- TDP is a representation of thermal output rather than power draw.
- Intel and AMD designate their TDP numbers very differently.
- The TDP rating has very limited advantages to the end user.
So you must have come across those TDP ratings that are mentioned on the product pages of everything from CPUs to coolers nowadays. Ever wondered what that number actually means and how it is calculated?
Without going too deep into the details, I’m here to tell you that the TDP ratings are quite misleading. In fact, you shouldn’t put much stock into that number at all, and here’s why.
What Exactly Is TDP?
The TDP (Thermal Design Power) is a rating you may have seen when shopping for a CPU. It measures the maximum heat output in watts, indicating how much heat the processor will produce under heavy load. This helps users understand the processor’s power requirements and cooling needs.

Since it is measured in watts, it can be confusing to differentiate between electrical power draw and thermal power output. The TDP is the latter and is usually the heat energy output of the processor after it consumes a portion of the incoming electrical energy to perform its task.
Pretty simple so far, right? Well…
Intel and AMD – Not On The Same Page
The TDP ratings’ misconceptions are fueled by differences in how major CPU manufacturers Intel and AMD select their TDP values, making direct comparisons difficult.
Intel’s method: Intel bases its TDP on the processor’s base clock, meaning its stated heat output is accurate only when the CPU operates at this speed, which is extremely rare in modern usage scenarios due to complex boosting mechanisms and auto-overclocking. This can mislead buyers into choosing inadequate power supplies or weaker coolers based solely on TDP, leading to potential cooling issues.
Intel also advertises other power limits called “power levels (PL)” which are a somewhat more accurate representation of power draw under normal boosting conditions.
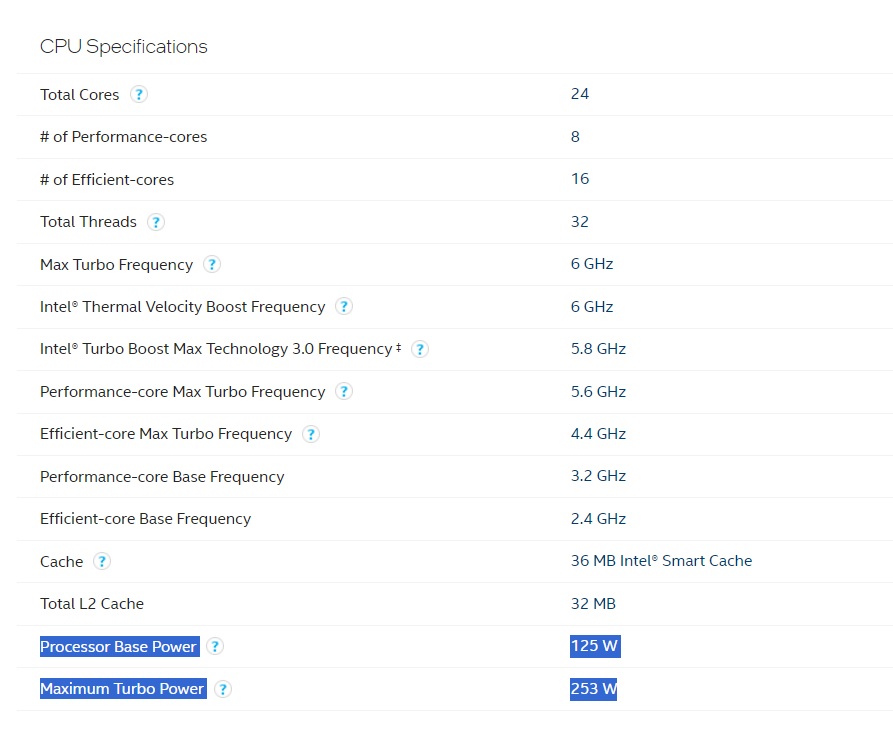
AMD’s way: AMD calculates TDP differently from Intel, measuring it at the CPU’s maximum boost clock rather than the base clock, which can offer a more accurate representation of real-world heat output. AMD’s definition only holds true when the processor is operating within its base and boost frequencies, excluding auto-overclocking features like Precision Boost, which adjusts performance based on available thermal and power limits.
During our Ryzen 7 7700X review, we measured the maximum all-core power consumption to be 136.869W while the average consumption was 90.932W. The TDP for this CPU is 105W.
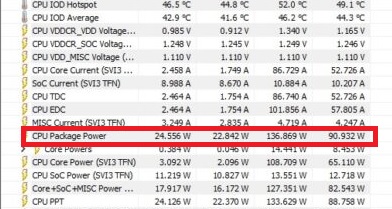
Despite this, AMD’s approach offers clearer guidelines for cooler manufacturers, aiding in the design of more suitable cooling solutions for their CPUs.
TDP – A Marketing Exercise
We have established that “TDP” can be tricky due to its loose regulation and varying interpretations by CPU manufacturers like Intel and AMD.
It is also important to understand that TDP is a number chosen by AMD and Intel, and not necessarily calculated. While there exists a formula that AMD uses to calculate the TDP in order to give a guideline to cooler manufacturers, the formula uses a lot of variables and can be manipulated to get a somewhat arbitrary “TDP” figure. This whole practice can be used as a marketing exercise should the manufacturers want it.
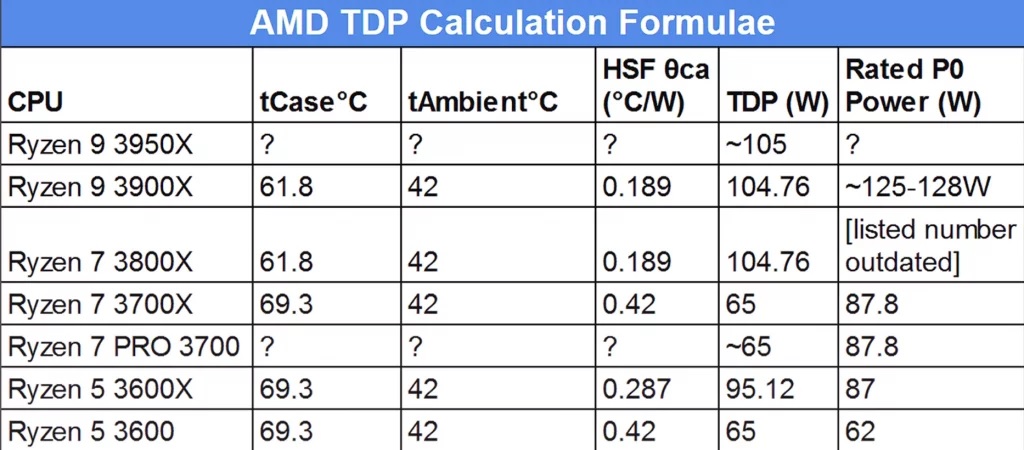
Although TDP can indirectly hint at power consumption, it’s not a precise indicator. While processors with higher TDP ratings may produce more heat and potentially draw more power, assuming a direct correlation between TDP and power draw is inaccurate, and we can see this in all modern CPUs from both Intel and AMD.
Cooler manufacturers, unsurprisingly, also take the provided TDP with a huge grain of salt. World-renowned CPU cooler manufacturer Noctua introduced its own Noctua Standardised Performance Rating (NSPR) system, which ranks the thermal capability of Noctua coolers against each other, just to avoid confusion due to TDP.
Can TDP Be Useful?
TDP is not, in fact, entirely useless. Under the right situations, and with the right context, it can still be useful.

- Comparisons: While not directly indicative of power consumption, TDP can help users roughly compare the heat output of different processors, especially those within the same product line or architecture.
- System Design: TDP ratings aid system builders in selecting compatible components like power supplies and cases, ensuring they can handle the thermal load generated by the CPU and avoid thermal throttling.
- Efficiency Improvements: From the perspective of the CPU manufacturer, the TDP number is vital in order to fine-tune the efficiency gains of a particular CPU in the succeeding generation, which has the same TDP as its predecessor.
Bottom Line
TDP is certainly an arbitrary and confusing number since it is not as simple and definitive as it seems to be. In most cases, the manufacturers select a desired number rather than calculating it.
If you want to know how much power a CPU really uses, don’t rely solely on the TDP number, which can be confusing at best and misleading at worst. Instead, check detailed reviews that measure power draw in different situations.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Reviews Specialist]
Usman Saleem brings 8+ years of comprehensive PC hardware expertise to the table. His journey in the tech world has involved in-depth tech analysis and insightful PC hardware reviews, perfecting over 6+ years of dedicated work. Usman’s commitment to staying authentic and relevant in the field is underscored by many professional certifications, including a recent one in Google IT Support Specialization.
8+ years of specialized PC hardware coverage
6+ years of in-depth PC hardware analysis and reviews
Lead PC hardware expert across multiple tech journalism platforms
Certified in Google IT Support Specialization
Get In Touch: usman@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads

