Intel Core i5 1235U
Rated: 7/10
AMD Ryzen 5 7530U
Rated: 8.5/10
Pros And Cons
| CPU | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 7 7530U | ✅ DDR4, DDR5 Compatible ✅ Better iGPU Performance | ❌ Less Performance Cores ❌ Older Processing Node |
| Core i5 1235U | ✅ Modern 6nm Design ✅ Better Power Efficiency | ❌ Worse iGPU Performance ❌ DDR |
- Based on our benchmark tests, the Ryzen 5 7530U outperformed the 1235U by approximately 6%.
- Additionally, the Ryzen 5 7530U consumed 8.5% less power compared to its competitors.
- The Ryzen 5 7530U is a processor based on newer technologies than the i5 1235U.
Core i5 1235U Vs Ryzen 5 7530U – Comparison Table
| Technical Specs | Intel Core i5 1235U | AMD Ryzen 5 7530U |
|---|---|---|
| Vendor | Intel | Amd |
| Type | Laptop | Laptop |
| Instruction set | x86-64 | x86-64 |
| Codename | Alder Lake | Zen 3 (Cezanne) |
| Model number | i5-1235U | - |
| Integrated GPU | Iris Xe Graphics (80EU) | Radeon RX Vega 7 |
| Multiplier | 13x | 20x |
| L1 Cache | 80K (per core) | 64K (per core) |
| L2 Cache | 1280K (per core) | 512K (per core) |
| L3 Cache | 12MB (shared) | 16MB (shared) |
| Unlocked Multiplier | No | No |
| Release Date | February 23, 2022 | January 5, 2023 |
Architectural Differences
- Core Count: The Ryzen 5 7530U uses a traditional core architecture, whereas the i5 1235U has a hybrid core architecture. This means that the Ryzen has only 6 performance cores, whereas the Intel processor packs in 2 performance cores as well as 8 efficiency cores in its package. This allows both processors to have a total of 12 threads.
- Clock Speeds: The Core i5 has two sets of boost and base frequencies because of its different core architecture. At its lowest, the 1235U has a frequency of 0.9GHz, while it can boost up to 4.4GHz. On the other hand, Ryzen can have a frequency of anywhere from 2.0GHz to 4.5GHz.
- TDP: Both the processors are fairly low-powered, which allows them to make do with a TDP of 15 watts.
- L3 Cache: The Ryzen outclasses the i5 in terms of L3 cache. It has 16 MB, whereas the i5 has a cache of 12 MB.
- Process Size: The Ryzen 5 7530U is based on a more modern processing size of 7nm, whereas the i5 1235U uses a slightly older lithography comprising processing nodes of 10nm.
- Memory: Both processors support up to 64GB of memory, though the Intel processor can accommodate both DDR4 and DDR5, whereas the Ryzen can only make use of DDR4.
Though the Ryzen 5 7530U seems like a processor using AMD’s latest architecture, it uses the fairly dated Zen 3 architecture for its design, as indicated by the second last number in its model name. Because of this, consumers might find this processor to be a better match for a slightly older Intel processor like the 1235U. In comparing the Core i5 1235U vs Ryzen 5 7530U, we will see if this new AMD processor using an older architecture is better than one of Intel’s last-generation processors.
Core i5 1235U Vs Ryzen 5 7530U – Benchmarks
The hardware specifications of these processors paint a picture of them being comparable in terms of performance, which might not translate into real-world performance.
To see if this hypothesis of equivalence holds up in real-world performance, we have rallied up a couple of laptops with each processor to test their performance difference.
The nature of mobile processors means that you are certain to experience a difference in performance from machine to machine, so take the numbers in this section with a grain of salt.
