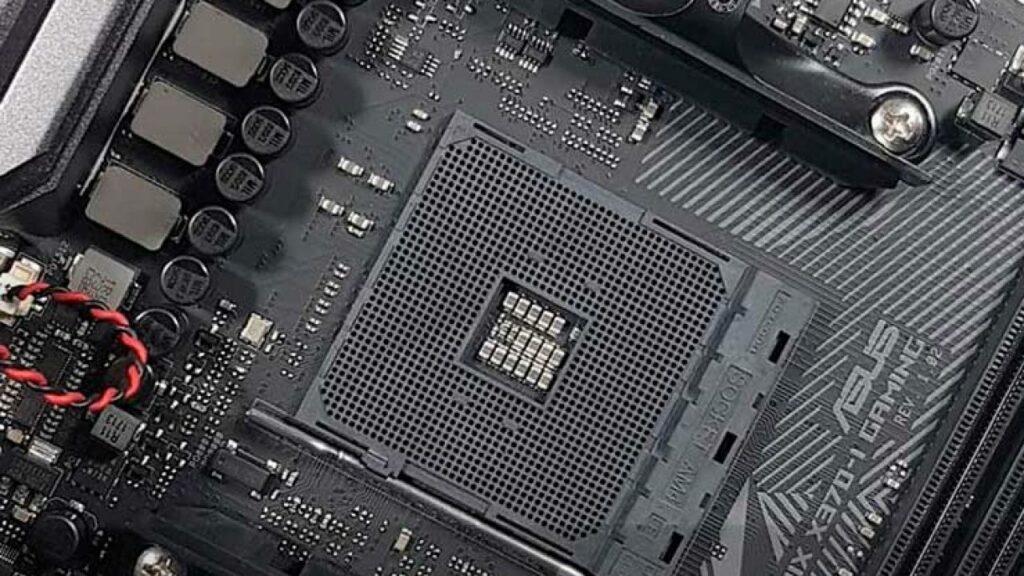

While PGA sockets offer resilience, removing a CPU can be challenging due to thermal paste adhesion, risking damage to both the CPU and cooler. However, with the introduction of the Ryzen 7000 series and the new AM5 socket, AMD has transitioned focus from PGA to LGA standards.
LGA Vs PGA Sockets: Which One Is Better?
LGA Sockets: We found LGA sockets impressive with their secure pin-to-pad connection, favored for their durability and power delivery, particularly by AMD. Opting for an Intel CPU with an LGA socket aligns well with our considerations of performance, budget, and component availability, promising efficient processing power.
PGA Sockets: Looking at PGA sockets, we observed that they offer simplicity in realigning CPU pins, favored for compatibility with AMD processors. Despite potential damage risks, both LGA and PGA sockets offer reliability in our opinion, with the choice depending on performance and budget considerations.
We leave the decision to the users, as they will have to choose them according to the desired performance, available budget, and the accessibility of the individual components. Depending on the users’ required processing power, this may steer them to either an Intel LGA socket or an AMD PGA Socket.
FAQs
Each option’s advantages and disadvantages are worthy of consideration. Some choose PGA because it is easier to realign the CPU’s pins than a motherboard’s LGA sockets. However, given the advantages of LGA, its pin count and power delivery are dramatically superior.
The new AM5 Socket, included with Ryzen CPUs, is based on the LGA Socket. With 1718 pins, the new LGA socket from AMD is officially known as LGA1718. Since the LGA Socket offers superior socket delivery and power, AMD was forced to switch to it. /wsfa] [wsfq]Is Intel PGA or LGA?[/wsfq][wsfa]Intel shifted towards the LGA Socket way back in the early days with the Pentium series and, since then, hasn’t looked back. Intel was once the undisputed king of CPU processors because of their enhancements in the LGA Socket.
The LGA Socket is superior to the previous AMD PGA socket in terms of pin density, which is why AMD opted to utilize it for Threadripper. Since it makes more power connections, it provides more efficient power. Additionally, there were several reports of CPU pins breaking. Therefore AMD often opts for a more secure design in their flagship chip, which is much more expensive than other CPUs. Because replacing a motherboard is often less expensive.
Related Reads:
- 120mm vs 140mm Case Fans
- Intel Core i3 Vs AMD Ryzen 3
- Ryzen 9 Vs Threadripper
- Intel 12th Gen vs 11th Gen
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Comparisons Expert]
Abdemanaf is a skilled creative writer who has been honing his craft since 2011. While initially working in different fields, he found a passion for technology and has been exploring the tech world since early 2015. Over the years, he has developed an in-depth knowledge of the latest tech trends and product offerings by various companies.
Abdemanaf’s writing reflects his analytical mindset and ability to think critically. He has a knack for breaking down complex technical information into easily digestible pieces, making his articles engaging and accessible to readers from all backgrounds. In February 2022, he joined Tech4Gamers as a blog and product comparison writer, where he has been able to hone his skills further.
As a writer, Abdemanaf is dedicated to staying up-to-date with the latest technological advancements and trends, enabling him to provide readers with the most relevant and accurate information. He is always eager to learn more and is constantly seeking new challenges to improve his skills.
Get In Touch: manaf@tech4gamers.com