GPU is a very crucial component of your PC build that contributes greatly to the overall performance bar. Many important parameters run a graphics card efficiently. Such an important factor is CUDA cores. Modern GPUs contribute to the processing along with the rendering through these CUDA cores. Therefore, you need a good understanding of these parallel processors to make an educated decision while buying a new GPU.
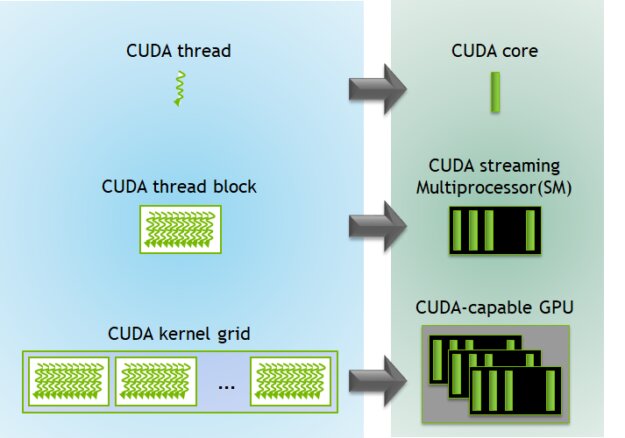
- Cuda cores are parallel processing units found specifically in NVIDIA GPUs.
- They have a significant impact on the performance of a GPU.
- The role of Cuda cores in modern Nvidia GPUs is vast. They ace in executing parallel computing along with facilitating various other tasks.
What Are CUDA Cores?
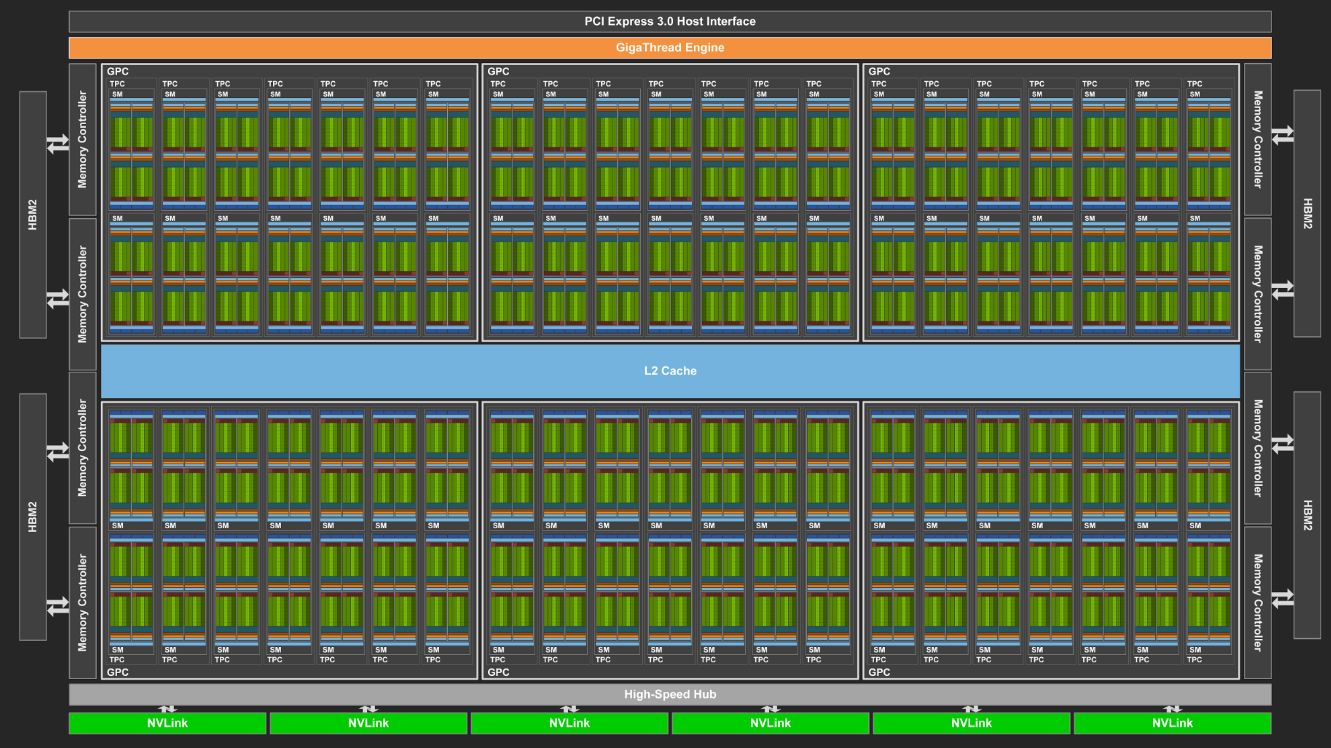
CUDA cores are parallel processing units found in NVIDIA GPUs. These cores enable GPUs to contribute to processing along with rendering applications by performing calculations and executing tasks in parallel with the CPU. Moreover, CUDA cores are specifically designed for CUDA programming, which allows developers to harness the power of GPUs for general-purpose computing tasks other than just rendering[1].
Furthermore, CUDA cores work together to process data simultaneously, which significantly speeds up computations compared to traditional CPU processing. Each CUDA core is capable of executing multiple instructions simultaneously which makes GPUs highly efficient for parallel workloads[2].
Tensor Cores Vs CUDA Cores
Tensor Cores and CUDA Cores are two different types of cores found in NVIDIA GPUs. Both of these cores serve distinct purposes in the field of parallel computing. Below is a table that compares these two:
| Tensor Cores | CUDA Cores |
|---|---|
| Available in NVIDIA Turing, Ampere, and Ada Lovelace architecture GPUs | Present in various NVIDIA GPU architectures, including Turing, Pascal, and Kepler |
| Accelerate matrix and tensor operations, widely used in AI and Deep Learning | Execute general-purpose CUDA kernels |
| Specialized hardware units with no contribution in general computing | Can contribute to general-purpose GPU computing and offer high parallelism |
What Do CUDA Cores Do?
The role of CUDA cores in modern NVIDIA GPUs is vast. They ace in executing parallel computing along with facilitating various other tasks. Some of the important roles of these cores are as follows:
- Parallel Processing: CUDA Cores are designed to handle parallel processing tasks efficiently. They offload the CPU workload and enable the GPU to perform multiple calculations simultaneously. Moreover, they make it possible to execute complex calculations in a fraction of the time that it would have taken by the CPU alone[3].
- Graphics Rendering: CUDA Cores were also initially developed for graphics processing. Other than parallel computing, they serve as the backbone of GPU-based rendering. They handle various graphics-related tasks, such as vertex processing, pixel shading, geometry processing, and texture mapping. Furthermore, CUDA Cores excel at rendering realistic 3D graphics, enabling smooth and immersive visual experiences in gaming, virtual reality, and computer-aided design (CAD)[4].
- General-Purpose GPU Computing (GPGPU): CUDA Cores can be utilized to accelerate a wide range of computational tasks beyond graphics which includes scientific simulations, machine learning, data analytics, and much more. By leveraging the parallel processing power of CUDA Cores, complex computations can be divided into smaller, parallel tasks that are executed simultaneously, resulting in marvellous performance gains[5].
- CUDA Toolkit and Programming: Additionally, if you are a developer then you can use the CUDA Toolkit which contains programming models and libraries for GPU programming. With the help of this toolkit, you can write code that exclusively runs on CUDA-enabled GPUs. In this way, you can harness the power of CUDA Cores and unlock the parallel processing capabilities of GPUs[6].
Stream Processors Vs CUDA Cores
Stream Processors and CUDA cores are almost the same things named differently by two leading GPU-producing giants i.e., AMD and NVIDIA, respectively. Let’s take a look at these two:
| Stream Processors | CUDA Cores |
|---|---|
| General-purpose parallel processing units within AMD GPUs | General-purpose parallel processing units within NVIDIA GPUs |
| Process data in SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) manners | Also operate in a SIMD manner |
RTX CUDA Cores Comparision

The below table enlists the number of CUDA cores contained in different RTX GPUs to provide you with a comparison of different latest RTX graphics cards based on CUDA cores:
| NVIDIA Graphics Cards | CUDA Cores |
|---|---|
| RTX 4090 | 16384 |
| RTX 4080 | 9728 |
| RTX 4070 Ti | 7680 |
| RTX 4070 | 5888 |
| RTX 4060 Ti | 4352 |
| RTX 4060 | 3072 |
| RTX 3090 Ti | 10752 |
| RTX 3090 | 10496 |
| RTX 3080 Ti | 10240 |
| RTX 3080 | 8960 |
| RTX 3070 Ti | 6144 |
| RTX 3070 | 5888 |
| RTX 3060 Ti | 4864 |
| RTX 3060 | 3584 |
Do CUDA Cores Matter?
CUDA cores are parallel computing workhorses of modern NVIDIA GPUs. So, they have a significant impact on the performance of a GPU. These cores enable the GPU to offload computation-intensive tasks from the CPU and process them on its CUDA cores[7]. Therefore, in this way, highly intensive computation tasks can be completed within a fraction of the time that would have been taken by the CPU if CUDA cores were not there.
Additionally, CUDA cores also contribute to general-purpose GPU computing (GPGPU) and graphics rendering[8]. Therefore, CUDA cores are very important performance parameters that greatly influence the performance of a graphics card.
How To Enable CUDA Cores?
CUDA cores are intrinsic and built-in in the NVIDIA GPUs. Every time you run a CUDA-enabled application, your CUDA cores automatically come into action. However, you can ensure that CUDA cores are running properly on your NVIDIA GPU by checking for and installing the latest GPU drivers and CUDA toolkit.
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
References:
- Jacob Knoles (California State University Chico). NVIDIA CUDA Parallel Programming and Computing Platform. Retrieved from: https://physics.csuchico.edu/~eayars/code/CUDA_presentation.pdf
- Kayvon Fatahalian. (CMU School of Computer Science). HOW A GPU WORKS? Retrieved from: https://web.engr.oregonstate.edu/~mjb/cs575/Handouts/gpu101.2pp.pdf
- Princeton Research Computing. GPU COMPUTING. Retrieved from: https://researchcomputing.princeton.edu/support/knowledge-base/gpu-computing#mps
- Shaohao Chen (Boston University). Introduction to High-Performance Computing. Retrieved from: https://www.bu.edu/tech/files/2017/09/Intro_to_HPC.pdf
- North Dakota State University. Introduction to Neural Networks. Retrieved from: https://kb.ndsu.edu/page.php?id=133762
- Justin Hensley (MIT). Hardware and Compute Abstraction Layers For Accelerated Computing
Using Graphics Hardware and Conventional CPUs. Retrieved from: https://archive.ll.mit.edu/HPEC/agendas/proc07/Day3/10_Hensley_Abstract.pdf - Oregon State University. GPU 101. Retrieved from: https://web.engr.oregonstate.edu/~mjb/cs575/Handouts/gpu101.2pp.pdf
- Mike Houston (Stanford University). A CLOSER LOOK AT GPUS. Retrieved from: https://graphics.stanford.edu/~kayvonf/papers/fatahalianCACM.pdf
FAQs
CUDA cores are parallel computing elements in NVIDIA GPUs. Along with graphics rendering, these cores offer high parallelism and process computation-intensive tasks.
CUDA cores are used in computation-intensive applications and can benefit from parallelism. These applications include scientific simulations, machine learning, data analytics, and image and video processing.
Yes, generally speaking, having more CUDA cores in a GPU can lead to better performance, especially in applications that can effectively utilize parallel processing.
While there is no distinct number of CUDA cores that are required for video editing but having more will enable faster video processing and rendering. So, the more, the better.
AMD also has parallel computing elements similar to ones in NVIDIA GPUs. But those parallel processing elements are known by the name of “Stream Processors” not CUDA cores.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble. Currently speaking, Ali’s about to complete his Bachelor’s in Business Administration from Bahria University Karachi Campus.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads
![PSU Voltage Regulation [What, Why & How] Corsair SF1000L 12V Rail MOSFETs](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Corsair-SF100L-5-218x150.jpg)
![How Long Do Power Supplies Last? [Explained] HOW LONG DO POWER SUPPLIES LAST?](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/HOW-LONG-DO-POWER-SUPPLIES-LAST-1-218x150.jpg)