AMD Ryzen 5 7530U
Rated: 8.5/10
AMD Ryzen 5 7520U
Rated: 8/10
Pros And Cons
| CPU | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 5 7520 | ✅ Higher Gaming Visuals ✅ More CPU Threads | ❌ Lower Clock Multipliers ❌ Bigger Processing Node |
| Ryzen 5 7530U | ✅ Better Overall Performance ✅ Smaller Processing Node | ❌Low Energy Efficiency ❌Slower CPU Speeds |
- Firstly, the Ryzen 5 7530U surpasses the Ryzen 5 7520U in both our single-core and multi-core performance benchmarks by 28.3% and 60.1% on average, respectively, making it the preferred choice for demanding tasks and multitasking scenarios.
- We also see the Ryzen 5 7530U’s impressive memory support of up to 64GB DDR4-3200 and LPDDR4x-4267 outshines the Ryzen 5 7520U’s 16GB LPDDR5-5500, catering to memory-intensive tasks.
- The individual performance profiles of the Ryzen 5 7530U’s 2.0 GHz (boosting up to 4.5 GHz) Base Clock and the Ryzen 5 7520U’s 2.8 GHz (boosting up to 4.3 GHz) Base Clock allow users to choose based on specific computing needs.
- Finally, the Ryzen 5 7530U’s support for ECC Memory adds an edge for critical computing applications, making it a compelling option for users seeking enhanced error correction capabilities.
Comparison Table
| Key Specifications | Ryzen 5 7520U | Ryzen 5 7530U |
|---|---|---|
| Vendor | AMD | AMD |
| Release Date | September 22, 2022 | January 5, 2023 |
| Device Type | Laptop | Laptop |
| Instruction Set | x86-64 | x86-64 |
| Integrated GPU | Radeon 610M | Radeon Graphics (Ryzen 7000) |
| Total Cores | 4 | 6 |
| Total Threads | 8 | 12 |
| L1 Cache | 64K (per core) | 64K (per core) |
| L2 Cache | 512K (per core) | 512K (per core) |
| Transistors | - | 10.7 billion |
| Socket | FT6 | FP6 |
| GPU Base Clock | 1500 MHz | 1500 MHz |
| GPU Boost Clock | 1900 MHz | 2000 MHz |
| Cuda Cores | 128 | 128 |
| Execution Units | 2 | 2 |
Architectural Differences
We can gain valuable insights by exploring the architectural differences between the Ryzen 5 7530U and the Ryzen 5 7520U. These distinctions play a vital role in shaping their performances and capabilities so we can figure out which processor is better suited for specific computing tasks.
- Process Node: The Ryzen 5 7520U and the Ryzen 5 7530U are built on different fabrication processes, with the former utilizing a cutting-edge 6nm process node and the latter adopting a refined 7nm process node.
- Clock Speed: When it comes to speed, the Ryzen 5 7520U boasts a Base Clock of 2.8 GHz (boosting up to 4.3 GHz), while the Ryzen 5 7530U impresses with a Base Clock of 2.0 GHz (boosting up to 4.5 GHz), offering distinct performance profiles.
- Memory Support Variation: Both chips cater to memory-intensive tasks, but the Ryzen 5 7520U supports up to 16GB of LPDDR5-5500 memory, while the Ryzen 5 7530U expands with support for up to 64GB of DDR4-3200 and LPDDR4x-4267 memory.
- TDP: With a focus on power efficiency, both the Ryzen 5 7520U and the Ryzen 5 7530U operate with a 15W TDP, delivering energy-efficient performance for various computing needs.
- Supported Technologies: Finally, the Ryzen 5 7530U stands out with its support for ECC Memory, enabling enhanced error correction capabilities for critical computing tasks, a feature not available in the Ryzen 5 7520U.
In this article, we will be comparing two formidable contenders from AMD, the Ryzen 5 7530U vs Ryzen 5 7520U. As the article progresses, we will dive into their specifications and put them through a series of rigorous performance benchmarks, uncovering the subtle differences that set them apart so you can pick the best chip that serves all of your computing needs.
Ryzen 5 7530U Vs Ryzen 5 7520U – Performance Benchmarks
To test the true potential of the Ryzen 5 7520U and the Ryzen 5 7530U, we will now dive into rigorous performance benchmarks and stress testing to gauge how these processors handle tasks and applications. From single-core tasks to multi-core multitasking, we’ll explore their capabilities and check which chip excels in different benchmark software.
Cinebench R23 (Single-Core)
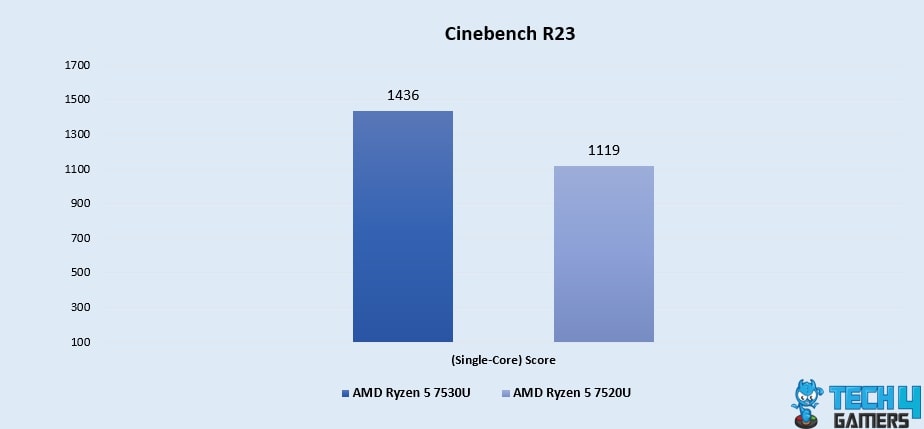
- In our Cinebench R23 Single-Core test, the Ryzen 5 7530U stands out with an impressive 28% performance boost, achieving a score of 1436, compared to the Ryzen 5 7520U’s score of 1119.
Cinebench R23 (Multi-Core)
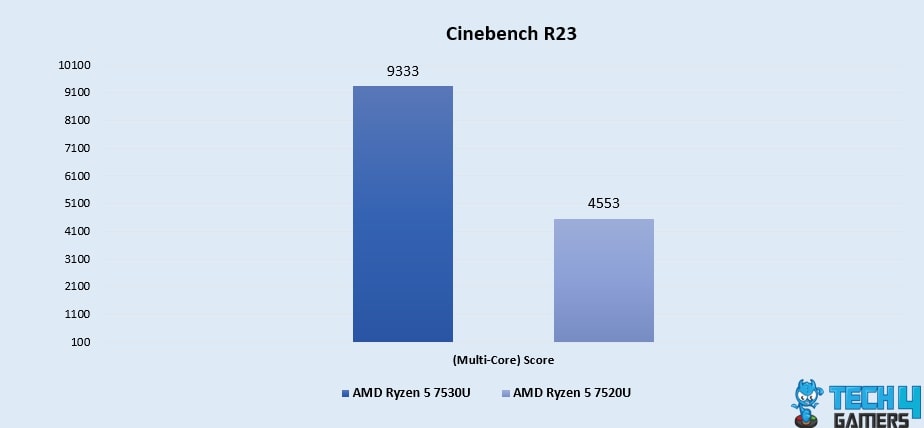
- When it comes to multi-core performance, we found the Ryzen 5 7530U shines with a remarkable 105% improvement, scoring 9333, leaving the Ryzen 5 7520U trailing behind at just the score of 4553.