Cinebench R23
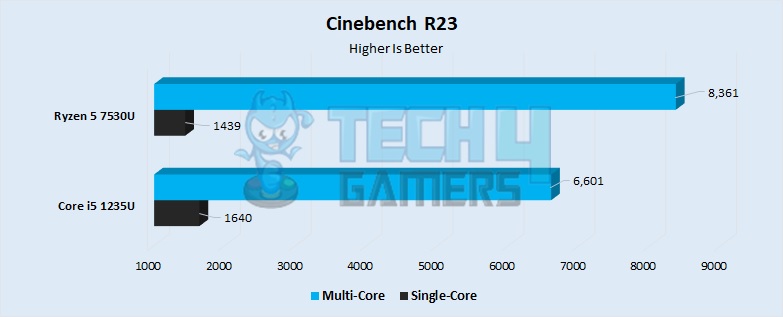
- Kicking off our benchmark suit with Cinebench R23, the 1235U outperformed the Ryzen in the single-core test by about 14%. It had a score of 1640 points, whereas the Ryzen had a score of 1439 points.
- The multi-core performance showed us the opposite result, with the Ryzen performing 26% better than the Intel processor, accumulating a score of 8361 points. In contrast, the i5 had a score of around 6601 points. This increase in performance on the Ryzen is due to the higher number of high-performance cores.
Geekbench 6
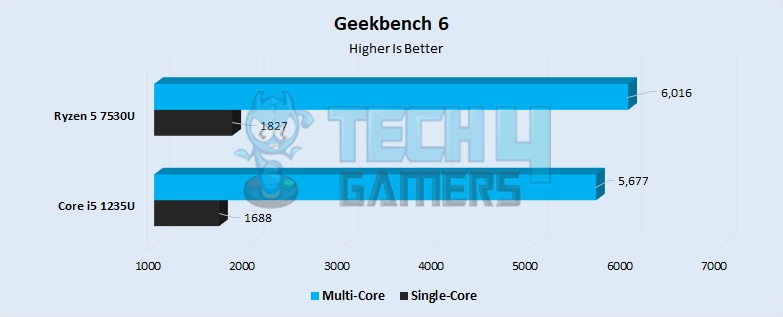
- Geekbench 6 seemed to favor the newer processor, with around 9% better performance in single-core score. The i5 had a score of 1688 points, whereas the Ryzen had a score of around 1827 points.
- The superiority of the Ryzen translated to the multicore performance, scoring 7% better than the i5. The R5 scored 6016 points, whereas the i5 1235U performed around 5677 points.
Geekbench 5.4
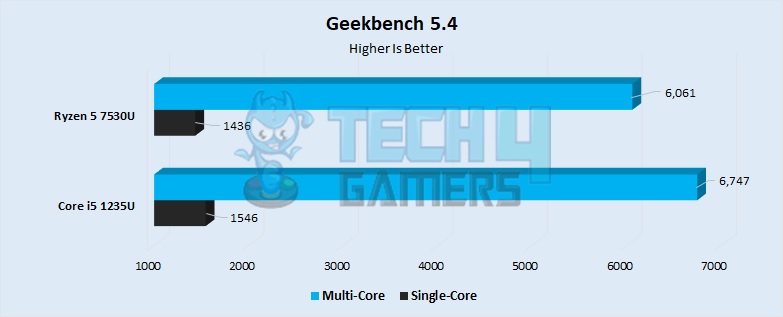
- Curiously enough, the test results were flipped over when we used the older Geekbenh 5.4. The Intel processor had an 8% lead over Ryzen in terms of single-core performance. The i5 1235U had a score of 1546 points, whereas the Ryzen 5 7530U had a score of around 1436 points.
- The pattern continued in the multicore performance of these processors, with the i5 having 11% higher performance than the Ryzen. It had a score of 6747 points, whereas the Ryzen 5 7530U had a score of around 6061 points.
