A storage drive is one of a computer’s key components; in the past few years, solid-state drives have been stamping their place as primary storage drives over hard disk drives. Now, if you’ve ever come across the specs sheet for an SSD, you must’ve come across its read/write speeds. It’s one of the key specifications to note when choosing an SSD.
Today, I’ll explain what these speeds mean and their importance in keeping your computer running speedily.
Key Takeaways
- Read/write speeds are the primary measure of an SSD’s performance.
- Read speed is how fast it takes to access data from a drive, while write speeds determine how fast data can be saved on a drive.
- For tasks like gaming or web browsing, read/write speeds of 500 MB/s are good enough. If you move large files around on a daily basis, consider an NVMe drive with speeds of at least 2500 MB/s.
What Are SSD Read/Write Speeds?
Read/write speeds are the most basic measure of an SSD’s[1] performance. Simply put, read speed refers to how long it takes to access (or read) data from a drive. Conversely, write speed measures how fast data can be saved (or written) onto a drive. Read/write speeds are divided into sequential and random speeds.

Sequential speeds measure the read/write times when the files being accessed are in a designated order. Meanwhile, random read/write speeds measure the time it takes to access files that are not in an orderly fashion. Sequential speeds are much faster than random speeds[2].
Read/write speeds are measured in MB/s and, often, in GB/s as well. SATA SSDs typically clock around 550 MB/s read and 500 MB/s write speeds[3]. PCIe NVMe SSDs are a whole different league, though. Samsung’s 990 PRO is the fastest PCIe Gen 4 SSD, clocking 7.45 GB/s read and 6.9 GB/s write speeds.[4]
What Is A Good Read/Write Speed?
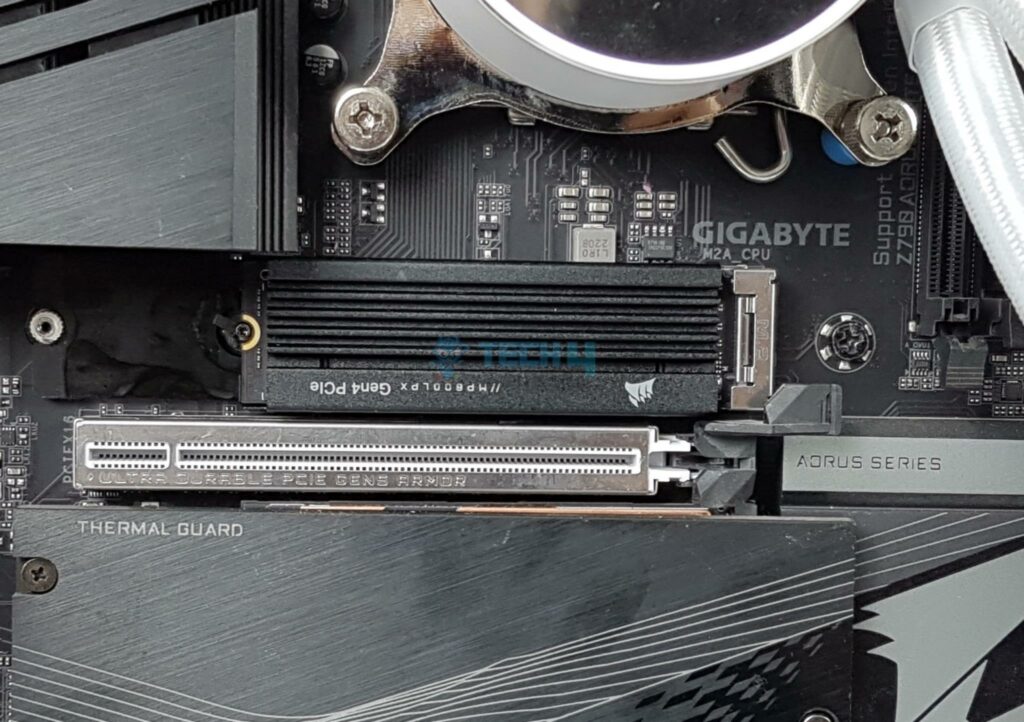
Generally, anything over 500 MB/s (about the average speed of a SATA SSD) is good. For large files, at least 2500 MB/s of throughput is a good landmark, which every NVMe SSD is capable of. For gaming and all other tasks that don’t involve large file transfers, a good SATA SSD, such as the Samsung 870 EVO[5], is plenty.
Again, though, I’ll reiterate that these speeds aren’t exactly the best measure of performance in most cases; more details below.
How Much Does Read/Write Speed Matter?
The difference in read/write speeds will cause a noticeable performance difference when moving from a mechanical hard drive (HDD) to an SSD. This includes everything from Windows boot times to copying files from one place to another. The same can’t be said for different SSDs (moving from a slower to a faster SSD) — at least in most tasks.
This is because mechanical hard drives have moving parts that limit how many reads/writes they can handle in a second. SSDs don’t have that problem, so moving from a hard drive to about any SSD is a massive upgrade — but moving from a slower to a faster SSD, not so much[6].
If you’re regularly dealing with large files (for example, saving and editing long 4K videos), the extra throughput will, in fact, be helpful. But other regular tasks, such as gaming, web-browsing, music, and video streaming, will display nothing more than a minor performance difference. So, instead, look for more capacity and get an SSD that can sustain its read/write speeds for long sessions.
In addition to the “normal” cells an SSD is made of, it contains a relatively smaller number of faster cells that are used as buffer[7]. It may fill up during a read/write operation (say, copying a large file), causing the speeds to drop immediately. However, a drive with good sustained performance can copy such files without dropping their speeds.
How To Check Read/Write Speed
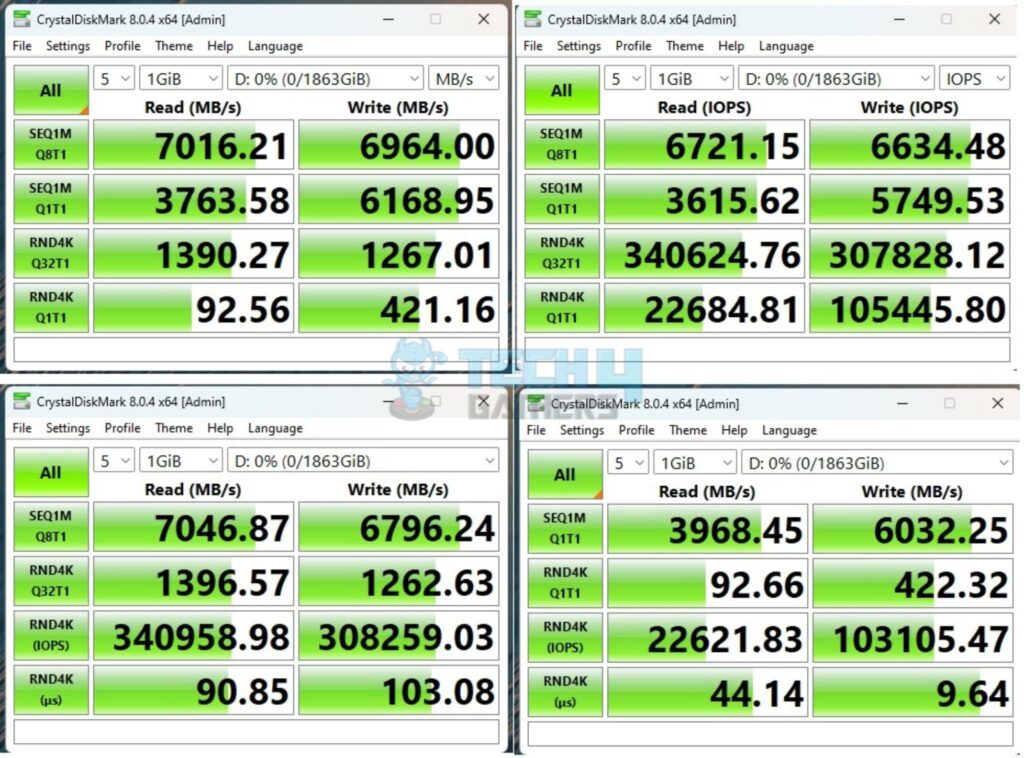
To check your read/write speeds, refer to the manufacturer’s website. Additionally, you can use CrystalDiskMark for Windows, Blackmagic Speed Test for Mac, or the dd utility on Linux. As mentioned before, the sequential read/write speeds shouldn’t be far off from the manufacturer-mentioned speeds. If they are, you may have stumbled upon a faulty drive.
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
- IOPS: Guide To SSD Performance
- What Is An SSD Controller & Is It Important?
- How To Buy the Right SSD For Your PC In 2024
References:
-
Ashwani K. (n.d). Computer Architecture and Engineering. Retrieved from: https://www.ddegjust.ac.in/2021/bca/Computer%20Architecture-243.pdf
- Arpaci-Dusseau, R. H. & Arpaci-Dusseau, A. C. (2018). Operating systems: Three easy pieces. Retrieved from: https://pages.cs.wisc.edu/~remzi/OSTEP/file-ssd.pdf
- Data retrieved from users on UserBenchmark: https://ssd.userbenchmark.com/
- Samsung Semiconductor. (2023). Samsung 990 Pro product specifications. Retrieved from: https://semiconductor.samsung.com/consumer-storage/internal-ssd/990-pro/
- Samsung Semiconductor. (2023). Samsung 87 QVO product specifications. Retrieved from: https://semiconductor.samsung.com/consumer-storage/internal-ssd/870qvo/
- Hugo R. & Shahid T. & Arif S. (2020). Survey of Solid State Drives, Characteristics, Technology, and Applications. Retrieved from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339884124_Survey_of_Solid_State_Drives_Characteristics_Technology_and_Applications
- Silberschatz, A., Galvin, P. B., & Gagne, G. (2012). Operating system concepts (9th ed.). John Wiley & Sons. Retrieved from: https://drive.uqu.edu.sa/_/mskhayat/files/MySubjects/2017SS%20Operating%20Systems/Abraham%20Silberschatz-Operating%20System%20Concepts%20(9th,2012_12).pdf
Frequently Asked Questions
Generally, you want to look for at least 500 MB/s of read and write speeds, which is more than double what a hard disk drive can manage. If you regularly edit and move around large files, consider an NVMe SSD with at least 2.5 GB/s of read/write speeds.
Like in HDDs, reading speed is faster than writing speed. This is caused by a few factors, including the NAND flash memory used by these SSDs. Reading data is straightforward for this memory. In the case of writing, however, it involves additional steps such as overwriting previous data.
The fastest write speed on an SSD is 11,800 MB/s, and this record is held by the Crucial T700 NVMe SSD, which runs on the PCIe Gen 5 interface.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble at an international level. Currently speaking, Ali has completed his A-Level GCEs with plans to go into either Allopathic Medicine or Business Studies, or who knows, perhaps a full-time dedicated technological journalist.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads
![How Often Should I Clean My PC? [Full Guide] HOW OFTEN SHOULD I CLEAN MY PC](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/HOW-OFTEN-SHOULD-I-CLEAM-MY-PC-218x150.jpg)

![PC Case Airflow [What, Why & How] PC Case Airflow Guide](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/HOW-TO-1-218x150.jpg)