If you have built or are building a PC, you must have often come across the term “bottleneck.” This term is essential to ensure that all the components you choose for your PC will run well together. A chain is only as strong as its weakest link. Consequently, you need to find out the weakest link in that chain (i.e., your PC build) and upgrade it to enhance the overall performance. I will help you do that in this guide.
Key Takeaways
- A bottleneck is a scenario in which one component of your PC build cannot keep up with others for various reasons, such as weak CPU, weak GPU, insufficient memory, or slow storage media.
- You can discover which component is bottlenecking by using “Task Manager” and spotting which component is at 100% or near 100% utilization. You can also use online bottleneck calculators to find out the weakest link.
- CPU and GPU are two common bottlenecks. Each refers to the scenario when that particular component (i.e., CPU or GPU) cannot keep up with others.
What Is A Bottleneck?
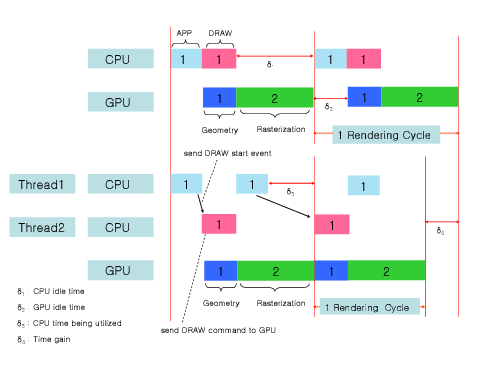
A “bottleneck” refers to a situation where one component of the computer is significantly slower or less capable than the others, thereby limiting the system’s overall performance.[1] Simply put, a PC bottleneck is like a traffic jam on a highway. It’s a point in your computer’s system where things slow down because one part can’t keep up with the others.
Addressing bottlenecks means upgrading the component causing the slowdown. For instance, a faster CPU or GPU can help. Similarly, upgrading to a faster storage drive can speed up loading times. Compatibility among PC parts is vital for smooth operation without slowdowns.
What Causes Bottleneck In PC?

Various factors, including hardware limitations and software demands, can cause bottlenecks in a PC.[2] Here are some common causes of bottlenecks in a PC:
- Imbalanced Hardware Components: One of the most common causes of bottlenecks is having imbalanced hardware components. For example, having a powerful CPU but a lower-tier graphics card can lead to a GPU bottleneck in graphics-intensive tasks like gaming.
- Outdated Hardware: Older or obsolete hardware components may not be able to keep up with the demands of modern software and applications. This can result in CPU, GPU, or RAM bottlenecks.
- Insufficient RAM: Running memory-intensive tasks without enough RAM can cause a bottleneck. When the RAM is full, the system may need slower storage devices to store data, leading to temporary performance degradation.
- Slow Storage Devices: Traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) are significantly slower than SSDs. Using an HDD as your primary storage device can lead to slow data access and longer loading times for applications and files.
- CPU Intensive Software: Some software, such as video editing or 3D rendering applications, can be very demanding on the CPU. If your CPU isn’t powerful enough for these tasks, it can become a bottleneck.
- GPU Intensive Software: Graphics-intensive tasks, like modern video games or GPU-based rendering, can overwhelm a less capable GPU, causing it to be a bottleneck.
- Software Multitasking: Running multiple resource-intensive applications simultaneously can strain the CPU and RAM, leading to performance bottlenecks, mainly if you have limited RAM.
- I/O Constraints: Slow data transfer rates between hardware components can lead to bottlenecks. For example, if the motherboard or storage interfaces cannot handle the speed of your CPU or GPU, it can limit overall performance.
- Overheating: If your CPU or GPU overheats, they may throttle their performance to prevent damage. This thermal throttling can cause a bottleneck as the hardware operates at reduced speeds.
How To Find Bottleneck In PC?
To identify and resolve bottlenecks, it’s essential to assess your system’s hardware components, monitor their performance, and ensure that they are appropriately matched to the tasks you want to perform. There are various methods for finding bottlenecks, but I have discussed two easy methods below:
Method 1: Use Monitoring Tools
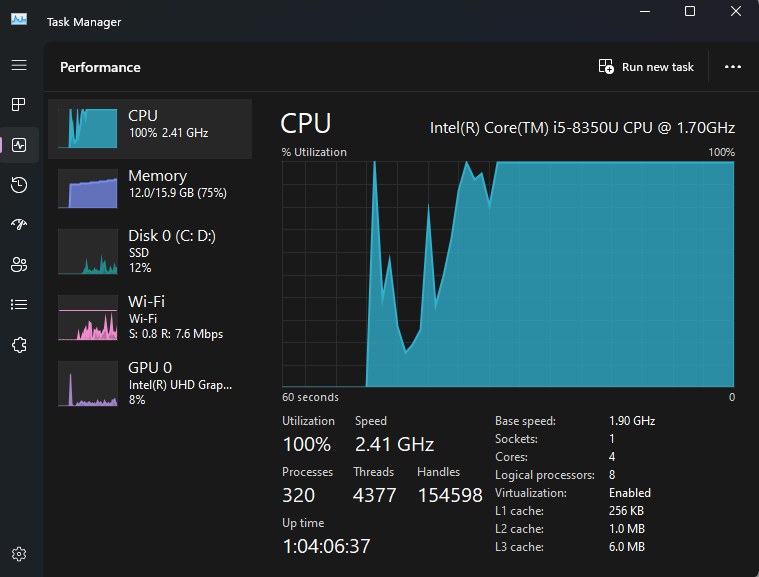
You can check which component is pushing its limit while running. In most cases, that is the component bottlenecking your whole PC build. To identify such elements, you can use “Task Manager.” You can monitor CPU, GPU RAM, disk, and network usage here. Check which component runs at or near 100% utilization during your task.
Alternatively, use MSI Afterburner, NVIDIA Inspector, or AMD Radeon Software to monitor GPU usage, temperature, and clock speeds for GPU-intensive tasks. You can also use third-party software applications, like HWMonitor, CPU-Z, or Speccy, that provide detailed information about your hardware components.
Additionally, high temperatures can lead to thermal throttling and reduced performance. Use software like HWMonitor, Core Temp, or GPU-Z to monitor CPU and GPU temperatures during intensive tasks.
Method 2: Use Bottleneck Calculator
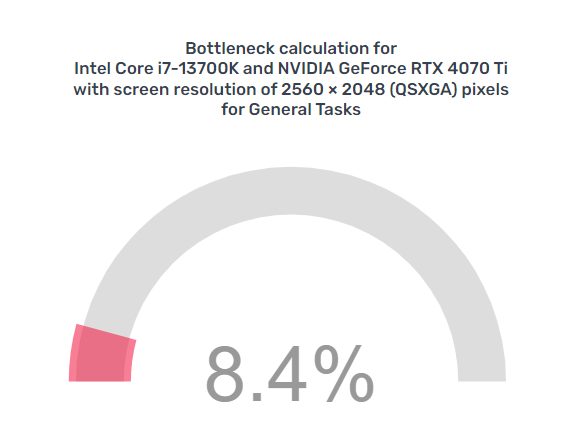
A bottleneck calculator is a tool or online service that helps you estimate potential bottlenecks in your PC configuration based on the hardware components you have or plan to use. These calculators consider the specifications of your CPU, GPU, RAM, and other hardware components and assess whether there might be imbalances or performance limitations in your system.
Here’s how you can typically use a bottleneck calculator:
- Input Your Hardware Specs: You must provide information about your PC’s hardware components. This usually includes the CPU model, GPU model, amount of RAM, and sometimes storage type (HDD or SSD).
- Calculate: After entering your hardware specifications, the calculator will analyze your components and their relative performance levels. It will then determine if there is a potential bottleneck and, if so, which component might be causing it.
- Results And Recommendations: The calculator will provide you with the results of its analysis. It may show whether your CPU or GPU will likely be the bottleneck and to what extent. It might also offer recommendations for optimizing your PC’s performance, such as upgrading a specific component.
Remember that bottleneck calculators can provide helpful insights but are not always 100% accurate. Below are some of the good bottleneck calculators that I found online:
GPU Bottleneck Vs. CPU Bottleneck

GPU and CPU bottlenecks are common in mainly PC builds. Such a scenario can occur when your CPU or GPU can’t complement the rest of your system.[3] It is essential to upgrade the bottlenecking element for good performance.[2] Below, I have provided a brief overview of these two common bottlenecks:
| GPU Bottleneck | CPU Bottleneck |
|---|---|
| GPU is the weakest link | CPU is the weakest link |
| GPU can’t keep up with data processing demands | CPU can’t process instructions and tasks fast enough |
| This can happen while running graphics-intensive applications, like games, at higher resolutions | This can happen while running computation-intensive software or while multitasking |
| This can lead to low FPS and slower rendering | This can lead to slower program execution and longer application load times |
| The solution includes upgrading to a more powerful GPU or lowering the graphics settings | The solution consists of upgrading to a faster CPU or limiting multitasking |
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
References:
- Diva. Performance Anomaly Detection and Bottleneck Identification. Retrieved from https://umu.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:839537/FULLTEXT01
- GeeksforGeeks. Bottleneck Conditions Identification in System Design. Retrieved from https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/bottleneck-conditions-identification-in-system-design/#causes-of-bottlenecks
- Alspach.org. Towards a better understanding of ‘bottlenecks’ in PC building. Retrieved from https://www.alspach.org/2020/09/towards-better-understanding-of.html
FAQs
The Bottleneck effect is when a PC component can’t keep up with the other components.
If your PC is bottlenecked, it means that not all the components in your PC can give their maximum performance. The overall performance is limited by some single component that is the weakest link.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads



![Is A Laptop Considered A PC? [Explained] Is Laptop a PC](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Is-Laptop-a-PC-218x150.jpg)