If you’re a gamer, you might have heard of VSync – a feature often mentioned in graphics settings. But what is VSync, and how does it affect your gaming experience?
Key-Takeaways
- VSync synchronizes the monitor’s refresh rate with the game’s frame rate.
- While VSync can reduce input lag and improve the visual experience for some gamers, it may also cause input delay, lower the frame rate, or cause stuttering, especially in fast-paced games.
- Different types of VSync have been developed to improve its performance, including Adaptive VSync, Triple Buffering, Enhanced Sync, G-sync, and FreeSynce, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
What Is VSync?
Have you ever played a game and noticed the graphics look choppy or split into parts? This is because of screen tearing. Screen tearing can occur when the monitor’s refresh rate does not match the game’s frame rate[1].
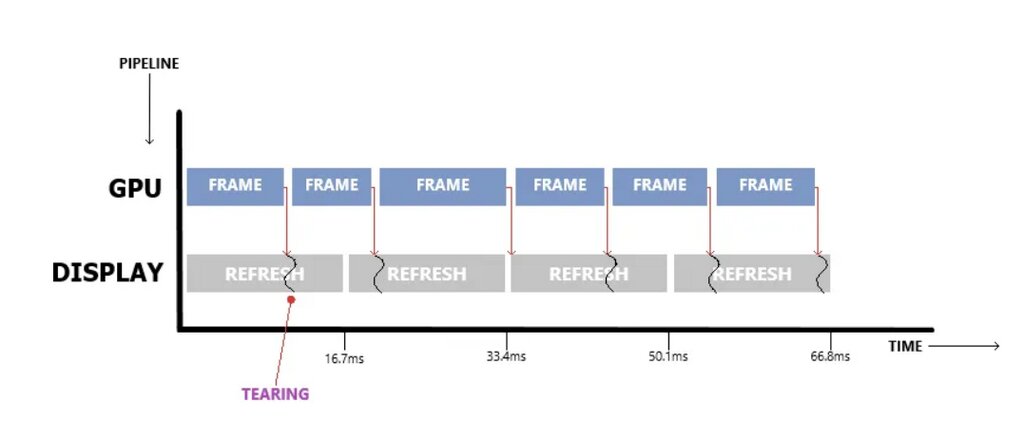
Video games use VSync, or vertical synchronization, to synchronize the game’s frame rate with the monitor’s refresh rate. This synchronization ensures that the images on the screen are smooth and consistent, providing an immersive gaming experience[2].
VSync makes the graphics card wait for the display to finish refreshing before sending a new frame[3]. This ensures that only one complete frame is displayed on the screen at a time, resulting in a smoother and more visually appealing experience for the viewer.
To achieve this, the graphics card will hold onto a newly rendered frame until the display updates the previous frame. Once the display is ready, the graphics card sends the completed frame to be displayed.
This process effectively synchronizes the display’s refresh rate with the graphics card’s output, preventing any inconsistencies that could lead to screen tearing.
Pros And Cons Of Using VSync
While it can improve the visual experience for some gamers, it also has its drawbacks. Let’s look at the pros and cons of using VSync.
Pros Of Using VSync
- Eliminates Screen Tearing: VSync synchronizes the graphics card and monitors, preventing this issue.
- Reduces Input Lag: When you hit a button on your keyboard or game controller, it takes some time for the corresponding response to appear on the screen, and that time interval is known as input lag. By making the graphics card wait until the previous frame has been fully displayed on the monitor before drawing the next one, VSync can shorten this delay.
- Improves Visual Consistency: VSync can help improve the visual consistency of a game. Without VSync, the frame rate can vary wildly from moment to moment, causing the game to feel choppy or uneven. By synchronizing the graphics card and monitor, VSync can help ensure a smooth and consistent frame rate.
Cons Of Using VSync
- May Cause Input Delay: While VSync can reduce input lag in some games, it can cause input delay in others. This is especially apparent in games that move quickly when even a slight delay can have a significant impact.
- Can Lower Frame Rate: Enabling VSync can sometimes lower a game’s frame rate. If the graphics card is not powerful enough to maintain a high frame rate, enabling VSync can cause the frame rate to drop even further.
- May Cause Stuttering: VSync can sometimes cause stuttering or micro-stuttering in a game. This happens when the graphics card is forced to hold off on drawing a frame until the monitor has finished showing it. If the frame rate fluctuates, the graphics card may need to wait longer for some frames than others, resulting in stuttering.
