The Intel Core i7 1355U and Ryzen 5 7530U are both amazing processors, and today we’ll be comparing them in detail. Our main goal is to highlight the major differences between the two processors so you can choose the right one for your rig.
Key Takeaways
- The Core i7 1355U holds a remarkable 16.5% lead in single-core benchmarks, making it an appealing choice for tasks demanding quick and responsive execution on an individual level.
- Although a minor 13.3% deficit in multi-core benchmarks, the Ryzen 5 7530U proves its mettle in handling demanding workloads and multitasking scenarios effectively.
- While both chips offer customizable TDPs, the Core i7 1355U operates between 12-15W, while the Ryzen 5 7530U maintains a consistent 15W TDP, catering to users seeking power efficiency to suit their preferences.
- The Ryzen 5 7530U’s support for ECC memory sets it apart for tasks that require heightened reliability and precision, providing an edge over the Core i7 1355U.
Core i7 1355U Vs Ryzen 5 7530U: Comparison Table
| Key Specifications | Core i7 1355U | Ryzen 5 7530U |
|---|---|---|
| Vendor | Intel | AMD |
| Release Date | January 3, 2023 | January 5, 2023 |
| Device Type | Laptop | Laptop |
| Instruction Set | x86-64 | x86-64 |
| Integrated GPU | Iris Xe Graphics (96EU) | Radeon Graphics (Ryzen 7000) |
| Performance Cores | 2 | 6 |
| Performance Threads | 4 | 12 |
| Base Clock | 1.7 GHz | 2.0 GHz |
| Boost Clock | 5 GHz | 4.5 GHz |
| Total Cores | 10 | 6 |
| Total Threads | 12 | 12 |
| L1 Cache | 80K (per core) | 64K (per core) |
| L2 Cache | 1280K (per core) | 512K (per core) |
| L3 Cache | 12MB (shared) | 16MB (shared) |
| Fabrication Process | 10nm | 7nm |
| TDP (PL1) | 12-15 W (configurable) | 15W |
| Socket | BGA-1744 | FP6 |
| GPU Base Clock | 300 MHz | 1500 MHz |
| GPU Boost Clock | 1300 MHz | 2000 MHz |
| Cuda Cores | 768 | 128 |
| Execution Units | 96 | 2 |
| Memory Support | 64GB | 64GB |
| ECC Support | 2 | 2 |
| Max. Memory Channels | 256GB | 64GB |
Architectural Differences
Amidst their architectural disparities lie the foundations that set the Core i7 1355U and Ryzen 5 7530U apart. These differences will become more pronounced as we delve into their real-world performance benchmarks, shedding light on how their unique design choices translate into tangible computing experiences.
- Process Node: Harnessing the advantages of a 10nm process node, the Core i7 1355U brings its computational prowess to life, while the Ryzen 5 7530U utilizes a 7nm process node, showcasing its efficiency-driven design.
- Clock Speed: Moreover, the Core i7 1355U sets its foundation with a Base Clock of 1.7 GHz, ready to surge to a Boost Clock of 5 GHz, while the Ryzen 5 7530U starts at a Base Clock of 2.0 GHz, with its Boost Clock reaching up to 4.5 GHz, offering a unique balance of power and efficiency.
- Memory Support Variation: Embracing memory-intensive tasks, the Core i7 1355U’s support for up to 64GB provides ample room for multitasking, mirroring the capabilities of the Ryzen 5 7530U, which also accommodates up to 64GB, catering to diverse memory demands.
- TDP: With configurable TDPs in the range of 12-15W, the Core i7 1355U provides adaptability to balance performance and energy efficiency, while the Ryzen 5 7530U maintains a steady 15W TDP.
- Supported Technologies: While the Ryzen 5 7530U embraces ECC memory for heightened reliability, the Core i7 1355U lacks this technology, a factor to consider for those requiring enhanced data accuracy and integrity in their computing tasks.
Performance Benchmarks
As we move to performance benchmarks, we can witness how these architectural distinctions manifest in actual usage scenarios. By subjecting the Core i7 1355U and Ryzen 5 7530U to a battery of benchmark tests, we gain insight into their capabilities across various computational tasks, offering a comprehensive view of their prowess and potential.
Cinebench R23 (Single-Core)
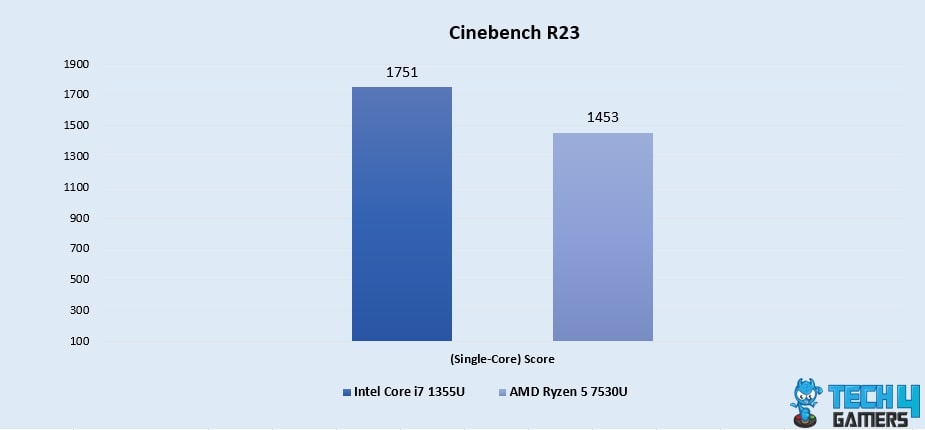
- Unveiling its processing prowess, the Core i7 1355U boasts a remarkable 18.6% lead over the Ryzen 5 7530U at 1751 vs 1453, reflecting its aptitude for swiftly handling individual tasks and applications.
Cinebench R23 (Multi-Core)
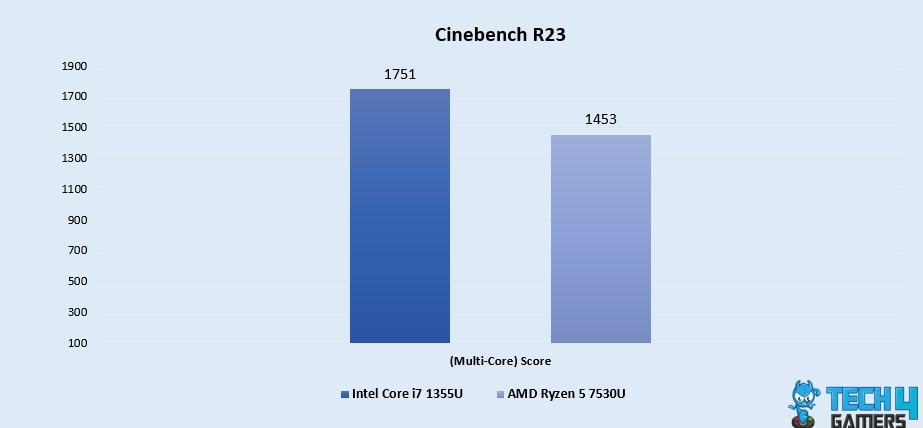
- In the realm of multi-core performance, the Core i7 1355U achieves a score of 8989, while the Ryzen 5 7530U holds its ground with a commendable 4.3% advantage at 9385, highlighting its capacity for managing resource-intensive workloads.
