In the ever-evolving landscape of PC hardware, one component that often gets overshadowed by processors, graphics cards, and storage devices is the memory type for data storage. To utilize the maximum potential of your PC setup, you should ensure every component can provide top-notch performance, including storage devices. Therefore, you need to understand various memory types to choose the best-performing storage solution. Multi-Level Cell (MLC) memory is one of those types that we will explore in this guide.
Also Read: What Are SSD Read/Write Speeds?
Key Takeaways
- MLC or Multi-Level Cell is a type of NAND flash memory that can store two bits of data per cell.
- The primary advantage of MLC over SLC is its decent enough performance and reliability at a comparatively low price.
- MLC NAND flash memory is commonly present in solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, and memory cards.
What Is MLC?
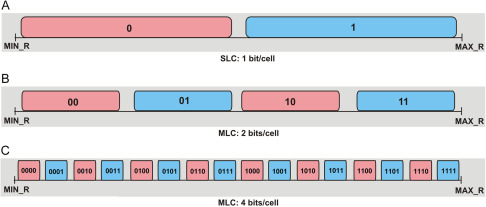
Multi-Level Cell (MLC) is a type of non-volatile storage medium (NAND flash memory) used in various electronic devices, including SSDs, USB drives, and memory cards. The key feature that sets MLC apart from other types is its ability to store multiple data bits in each memory cell[1]. Specifically, MLC can store two bits per cell, making it a more efficient and cost-effective solution than Single-Level Cell (SLC) memory, which only stores one bit per cell[2].
SLC Vs. MLC Vs. TLC
If you pay attention to the details of your storage solution, you will encounter various types of cell technology in use. Therefore, I have briefly compared the three common cell types used in modern storage solutions like SSDs.
| SLC | MLC | TLC |
|---|---|---|
| SLC (Single-Level Cell) stores only one piece or bit of data in one cell | MLC (Multi-Level Cell) stores two pieces or bits of data in one cell | TLC (Triple-Level Cell) stores three pieces or bits of data in one cell |
| Offers superior performance when compared with MLC and TLC | Offers good performance but not better than SLC | Offers reasonable performance for most applications |
| It is known for high reliability and endurance | It has moderate endurance | It has comparatively low endurance |
| Expensive | Moderate price | Economical |
Where Is MLC Used?

Read out: What Is An SSD Controller?
Multi-Level Cell (MLC) memory is present in various electronic devices where a balance between cost and performance is essential[3]. It is a popular choice in consumer-grade SSDs for laptops and desktop computers due to their price-to-performance ratio. MLC-based SSDs help these devices boot up quickly, load applications faster, and store data efficiently.
High-quality USB flash drives also contain MLC memory, providing faster data transfer speeds and a longer lifespan. Furthermore, digital cameras and smartphones use MLC memory in their memory cards.
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
References:
- Multi-level cell (dpedia). Retrieved from https://dbpedia.org/page/Multi-level_cell
- SLC vs. MLC: An Analysis of Flash Memory. Retrieved from http://www.supertalent.com/datasheets/SLC_vs_MLC%20whitepaper.pdf
- J.R. Jameson & M. Van Buskirk (2014). Minimum stored charge and MLC. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/multi-level-cell
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble. Currently speaking, Ali’s about to complete his Bachelor’s in Business Administration from Bahria University Karachi Campus.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads![What Are Fan Bearings? [Sleeve, Ball & Fluid] Fan Bearings](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/HOW-TO-3-1-218x150.jpg)
![When Xbox Is Off, Turn Off Storage [Feature Explained] When Xbox Is Off, Turn Off Storage](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/When-Xbox-Is-Off-Turn-Off-Storage-1.jpg)


![PSU Voltage Regulation [What, Why & How] Corsair SF1000L 12V Rail MOSFETs](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Corsair-SF100L-5-218x150.jpg)