Geekbench 5 (Single-Core)
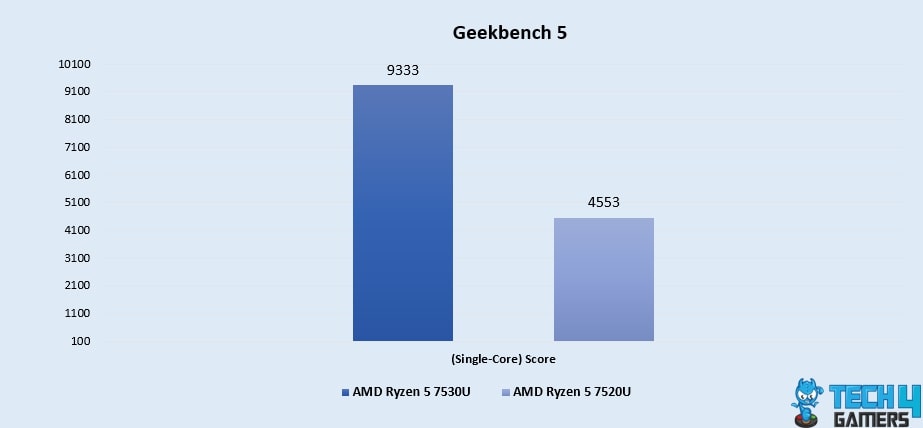
- The Geekbench 5 Single-Core test highlights the Ryzen 5 7530U’s strength in our results, with a notable 38% increase in performance, achieving a score of 1464, surpassing the Ryzen 5 7520U’s score of 1061.
Geekbench 5 (Multi-Core)
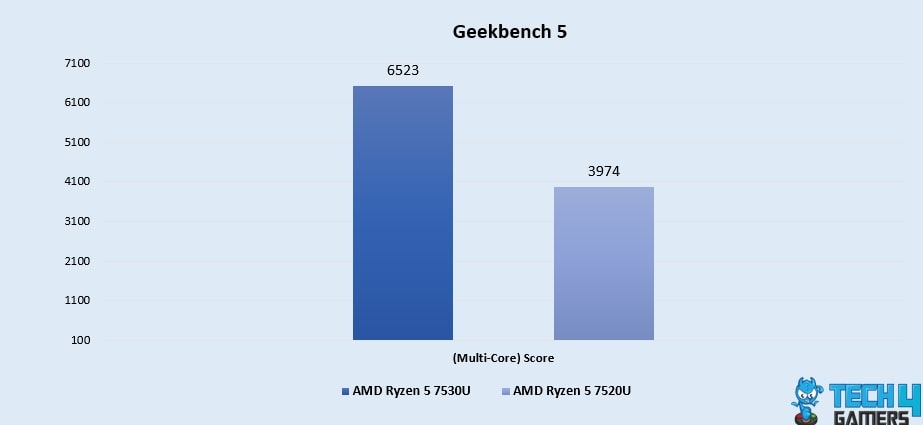
- Demonstrating its capabilities in multi-core tasks, the Ryzen 5 7530U boasts a significant 64% lead in our testing with a score of 6523 in the Geekbench 5 Multi-Core test, outperforming the Ryzen 5 7520U’s score of 3974 by a wide margin.
Ryzen 5 7520U Vs Ryzen 5 7530U – Which Chip Would We Recommend
AMD Ryzen 5 7520U: The Ryzen 5 7520U lags in memory support and performance results as well. It provides a lower result chart of single-core and multicore performances in our benchmarks. The advantage that makes it considerable is its power efficiency and lower price for budget users.
AMD Ryzen 5 7530U: The Ryzen 5 7530U easily gets in the good books with its higher memory support and better results showcased in the benchmarks. The processor also supports ECC memory format which can be a vital feature for consideration.
As we compile our results, we can easily recommend the Ryzen 5 7530U for its superior performance in both single-core and multi-core tasks. With greater memory support and the added advantage of ECC memory, it excels in demanding tasks and critical computing applications, making it our preferred choice.
More From Ryzen 5 7520U:
More From Ryzen 5 7530U:
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Comparisons Specialist]
I’m a passionate computer hardware expert specializing in CPUs and GPUs. With a lifelong curiosity for hardware and extensive hands-on experience, I provide valuable insights, practical advice, and in-depth analysis on these components. Engaging with the hardware community, I exchange knowledge and stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
Get In Touch: uzair@tech4gamers.com








