In the modern world, where all the information is stored digitally in devices, it is very important to ensure the integrity of that stored data. In addition to fast speed and quick data retrieval, storage solution manufacturers also focus on enhancing the lifespan of their devices. One way to do it is by utilizing the wear-leveling technique. In this article, we will see what it is and why it is essential.
Key Takeaways
- The wear-levelling technique, as apparent by name, evenly distributes the data across all the memory cells of NAND flash memory so that no single cell wears out faster than others.
- There are two common types of wear-leveling techniques, i.e., dynamic and static.
What Is Wear Leveling?
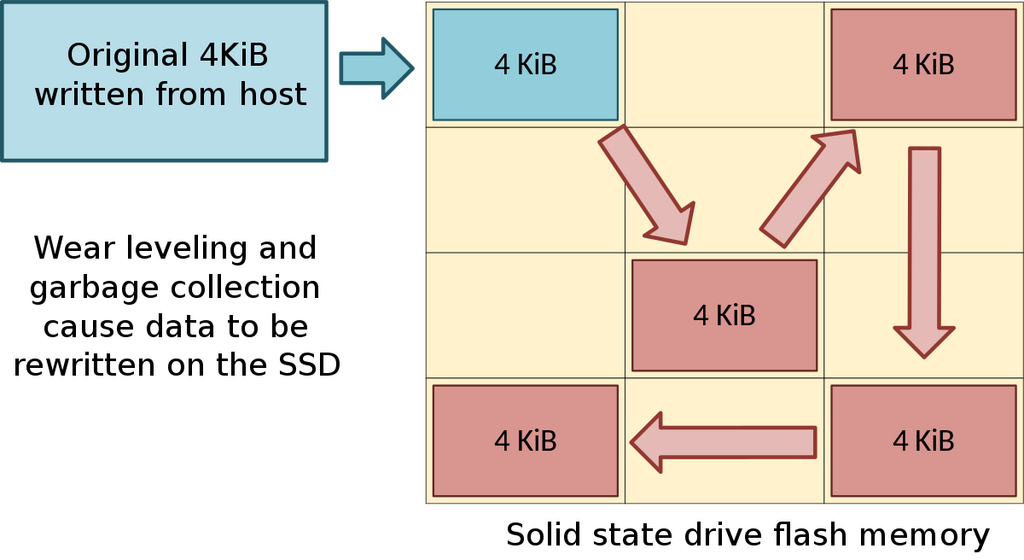
Wear-levelling is a process for preserving the life of flash-based storage devices. These storage devices rely on NAND flash memory, which has a limited number of write and erase cycles for each memory cell. Over time, if data is constantly written to the same memory cells, those cells wear out faster, leading to them wearing out[1].
The wear-levelling technique distributes the data evenly across the memory cells of a storage device. This process ensures that each cell is used in a balanced manner, preventing premature wear on any specific cells.[2]
Types Of Wear Leveling

There are usually two types of wear levelling techniques used in storage devices. Let’s look at both of them below:
Static Wear-Levelling
Static Wear Leveling uses its erase count calculations on an individual Flash chip unit, including both empty and previously written data blocks. Blocks with lower erase counts will have their data moved to other blocks. By doing this, the blocks with low erase counts may be freed up for additional usage[3].
Dynamic Wear-Levelling
Only available space is taken into account by Dynamic Wear Leveling. This technique continuously monitors the usage of memory cells and moves data around as needed to ensure that no cell is overused. It ensures that a write operation is performed on the blocks with lower erase counts within this space.[3].
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
References:
- Electronic Frontier Education. Wear Levelling. Retrieved from: https://ssd.eff.org/glossary/wear-leveling
- Williams College. SOLID STATE DRIVES. Retrieved from: http://cs.williams.edu/~jannen/teaching/s21/cs333/meetings/SSDs.html
- Transcend. Static Wear Levelling. Retrieved from: https://us.transcend-info.com/embedded/technology/wear-leveling
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads![How Long Do Laptops Last? [Answered] How Long Do Laptops Last?](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/How-Long-Do-Laptops-Last-218x150.jpg)

![What Are Semiconductor Process Nodes? [Definitive Guide]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/HOW-TO-218x150.jpg)