Geekbench 5 (Single-Core)
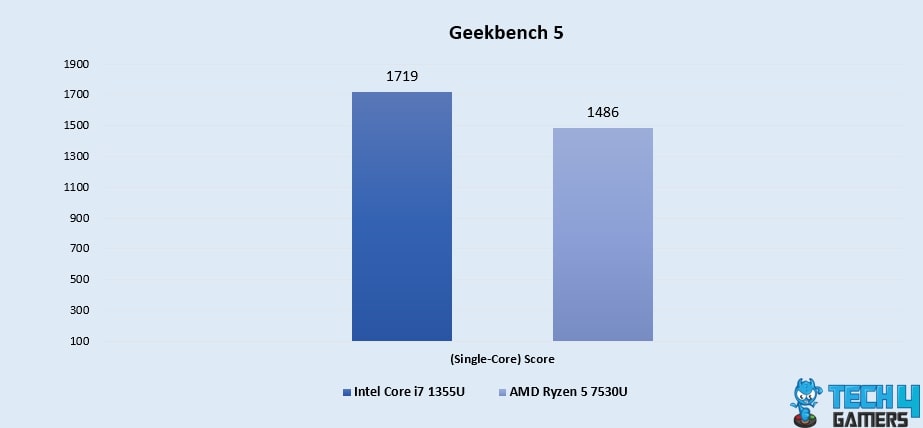
- A single-core powerhouse, the Core i7 1355U secures a 14.5% advantage with a score of 1719, outshining the Ryzen 5 7530U’s score of 1486, underlining its aptness for responsive and efficient individual operations.
Geekbench 5 (Multi-Core)
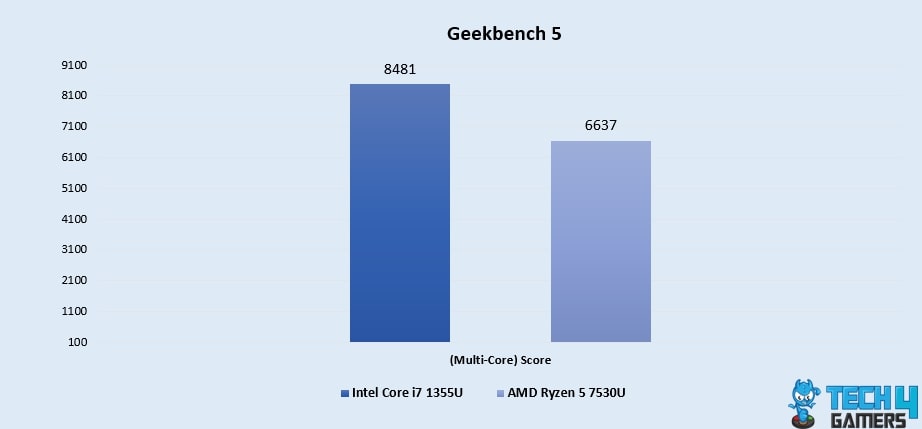
- In the multi-core arena, the Core i7 1355U demonstrates its prowess once again, boasting a notable 24.3% lead with a score of 8481, while the Ryzen 5 7530U’s score of 6637 showcases its competency in juggling multiple tasks.
Ryzen 5 7530U Vs Core i7 1355U: Which Chip Should You Be Picking?
- With a substantial 16.5% advantage in single-core benchmarks, the Core i7 1355U establishes itself as an excellent choice for users who prioritize quick and responsive execution of individual tasks and applications.
- Despite a slight 13.3% lag in multi-core benchmarks, the Ryzen 5 7530U remains a strong contender, showcasing its ability to handle resource-intensive workloads and multitasking scenarios effectively.
- While both chips offer configurable TDPs, the Core i7 1355U operates within a range of 12-15W, while the Ryzen 5 7530U maintains a steady 15W TDP, providing options for users seeking power efficiency tailored to their needs.
- Moreover, for users who prioritize enhanced reliability and accuracy in their computing tasks, the Ryzen 5 7530U’s support for ECC memory provides an advantage over the Core i7 1355U, making it suitable for critical applications that demand error correction.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Comparisons Expert]
Shehryar Khan, a seasoned PC hardware expert, brings over three years of extensive experience and a deep passion for the world of technology. With a love for building PCs and a genuine enthusiasm for exploring the latest advancements in components, his expertise shines through his work and dedication towards this field. Currently, Shehryar is rocking a custom loop setup for his built.
Get In Touch: shehryar@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads



![Intel i5-13600K Vs i5-13600KF [We Checked The Difference]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/CPU-Comparison-Template-NEW-1-218x150.jpg)