In the world of PC hardware, people want faster, more dependable, and affordable storage. One big change in this area is TLC (Triple-Level Cell) NAND flash memory. It’s a technology that’s essential for the storage in most of our devices. This article will explain what TLC is, how it’s different from other types like SLC and MLC, and where you can see TLC in your PC setup.
Also Read: What Are DIMM Slots?
Key Takeaways
- TLC (Triple-Level Cell) is a type of NAND flash memory that stores up to three data bits per cell.
- Compared to SLC and MLC, it offers better affordability at the expense of speed and durability.
- TLC NAND flash memory is commonly present in consumer-grade SSDs and high-capacity USB drives.
What Is TLC?
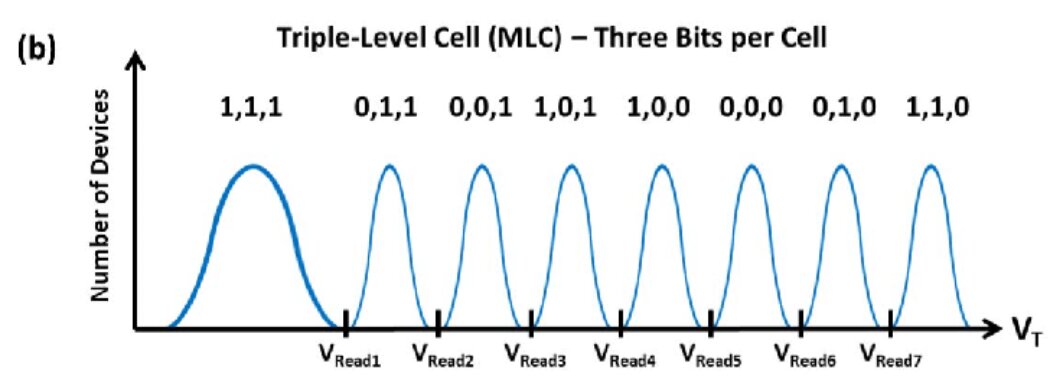
TLC or Triple-Level Cell is a type of NAND flash memory used in various storage devices like Solid-State Drives (SSDs). As apparent by name, it can store up to three data bits in one cell[1]. This, in turn, provides a higher storage capacity compared to SLC and MLC, which can only store one and two bits per cell, respectively. The unique feature of TLC lies in its better affordability while still giving good speed and reasonable durability[2].
SLC vs MLC vs TLC
SLC NAND flash memory is known for its speed and durability, making it ideal for high-performance applications where cost is not a primary concern[3]. MLC NAND offers a balance between performance and cost and is commonly available in consumer-grade SSDs and data centers. Finally, TLC NAND provides a higher storage capacity at a lower cost, making it a popular choice for consumer-grade SSDs and portable devices[4]. To better understand the differences between these three, I have created a comparative table:
| Attribute | SLC | MLC | TLC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bits per Cell | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Performance | Fast | Moderate | Moderate |
| Endurance | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Capacity | Low | Moderate | High |
| Cost per GB | High | Moderate | Low |
| Common Use Cases | Enterprise storage, high-performance computing | Consumer-grade SSDs, data centers | Consumer-grade SSDs, portable devices |
Where Is TLC Used?

You can find TLC NAND flash memory in various PC hardware components, mainly in consumer-grade SSDs. These drives are often the go-to choice for those looking to enhance their PC’s performance without breaking the bank. TLC-based SSDs offer a compelling mix of affordability and decent performance, making them suitable for various applications, from gaming to general productivity tasks[1].
Check Out: What Are SSD Read/Write Speeds?
Furthermore, high-capacity USB drives commonly use TLC NAND, offering users ample storage for their data, files, and multimedia content. This allows users to carry large amounts of data in a compact, durable, and affordable package.
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
References:
- What Is Triple-level Cell (TLC) Flash Memory and How Does It Work. Retrieved from https://www.purestorage.com/knowledge/what-is-tlc-flash-memory.html
- Pedro Hernandez (June 2018). SLC vs MLC vs TLC NAND Flash. Retrieved from https://www.enterprisestorageforum.com/hardware/slc-vs-mlc-vs-tlc-nand-flash/
- KIOXIA Singapore Pte. Ltd. SLC NAND Flash Memory. Retrieved from https://apac.kioxia.com/en-apac/business/memory/slc-nand.html
- Difference between SLC, MLC, TLC and 3D NAND in USB flash drives, SSDs and memory cards. Retrieved from https://www.kingston.com/en/blog/pc-performance/difference-between-slc-mlc-tlc-3d-nand
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble. Currently speaking, Ali’s about to complete his Bachelor’s in Business Administration from Bahria University Karachi Campus.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads
![Can You Use A Monitor Without PC? [SOLVED] Can You Use A Monitor Without PC?](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Can-You-Use-A-Monitor-Without-PC-218x150.jpg)
![What Is SSD Endurance? [Everything You Need To Know]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/SSD-Endurance-1-218x150.jpg)

![What Are Fan Bearings? [Sleeve, Ball & Fluid] Fan Bearings](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/HOW-TO-3-1-218x150.jpg)