- Two CPUs can share the same model but still have performance differences.
- These differences arise from manufacturing processes, binning, and yield variability.
- The silicon lottery can impact a CPU’s clock speeds, overclocking behavior, and power consumption.
Have you ever wondered why your friend’s computer, equipped with the same CPU model as yours, seems to perform better or worse than your system? The answer lies in a phenomenon known as the “silicon lottery.”
What Is The Silicon Lottery?
Despite being marketed as identical products, individual CPUs can exhibit varying levels of performance due to inherent variations in the manufacturing process. The silicon lottery refers to these subtle differences that lead to performance discrepancies among supposedly identical CPUs.
At the core of every CPU lies a silicon wafer, which undergoes a complex manufacturing process to create the intricate circuitry and transistors that power these processors. However, even with the most advanced manufacturing techniques, slight variations in the quality of the silicon wafer, the presence of impurities, and the specific conditions during the fabrication process can lead to performance differences among individual CPUs.
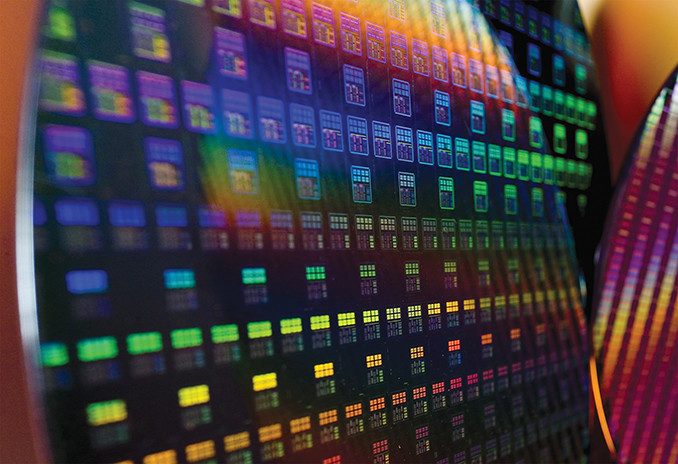

These variations are often imperceptible to the naked eye, but they can have a significant impact on the final product’s performance. As a result, even CPUs from the same batch and model can exhibit varying degrees of performance, with some units outperforming others in terms of clock speeds, power efficiency, and overclocking potential.
Factors Influencing The Silicon Lottery
Manufacturing Variability
CPU manufacturing involves a complex process of layering materials, etching transistors, and connecting billions of components. During this process, tiny imperfections can occur, such as impurities in the silicon or slight variations in the manufacturing equipment. These imperfections can impact how well a CPU performs, leading to variations in speed, power consumption, and overall performance.
Binning
To manage these variations, CPU manufacturers use a process called binning. Binning involves sorting CPUs into different categories based on their performance characteristics, such as frequency, voltage, and power consumption. CPUs that meet the highest specifications are typically reserved for high-end models or sold at a premium price. Those that don’t meet the desired specs may be sold as lower-end models or used in other applications.

Yield
Another factor that contributes to the silicon lottery is yield. Yield refers to the percentage of CPUs that meet the desired specifications during manufacturing. Not all CPUs produced will meet the desired standards, and those that don’t are often sold as lower-end models or repurposed. The yield rate can vary depending on the manufacturing process, with higher yields resulting in more consistent performance.
Wafer Variations
Wafer-level variations also play a role in the silicon lottery. Wafers are the circular slices of silicon used to create CPUs. Each wafer can have variations in impurities, crystal structure, and other factors that affect CPU performance. These variations can result in differences in performance between CPUs, even if they’re from the same wafer.
Process Node Variations
Finally, differences in process nodes can also impact CPU performance. Process nodes refer to the size and density of transistors on a CPU. Newer process nodes, such as 7nm or 5nm, offer improved performance and power efficiency compared to older nodes like 10nm or 14nm. However, even within the same process node, variations can occur that affect performance.
Effects Of Silicon Lottery
The silicon lottery has significant implications for consumers and enthusiasts alike. For general users, it means that even when purchasing identical CPU models, there is a possibility of performance variations between systems. This can be particularly noticeable in tasks that heavily rely on CPU performance, such as video rendering, 3D modeling, or gaming.
For overclockers and enthusiasts, the silicon lottery can be both a blessing and a curse. While some individuals may get lucky and receive a “golden sample” CPU that can achieve impressive overclocking results, others may end up with a less capable unit that limits their overclocking potential. Some units may be able to achieve higher stable clock speeds than others, even when using the same cooling solution and voltage settings.
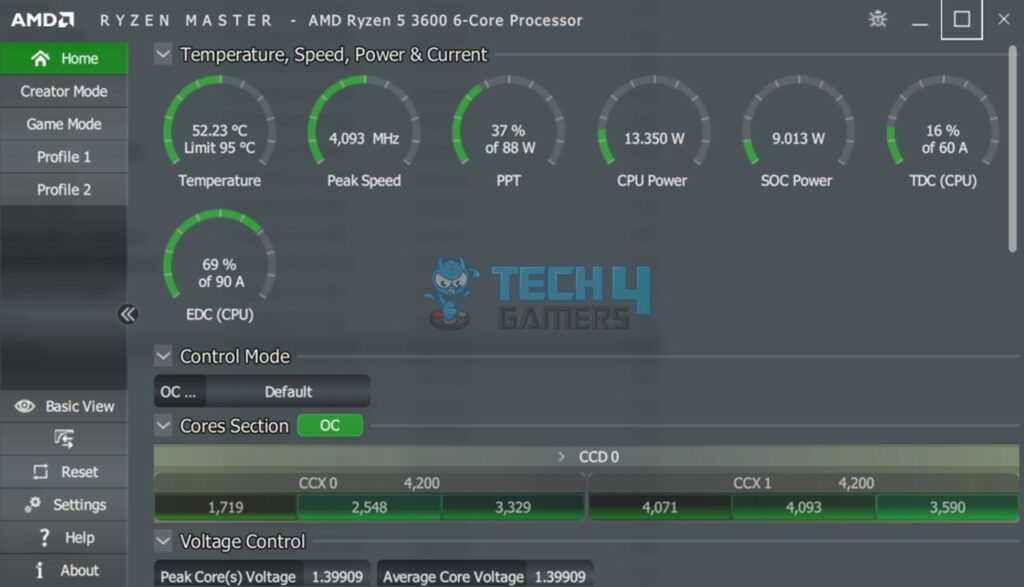
Manufacturers are aware of the silicon lottery and often bin CPUs based on their performance characteristics. This process results in different product tiers and pricing, with higher-performing units often commanding a premium price.
It’s All Just Luck
Variations in manufacturing, binning, yield, wafer-level variations, and process nodes all contribute to differences in CPU performance. While these differences may seem small, they can have a significant impact on real-world performance. While these differences may be subtle for everyday tasks, they can become more pronounced in demanding applications or when attempting to overclock the processor.
Manufacturers continue to refine their manufacturing processes to minimize the impact of the silicon lottery, but it remains an unavoidable aspect of CPU production.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Reviews Specialist]
Usman Saleem brings 8+ years of comprehensive PC hardware expertise to the table. His journey in the tech world has involved in-depth tech analysis and insightful PC hardware reviews, perfecting over 6+ years of dedicated work. Usman’s commitment to staying authentic and relevant in the field is underscored by many professional certifications, including a recent one in Google IT Support Specialization.
8+ years of specialized PC hardware coverage
6+ years of in-depth PC hardware analysis and reviews
Lead PC hardware expert across multiple tech journalism platforms
Certified in Google IT Support Specialization
Get In Touch: usman@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads