- First, we conduct a 5-step performance analysis, which includes general tests, rendering tests, transcoding, web-based benchmarks, and gaming benchmarks. This process gives us a complete overview of a processor’s performance.
- During testing, we monitor the CPU’s frequency behavior to understand its clock speeds under intensive workloads. We also keep track of temperature and power consumption to recommend the best CPU cooler and power supply.
- Finally, we overclock the processors incrementally to find out how much additional performance can be achieved without stability issues.
how we test processors
At Tech4Gamers, our team of hardware experts uses a specific methodology for testing and reviewing processors. This thorough process examines every aspect of a CPU's real-world performance across various scenarios. By applying the same testing methods to each processor, we ensure fair comparisons and accurate CPU roundups.
On this page, we’ll reveal how Tech4Gamers tests processors, providing insights into our review process. This guide will also help you choose the right processor by explaining the significance of each benchmark and its impact on performance.
Key Takeaways
General Tests
In our general tests, we aim to evaluate a CPU’s performance in everyday tasks and common computing scenarios. These tests encompass a range of benchmarks that assess the processor’s capabilities in file compression, data encryption, mathematical calculations, single-threaded and multi-threaded performance, memory speed, and overall system productivity.
By conducting these tests, we can gain insight into how well a CPU handles typical user activities such as web browsing, office productivity, digital content creation, and more. The results from these benchmarks provide us with a comprehensive overview of the processor’s efficiency, speed, and responsiveness in managing a variety of standard applications and operations.
| Test | Description | Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| 7-Zip | Tests file compression and decompression capabilities using different algorithms. | MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) |
| AIDA64 | Offers a suite of benchmarking tests including CPU AES, CPU Queen, and Memory benchmarks. | AES -> MB/s Queen -> Score Memory Benchmark -> MB/s Latency -> Time (ns) |
| PCMark 10 | Evaluates CPU performance across web browsing, office productivity, digital content creation, and other tasks. | Overall score |
| PassMark PerformanceTest | Includes integer math, floating point math, prime numbers, extended instructions, encryption, compression, sorting, and physics. | Overall score |
| Super-PI | Tests single-threaded performance by calculating the value of PI to a specific number of digits. | Time to calculate digits |
| wPrime | Uses Newton’s method to calculate square roots for multi-core and multi-threaded benchmarks. | Time to complete calculation |
| Fritz Chess | Analyzes as many chessboard positions as possible using the Deep Fritz 12 engine. | Kilo nodes per second |
| 3DMark CPU Profile | Tests multi-threaded performance with six different profile tests (max threads, 16, 8, 4, 2, and 1 thread). | Score per thread profile |
| Vera-Crypt | Evaluates performance through disc encryption and decryption of large files. | Encryption/decryption speed (GB/s) |
| Test | Description | Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Blender | Uses the Cycles render engine to assess CPU performance by rendering scenes. | Samples per minute |
| Corona | Measures rendering time per second and rays per second. | Rays per second |
| FryBench | Multi-core CPU test developed using Fryrender engine for photo-realistic rendering. | Time to render |
| V-Ray | Evaluates rendering speed with test scenes dedicated to CPUs and GPUs. | Render speed |
| POV-Ray | Ray tracing program that produces images using text-based scene descriptions. | Render time |
| Indigo | GPU and CPU renderer known for unbiased and photorealistic rendering. | Render time |
| Cinebench R23 | Real-world test suite for measuring system performance on Windows and OS X. | Score |
| Geekbench 5 | Benchmark tool for evaluating CPU and GPU performance across multiple platforms. | Score |
Rendering Tests
In our rendering tests, we evaluate a CPU's performance with demanding, CPU-intensive tasks. Using various benchmarking tools, we measure how quickly and efficiently a processor can render complex scenes.
We test the CPU's capability to handle detailed tasks involving materials, lights, cameras, and intricate computations. These tests help us determine the processor's speed and efficiency in producing high-quality visual outputs.
Transcoding
CPU transcoding performance, which refers to the ability of a CPU to encode or decode media files using various codecs, is crucial for efficiently processing and converting media content, such as videos and audio.
This performance is significant in many scenarios where media files need to be transformed or compressed. For example, in video editing, transcoding is essential for converting videos into different formats or compressing them for optimal storage and seamless streaming.
To test a CPU's speed and efficiency in transcoding, we use two benchmarks: x264 HD and x265 HD.
| Test | Description | Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| x264 HD Benchmark | Analyzes CPU performance in encoding a 1080p video using the x264 codec. | Encoding time, frames per second |
| x265 HD Benchmark | Encodes 1080p videos using the HEVC x265 video standard. | Encoding time, frames per second |
| Test | Description | Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Strike | DirectX 11-based benchmark for contemporary gaming PCs, testing physics and combined CPU and GPU performance. | Score |
| Time Spy | DirectX 12-based benchmark designed for contemporary graphics cards, testing the capabilities of the API’s advanced features. | Score |
| 1080p Gaming | Tests gaming performance at 1080p resolution with ultra settings in a variety of AAA titles. | Framerates |
| 1440p Gaming | Tests gaming performance at 1440p resolution to observe performance shifts. | Framerates |
Gaming Benchmarks
These tests involve running a series of benchmarks and games at different resolutions to measure the processor's ability to handle gaming workloads. We start with software tests like Fire Strike and Time Spy, which assess the CPU's performance with DirectX 11 and DirectX 12 technologies, respectively.
Following these, we run various AAA titles at 1080p and 1440p resolutions with ultra settings to record framerates and overall gaming performance. By conducting these tests, we can determine how well a CPU manages gaming tasks, ensuring smooth gameplay and high performance.
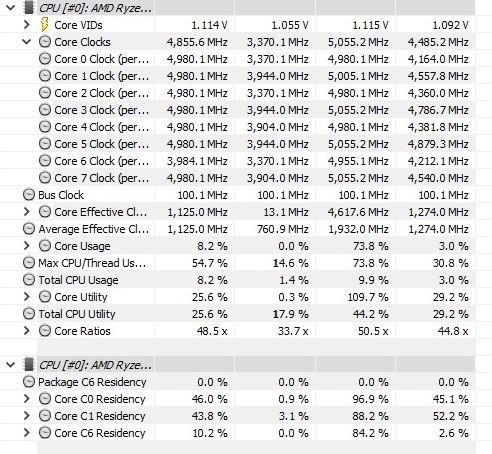
Frequency Behavior
During our performance testing, we also keep an eye on the clock speeds of the processors we are testing. We review how the frequencies behave under different workloads and how the processor reaches its boost clock speed as we ramp up the loads.
It should be noted that there are a ton of factors that have an impact on a CPU's ability to reach its turbo frequency.
However, considering the fact that our test build and workload remain the same throughout different processors, these factors are minimized to some extent.
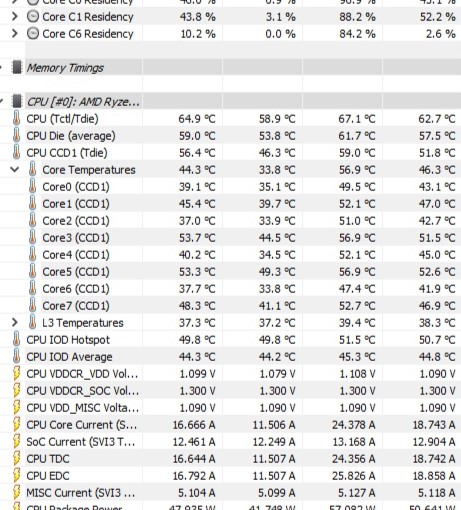
Thermal And Power Efficiency
Thermal and power efficiency are two fundamentals that must always be reviewed thoroughly when testing processors.
These two factors not only impact performance and overclocking but also dictate the tier of PSU and CPU cooler you will need in your PC build.
First, to set the base, we leave the test bench idle for exactly 30 minutes and then note down the temperature and power consumption. After that, we run a 30-minute Cinebench R23 test to test the power consumption and thermal efficiency of the CPU.
We perform this test for both single-core load and multi-core load.
In Short
The Tech4Gamers hardware reviewers follow a specific guideline to test and review processors. This guideline is created to keep the readers as informed as possible while also maintaining authenticity and reliability. As such, we test our processors over a series of benchmarking tools along with games to judge them based on their real-world performance.
From day-to-day tasks to CPU-intensive rendering, transcoding, and web-based benchmarks, we leave no stone unturned in testing our processors. We also benchmark high-end games at 1080p and 1440p resolutions to review the gaming performance of our processors.
To ensure accurate performance representation, our testing rig is equipped with state-of-the-art equipment. Rest assured that the figures you see reflect the actual performance you can expect from these processors.
Apart from processors, we also test a variety of gaming hardware. If you want to learn more about our testing process, be sure to check out the following guides:

