If you’ve been on the lookout for a CPU cooler (or a case fan), you’ve likely come across the CFM ratings of its fans. But what does CFM mean, and why should you know about it? Well, in short, choosing the fan with the right CFM value is crucial to keep air moving optimally across your case — and this article will teach you why.
- CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) measures how much air a fan can move through an area in a minute.
- High CFM fans are ideal as case fans, particularly where they don’t have to move air through resistance.
- Airflow fans maintain optimal airflow inside your case, working in conjunction with static-pressure fans.
What Is CFM?
Cubic Feet per Minute is a measure of airflow[1]. Specifically, it measures the amount of air (in Cubic Feet) the fan can move through a given area in a minute. A higher CFM rating means the fan can move more air, creating better airflow[2]. High CFM fans are typically called airflow fans.
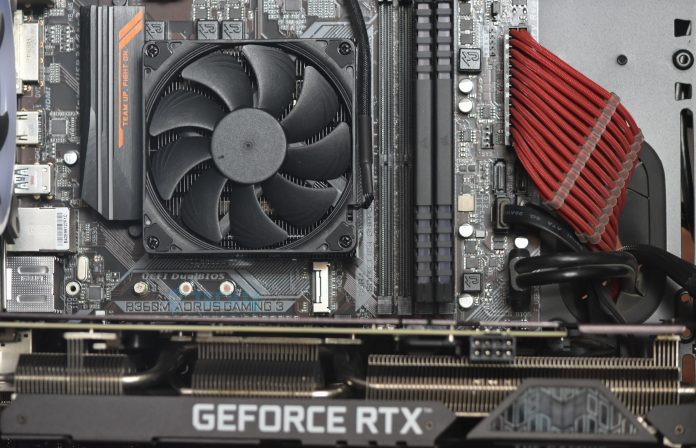

Airflow fans can move much air quickly but are ineffective against resistance. Thus, they should be used for configurations where they don’t have to move air against resistance.
This includes the front (given there is no mesh or hard drive cage), top (exhaust), or back (exhaust). High airflow fans have more blades, but the blades are curvy and have less surface area. Also, the blades are further apart.
Why Is CFM Important?
As mentioned, high CFM fans are ideal for exhaust (and, in some cases, intake) configurations. For optimal airflow, you need to have a balanced intake and exhaust configuration in your system[3]. High CFM fans serve in both these departments and thus are crucial for maintaining good airflow inside your system. So, fans with the right CFM are necessary to keep your PC cool and running at its best.
How Much CFM Is Ideal?
When looking for solid airflow, anything more than 50 CFM is generally a good value for your case fan. For large cases, 60-70 CFM is enough to generate good airflow. It’s also important to keep the noise rating (dBA) in mind, so ideally, you should get a fan that’s not too loud and will move enough air.
CFM Vs Static Pressure
There are generally two characteristics of computer fans that you should keep an eye on. One is the CFM rating[4], and the other is the static pressure rating. Static pressure[5] is defined as the ability of a fan to push air against resistance. It is measured in Pascals (Pa) or inches of water.[6]
As static pressure fans specialize in moving air against resistance[7], they are optimal for air coolers and radiators. Additionally, they can be used as case fans at, say, the front of the case where a hard drive bay is creating resistance. Static pressure fans typically move less air than airflow fans but push it with more force.
Static pressure fans have fewer blades, but the blades are wider and have a larger surface area.
| CFM | Static Pressure |
|---|---|
| CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) measures how much air a fan can move through an area in a minute. | Static pressure is the ability of a fan to move air against resistance. |
| High-CFM fans are optimal for usage as case fans. Specifically, they can be used for intake at the front and bottom of your case and exhaust at the back. | High-static pressure fans are best for moving air through obstruction, so they should be used in radiators and air coolers. |
| Airflow fans have more blades that have less surface area. | Static pressure fans have fewer blades with a wider surface area. |
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
References:
-
Ryan S. (2018). Understanding Fan Performance Metrics And Variability. Retrieved from: https://extension.sdstate.edu/understanding-fan-performance-metrics-and-variability
- Energy Star. Ceiling Fan Performance: Components That Count Retrieved. (n.d). Retrieved from: https://www.energystar.gov/products/ceiling_fans/performance-components-count
- E. Harrison. (n.d). Balancing Airflow In Ventilating Duct Systems [PDF]. Retrieved from: https://www.aivc.org/sites/default/files/airbase_13493.pdf
-
IEEE Standard Letter Symbols for Units of Measurement. (2004, reaffirmed. 2010). Retrieved from: https://web.archive.org/web/20180612141002/http://standards.ieee.org/findstds/standard/260.1-2004.html
- The American Society of Mechanical Engineers. (2008, reaffirmed 2018). Fans: Performance Test Codes [PDF]. Retrieved from: https://www.asme.org/codes-standards/find-codes-standards/ptc-11-fans/2008/drm-enabled-pdf
- Elizabeth J. (2020) Inches Of Water Column. Retrieved from: https://www.equilibar.com/blog/glossary/inches-water-column-in-wc
- U.S. Department of Energy Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy. Improving
Fan System Performance: A Sourcebook For Industry [PDF]. Retrieved from: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy03osti/29166.pdf
Frequently Asked Questions
CFM stands for Cubic Feet per Minute. It measures the volume of air (in cubic feet) a fan moves through an area in one minute.
A 1 CFM rating means a fan can move 1 Cubic Foot of air through an area in One Minute.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads![Motherboard Form Factors [All Types & Difference] Motherboard Form Factors](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Motherboard-Form-Factors-Featured-Image-218x150.jpg)

![What Are DIMM Slots? [Which One To Use First?]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/HOW-TO-10-218x150.jpg)