7-Zip
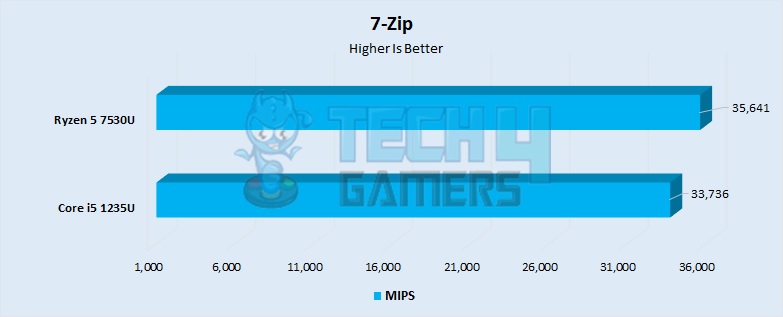
- Synthetic tests aside, you are more likely to feel the difference in performance between these processors in real-world tasks, like 7-Zip decompression. In this regard, the Ryzen outpaced the i5 by about 6%.
- The Ryzen 5 7530U had a performance of 35641 MIPS, whereas the i5 1235U was not very far behind with a score of 33736 MIPS.
HWBOT x265
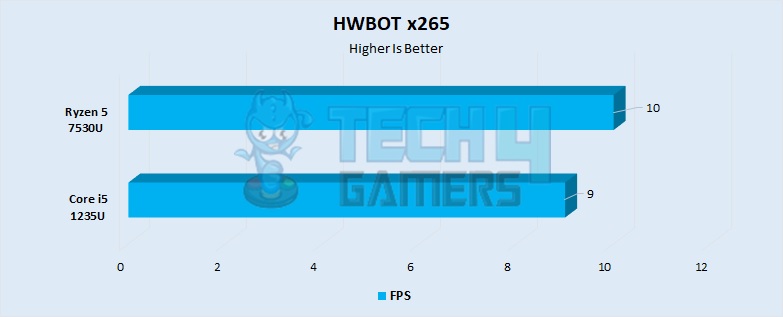
- The HWBOT x265 benchmark at the 4k preset also favored the Ryzen processor by about 11%.
- The i5 1235U had a video playback framerate of around 9 FPS, whereas the Ryzen had a framerate of 10 FPS.
Blender
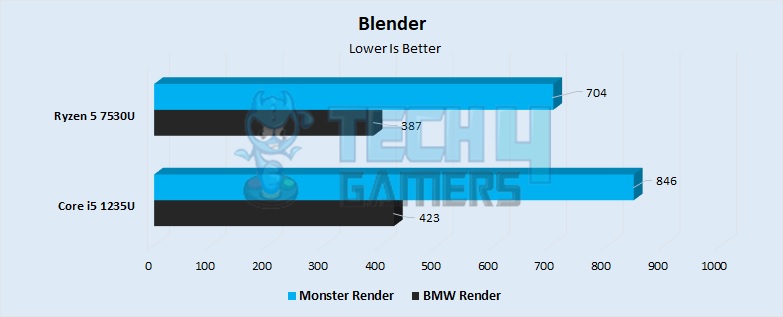
- The Ryzen 5 7530U also managed to eke out a victory in our Blender renders. The Monster scene had a 20% quicker render time on the Ryzen, finishing in 704 seconds compared to the 846 seconds on the i5 1235U.
- The BMW render was no kinder to the i5. The 7530U had a 9% lead over the processor, rendering out the scene in 387 seconds compared to 423 seconds on the i5 1235U.
3DMark 11
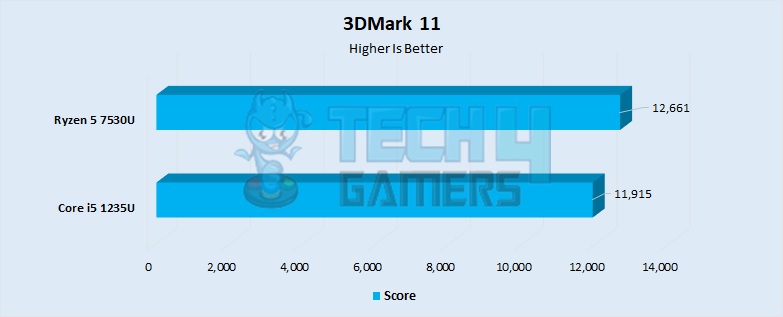
- This popular physics renderer was also more performant on the Ryzen processor by about 7%.
- The Ryzen 5 7530U performed around 12661 points, whereas the 1235U scored around 11915 points.
FP32
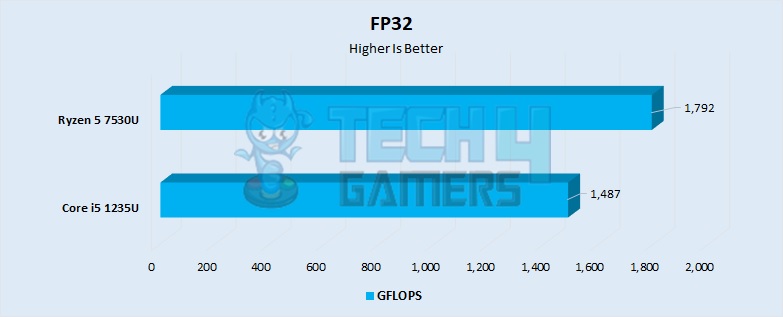
- The Ryzen kept dominating the Intel processor in terms of iGPU performance as well, with a performance about 20% better than the i5.
- The 7530U performed around 1792 GFLOPS, whereas the i5 1235U had a performance of around 1487 GFLOPS. This means that the Ryzen will be significantly more performant than the i5 in GPU-bound workloads.
Power Consumption
| Games | Ryzen 5 7530U (W) | Core i5 1235U (W) |
|---|---|---|
| Average Power Consumption | 44⚡️ | 48⚡️ |
| Winner: Ryzen 5 7530U | ||
Measuring the power consumption of these two processors using Prime95 and an external monitor, we found the Ryzen to consume about 8.5% less power than the Core i5. The 7530U had a power consumption of 44 watts, whereas the 1235U consumed about 48 watts of power.
Ryzen 5 7530U Vs Core i5 1235U: Which One Should You Go For?
AMD Ryzen 5 7530U: According to our benchmark suite, the Ryzen 5 7530U performed around 6% better than the 1235U. Moreover, the power consumption of the Ryzen 5 7530U was also 8.5% lower than its competition. This greatly enhances the Ryzen 5 7530U’s leverage against its rival in real-time comparison.
Intel Core i5 1235U: The 1235U can be sold for a lower price due to its age while still giving great performance. While both processors are best suited for low-powered use in ultrabooks, the i5 1235U is known especially for its sleek design and tremendous compatibility with the Ultrabook models, which gives it an edge.
We recommend that consumers buy the AMD Ryzen 5 7530U because of its efficient power solution and the dominance in benchmarks performed by our team. Moreover, it has a better price-to-performance ratio as it has a more modern semiconductor fabrication process.
Frequently Asked Questions
AMD has introduced a confusing naming scheme with its 7000 series of mobile processors. The first number in the model number represents the year, the second represents the model segment (Ryzen 3/5/7/9), and the third represents the architecture.
The U at the end of Ryzen 5 7530U and Core i5 1235U means that both these processors are Ultra-low powered.
Though the i5 has a higher number of cores in its architecture, most are weak efficiency cores instead of powerful performance cores.
More From Core i5 1235U:
More From Ryzen 5 7530U:
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Comparisons Expert]
Shehryar Khan, a seasoned PC hardware expert, brings over three years of extensive experience and a deep passion for the world of technology. With a love for building PCs and a genuine enthusiasm for exploring the latest advancements in components, his expertise shines through his work and dedication towards this field. Currently, Shehryar is rocking a custom loop setup for his built.
Get In Touch: shehryar@tech4gamers.com