How To Enable Or Disable VSync
The steps to enable or disable VSync may vary depending on your graphics card or platform[4]. Here are some general steps to enable or disable VSync on Windows:
- To access your graphics card settings, right-click on your screen and choose ‘NVIDIA Control Panel‘ or ‘AMD Radeon Settings,’ depending on which graphics card you installed on your system.
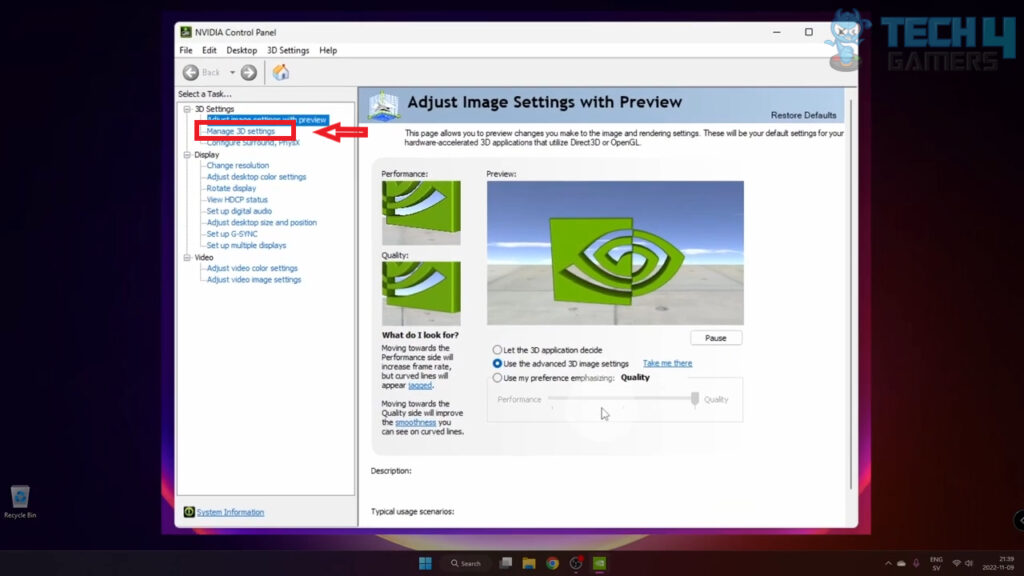
- Click on “Manage 3D Settings” or “Gaming.”
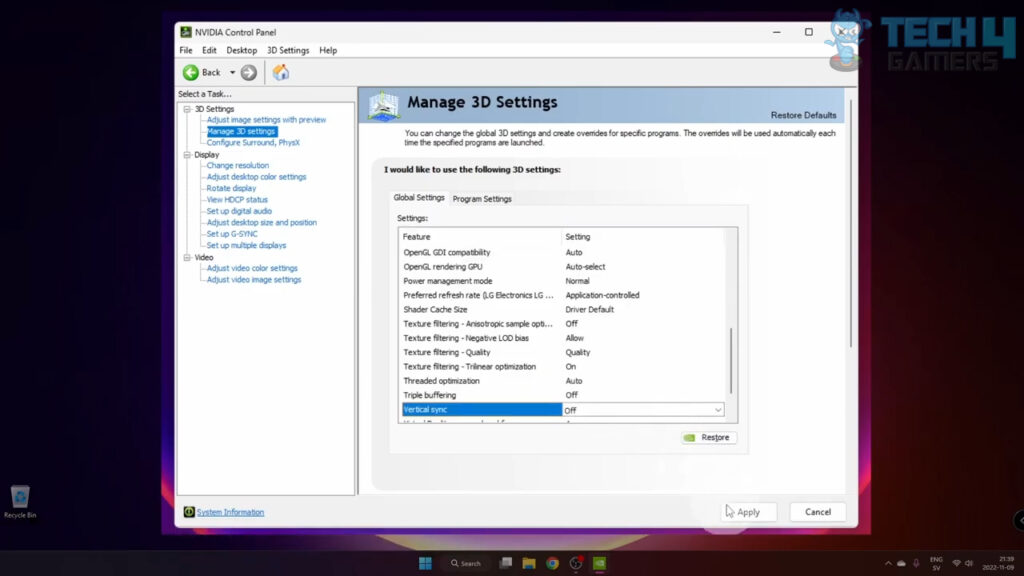
Manage 3D Settings. Image Credits (Tech4Gamers) - Find the “Vertical sync” option and select “On” to enable or “Off” to disable.
Vertical sync – Image Credits (Tech4Gamers)
Types Of VSync
Different types of VSync have been developed to improve its performance. Now, I will discuss the main types of VSync.
Adaptive VSync
Adaptive VSync is a technology used in modern graphics cards that significantly improves over traditional VSync. VSync compels the graphics card to render frames at a set rate, but Adaptive VSync is different as it can modify the frame rate in real time to align with the monitor’s refresh rate[5].
Also Check: Does Overclocking Reduce GPU’s Lifespan?
If the graphics card can render frames faster than the monitor’s refresh rate, Adaptive VSync will automatically disable itself, preventing the input lag and stuttering associated with traditional VSync. Despite its many benefits, Adaptive VSync does come with a few drawbacks. These are:
- Adaptive VSync may cause variable input lag.
- It can make it challenging to achieve consistent gameplay.
- It can only work within a specific range of frame rates.
Triple Buffering
Triple Buffering is a technique that uses three buffers instead of two to hold frames in memory before displaying them on the screen. With this technique, the third buffer is a backup buffer, holding an extra frame before displaying it on the screen[6].
By allowing the graphics card to work on the next frame while the previous one is displayed, Triple Buffering reduces input lag, ensuring that there is always a complete frame ready to be displayed, even if the graphics card is working on the next frame.
Most modern graphics cards have Triple Buffering available, and you can enable or disable it in the graphics card’s control panel. Despite its many benefits, Triple Buffering does come with a few drawbacks. These are:
- Triple Buffering can increase the memory requirements of a graphics card.
- More memory is needed to store and swap frames.
- It can introduce additional latency, a problem for fast-paced games.
Enhanced Sync
With Enhanced Sync, your graphics card’s frame rate synchronizes with the game’s frame rate rather than the monitor’s refresh rate[7]. As a result, you can enjoy a better and smoother gaming experience.
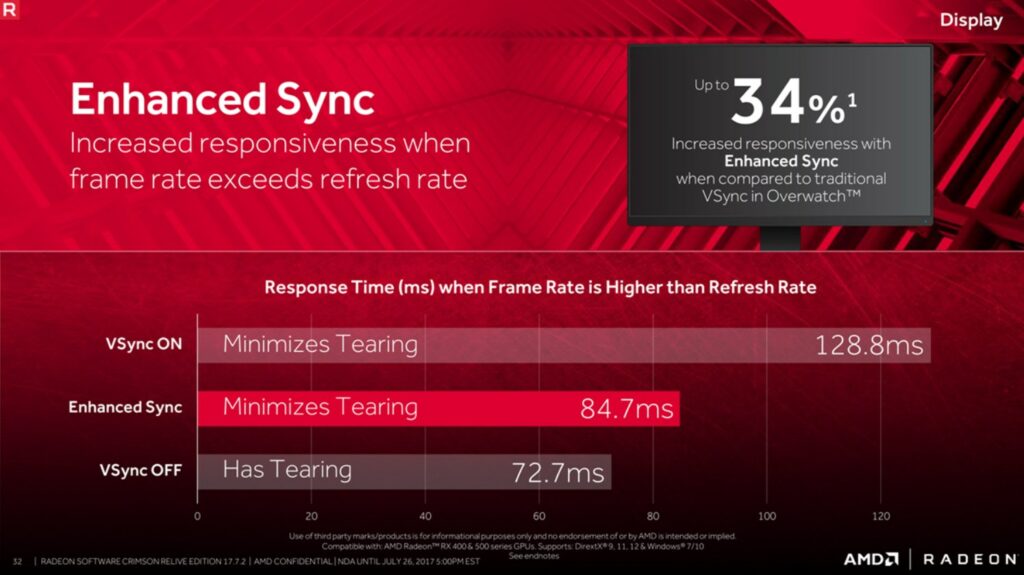
This allows the graphics card to render as many frames as possible and sends the latest frame to the monitor, providing a smooth and responsive gaming experience.
Enhanced Sync also provides a low-latency mode, which reduces input lag by minimizing the time it takes for the graphics card to process the input and display the output[7]. This makes it a fantastic option for intense action games or competitive gaming.
It also has some drawbacks, which are:
- Tearing can occur when the graphics card’s frame rate surpasses the monitor’s refresh rate.
- Only available on AMD graphics cards.
FreeSync
FreeSync is an adaptive sync technology created by AMD that aligns a monitor’s refresh rate with a graphics card’s frame rate[8]. Doing so effectively eliminates screen tearing and stuttering without the input lag penalty that traditional VSync incurs.
Also Read: Can Motherboard Bottleneck Your PC? [CPU & GPU]
FreeSync is also more flexible than VSync, as it can work with a wide range of frame rates, allowing for a smoother and more responsive gaming experience. FreeSync is an open standard, meaning it can be used with various monitors and graphics cards.
Some drawbacks of FreeSync include:
- Requires compatible monitor and graphics card.
- It may require a new hardware purchase.
- It may not correctly remove screen tearing and stuttering at high frame rates.
G-Sync
Nvidia created G-Sync, a technology that enables a monitor’s refresh rate to sync with the frame rate of a graphics card[9]. Unlike Vsync, which caps the frame rate at the monitor’s refresh rate.
This results in a better, more responsive gaming experience by minimizing issues like screen tearing, stuttering, and lag.
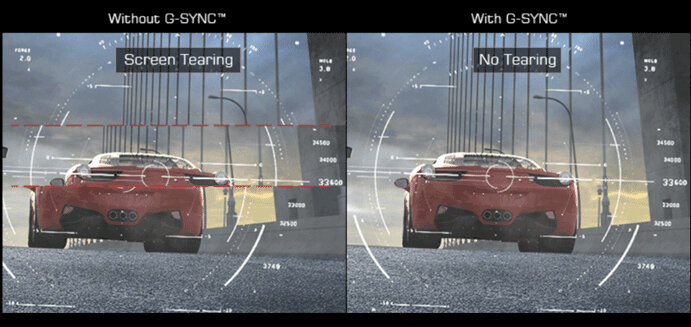
- It requires a specialized G-Sync module on the monitor, which can increase the cost of the display.
- Only works with Nvidia graphics cards, limiting its compatibility.
- G-Sync monitors may have a limited range of adaptive refresh rates, leading to potential issues at very low or high frame rates.
Reasons To Disable VSync
Here are some reasons why one might want to disable VSync:
- Input Lag: VSync can introduce input lag or delay in the game. Turning off VSync may be necessary to ensure proper game functionality and prevent issues like stuttering or input lag.
- Reduced Performance: If the graphics card cannot maintain a steady 60 frames per second, it will have to wait longer, leading to reduced performance.
- Compatibility Issues: Some older games or emulators may not be compatible with VSync, leading to graphical glitches, black screens, or crashes. Disabling VSync may be necessary to ensure a smooth gaming experience in certain circumstances.
- Competitive Gaming: In competitive gaming, every millisecond counts, and players often disable VSync to reduce input lag and increase responsiveness.
Final Words
To sum up, VSync can enhance or hinder your gaming experience, depending on your preferences and hardware. While it can remove screen tearing, it may cause input lag or degrade visual quality. Therefore, it’s essential to understand the pros and cons of VSync and adjust the setting accordingly.
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
References:
- Jerry3904 (February 5, 2019). MX Linux. Screen Tearing. Retrieved from https://mxlinux.org/wiki/hardware/screen-tearing/
- Jeremy Tang. A Measurement Study of Vertical Synchronization Configurations in PC Video Games. Retrieved from https://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse567-15/ftp/vsync/index.html
- Lenovo. What is VSYNC. Retrieved from https://www.lenovo.com/sg/en/glossary/vsync/orgRef=https%253A%252F%252Fwww.google.com%252F
- Intel. Enabling and Disabling Vertical Synchronization. Retrieved from https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/support/articles/000005552/graphics.html
- Nividia. Adaptive VSync. Retrieved from https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/geforce/technologies/adaptive-vsync/technology/
- Intel. Advantages of Using Triple Buffering in 3-D Games. Retrieved from https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/support/articles/000006930/graphics.html
- Hp. VSync – Should I turn it on or off. Retrieved from https://www.hp.com/in-en/shop/tech-takes/post/vsync-should-i-turn-it-on-or-off
- AMD. No Tearing. No Stuttering. Just Gaming. Retrieved from https://www.amd.com/en/products/graphics/technologies/freesync.html
- Nvidia Developer. G Sync. Retrieved from https://developer.nvidia.com/g-sync
Frequently Asked Questions
No, VSync is unnecessary for watching videos or streaming content. This technology is designed for gaming purposes to prevent screen tearing and enhance the overall visual quality of games.
Yes, VSync should work on most types of monitors, including CRT, LCD, and OLED displays. However, the effectiveness of VSync may vary depending on the monitor’s refresh rate, response time, and other factors.
Yes, enabling VSync on a laptop or mobile device can increase power consumption and reduce battery life. This is because VSync requires the graphics card to work harder to synchronize with the monitor’s refresh rate.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble. Currently speaking, Ali’s about to complete his Bachelor’s in Business Administration from Bahria University Karachi Campus.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads