As a PC enthusiast, it is important to understand common terminologies in the realm of PC hardware. With proper knowledge and awareness, you can make better decisions while spending on your PC components. Such an important term is static pressure which has a wide scope in various fields. In this guide, I will explain it in the context of PC hardware.
Key Takeaways
- Static pressure is the ability of fluid (air) to move through tight spaces within a PC case or components like radiator and heatsinks.
- It is important for fans as it ensures fans have enough potential to move air through resistance to provide effective cooling while minimizing noise.
- Dynamic pressure is the fluid pressure due to its velocity. It finds its applications in areas of fluid dynamics rather than PC hardware areas.
- Airflow is the volume of air that is moved per unit time.
What Is Static Pressure?
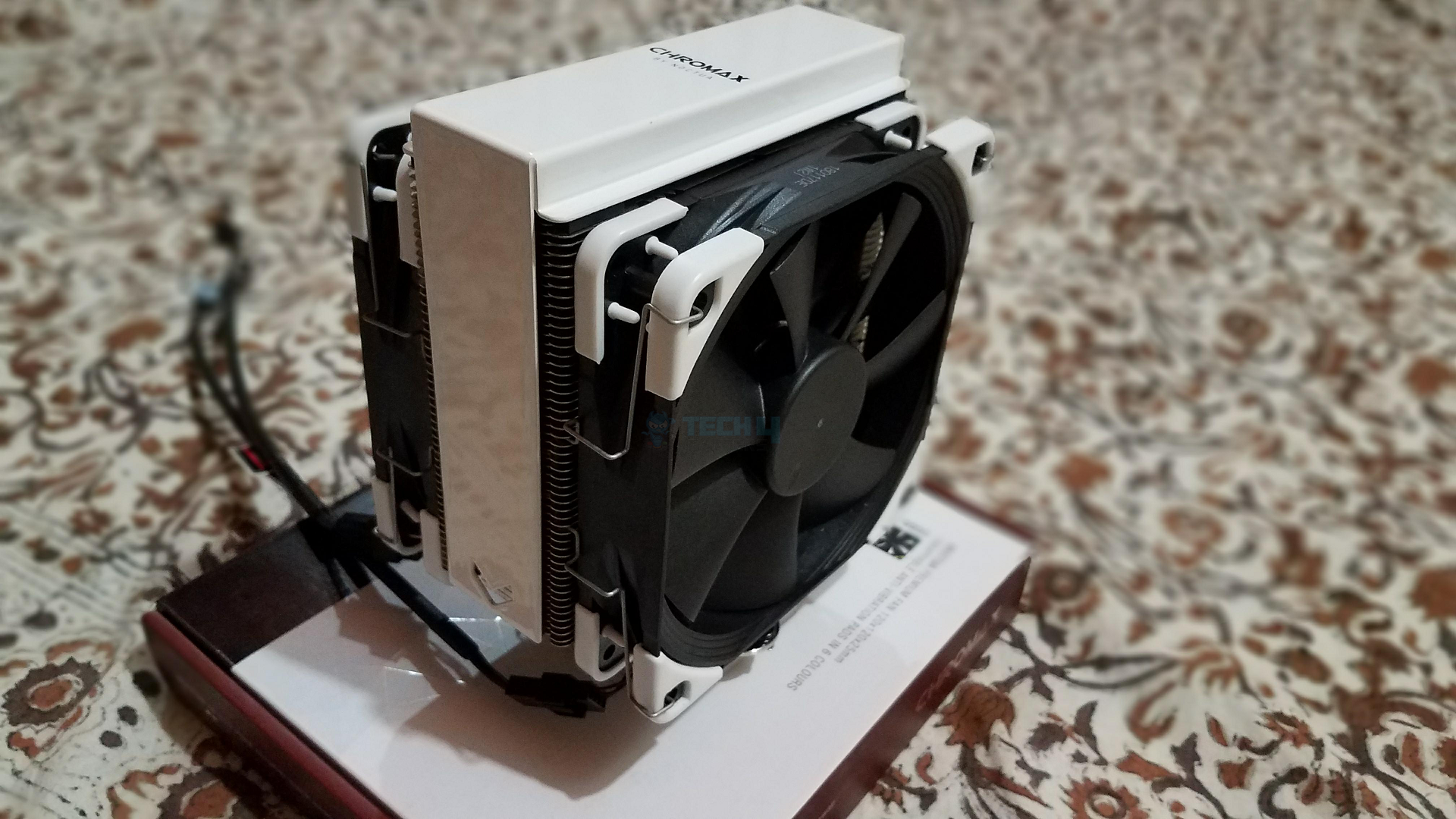

Static pressure refers to the pressure exerted by air or other cooling mediums on surfaces within a PC case or on a component like a CPU cooler or radiator. It is the measure of force that the air exerts on these surfaces as it overcomes this resistance. Components like fans generate static pressure to push air through these restrictive areas, helping to maintain proper cooling[1].
Why Is Static Pressure For Fans Important?
It is important for several reasons, primarily related to effective cooling and optimal airflow within various environments, such as PC cases, radiators, and heatsinks. Here’s why it matters:
- Overcoming Resistance: In environments with restricted airflow, such as between closely packed components, the air encounters resistance. High static pressure fans are designed to push air through these obstacles more effectively, ensuring that the components receive adequate cooling[2].
- Case Airflow: Static pressure tackles problems head-on, as airflow works on the principle of maximum volume with little effort. In order to distribute more unrestricted air across a greater area, fans designed for high airflow are frequently utilized. This makes them ideal for unobstructed air direction towards hot regions or overall case cooling.[3].

Lian-Li-O11 – Image Credits (Tech4Gamers) - Radiators and Heatsinks: Radiators used in liquid cooling systems and heatsinks have densely packed fins that can restrict airflow. Fans with high static pressure can force air through these fins, maximizing the heat dissipation capability of these cooling solutions[4].

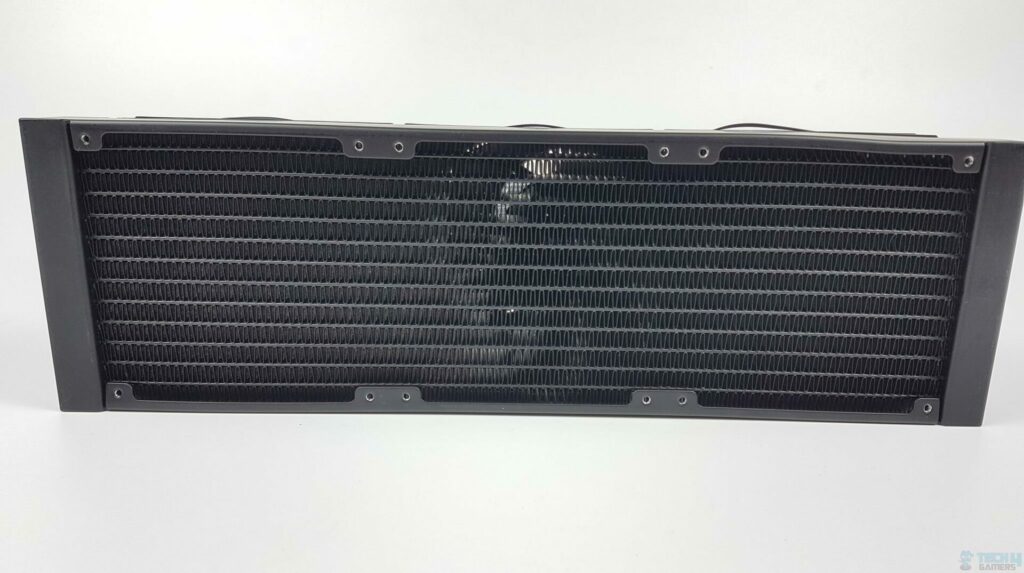
ARCTIC Liquid Freezer II 360mm radiator back. Image by Tech4Gamers - Liquid Cooling: In water-cooling setups, fans with high static pressure are commonly used to move air across radiators to dissipate heat from the liquid coolant. The ability to push air through the dense radiator fins ensures efficient heat exchange between the coolant and the surrounding air[5].

AIO Cooler RGB – Image Credits: Tech4Gamers
Static Pressure Vs Dynamic Pressure Vs Airflow
Here is a brief comparison of three commonly confused terms:
| Static Pressure | Dynamic Pressure | Airflow |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure exerted on surfaces in airflow-restricted environments. | Pressure is exerted on surfaces due to the velocity of the fluid (air or liquid). | The volume of air moved per unit of time. |
| Essential for overcoming resistance in tight spaces and pushing air through obstructions like heatsinks and radiators. | Important for understanding the force exerted by a moving fluid. | Important for overall ventilation and heat dispersion within the case. |
| Ideal for cooling components with tightly packed fins, radiators, and heatsinks. | Less relevant in typical PC cooling scenarios and more relevant in fluid dynamics and aerodynamics studies. | Ensuring consistent air circulation throughout the PC case. |
| Effective at pushing air through obstacles like fins, filters, and closely spaced components. | Less effective at overcoming resistance and moving air through tight spaces. | May struggle to move air through restrictive spaces like heatsinks or radiators. |
| Measured in millimeters of water column (mmH2O) or Pascals (Pa). | Not commonly measured directly in PC cooling discussions. | Measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM) or cubic meters per hour (m³/h). |
Final Words
Static pressure is the ability of a fan to push air through tight spaces. It is important for several reasons that contribute to effective cooling while maintaining a peaceful environment. Moving on, dynamic pressure is the pressure of the fluid that it exerts due to its velocity. Dynamic pressure is usually discussed in the areas of aerodynamics and fluid mechanics. Lastly, airflow is the volume of air that the fan moves per unit time.
FAQs
It is the fluid’s potential to overcome resistance and move through tight spaces.
It is measured using a manometer.
Yes, such a fan will not push air through tight spaces, which will create hot spots at some locations.
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
References:
- Johann Tang (Iowa State University). . Retrieved from: https://blog.orientalmotor.com/fan-basics-air-flow-static-pressure-impedance
- J. Zulovich (University of Missouri). Fans: Airflow versus Static Pressure? Retrieved from: https://www.asi.k-state.edu/doc/dairy/fans-airflow-vs-static-pressure.pdf
- Corsair. STATIC PRESSURE VS AIRFLOW. Retrieved from: https://www.corsair.com/us/en/explorer/diy-builder/fans/pc-fans-static-pressure-vs-airflow/
- Eric Hazen (Versus Engineering). Radiator Fans In-Depth Explanation. Retrieved from: https://www.verus-engineering.com/blog/informative-8/radiator-fans-in-depth-explanation-and-information-32
- Atila Gobor (EKWB). FANS FOR LIQUID COOLING. Retrieved from: https://www.ekwb.com/blog/fans-for-liquid-cooling-what-you-need-to-know/
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads




![How Long Does Thermal Paste Last? [Answered] How Long Does Thermal Paste Last](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/How-Long-Does-Thermal-Paste-Last-218x150.jpg)
![What Are DIMM Slots? [Which One To Use First?]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/HOW-TO-10-218x150.jpg)