AMD Ryzen 5 7640U
Rated: 8.5/10
AMD Ryzen 5 6600U
Rated: 7.5/10
Pros And Cons
| CPU | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 5 7640U | ✅ Better CPU Performance ✅ Better RAM Speed | ❌ Lesser GPU Execution Units ❌ Higher Price |
| Ryzen 5 6600U | ✅ Lower TDP ✅ More Memory Channels | ❌Multithreading Not Supported ❌Lower Clock Speeds |
- Starting, the Ryzen 5 7640U’s cutting-edge 4nm process node and the Ryzen 7 6800U’s advanced 6nm process node impacted both performance and power efficiency in our benchmarks.
- Moreover, the Ryzen 5 7640U’s support for DDR5-5600 and LPDDR5x-7500 memory provides higher bandwidth and faster data access in this comparison compared to the Ryzen 7 6800U’s DDR5-4800 and LPDDR5-6400 support.
- In addition, the Ryzen 5 6600U excels with a configurable TDP ranging from 15W to 28W, while the Ryzen 5 7640U’s TDP ranges from 15W to 30W, offering power efficiency options.
- In our experience, the Ryzen 5 7640U outperforms the Ryzen 7 6800U with impressive leads in single-core and multi-core performance, making it a versatile choice for computing tasks.
Comparison Table
| Key Specifications | Ryzen 5 7640U | Ryzen 5 6600U |
|---|---|---|
| Release Date | May 3, 2023 | January 4, 2022 |
| Integrated GPU | Radeon 760M | Radeon 660M |
| Performance Cores | 6 | 6 |
| Performance Threads | 12 | 12 |
| Total Cores | 6 | 6 |
| Total Threads | 12 | 12 |
| L1 Cache | 64K (per core) | 64K (per core) |
| L2 Cache | 1MB (per core) | 512K (per core) |
| Transistors | 25 billion | – |
| Socket | FP8 | FP6 |
| GPU Base Clock | 1500 MHz | 1500 MHz |
| GPU Boost Clock | 2600 MHz | 1900 MHz |
| ECC Support | Yes | No |
| Memory Size | 256GB | 64GB |
Architectural Differences
- Process Node: Embracing the forefront of technology, the Ryzen 5 7640U boasts a cutting-edge 4nm process node, while the Ryzen 5 6600U adopts an advanced 6nm process node, showcasing AMD’s commitment to innovation.
- Clock Speed: Showcasing unparalleled speed with the Ryzen 5 7640U leads with a swift 3.5 GHz base clock (boosting up to 4.9 GHz), while the Ryzen 5 6600U competes admirably with a solid 2.9 GHz base clock (boosting up to 4.5 GHz).
- Memory Support Variation: Elevating memory performance, the Ryzen 5 7640U’s support for DDR5-5600 and LPDDR5x-7500 delivers higher bandwidth and faster data access than the Ryzen 5 6600U’s DDR5-4800 and LPDDR5-6400 support.
- TDP: Moreover, the Ryzen 5 6600U excels with a configurable lower TDP ranging from 15W to 28W, guaranteeing power efficiency, while the Ryzen 5 7640U demands a configurable TDP of 15W to 30W.
- Supported Technologies: Expanding its capabilities, the Ryzen 5 7640U introduces ECC Memory support, a distinctive feature not present in the Ryzen 5 6600U, catering to users seeking enhanced error correction capabilities.
In this in-depth analysis, we embark on a captivating journey to explore the battle of processors: AMD Ryzen 5 7640U vs Ryzen 5 6600U. Through an unbiased lens, we uncover the intricacies of their specifications and unveil real-world performance benchmarks, shedding light on the ultimate showdown between these two powerful contenders.
Performance Benchmarks
With a solid grasp of their architectural differences, it’s time to put the AMD Ryzen 5 7640U and Ryzen 5 6600U to the test through our rigorous performance benchmarks. These benchmarks serve as our window into real-world scenarios, gauging how these CPUs handle various tasks and applications.
Cinebench R23 (Single-Core)
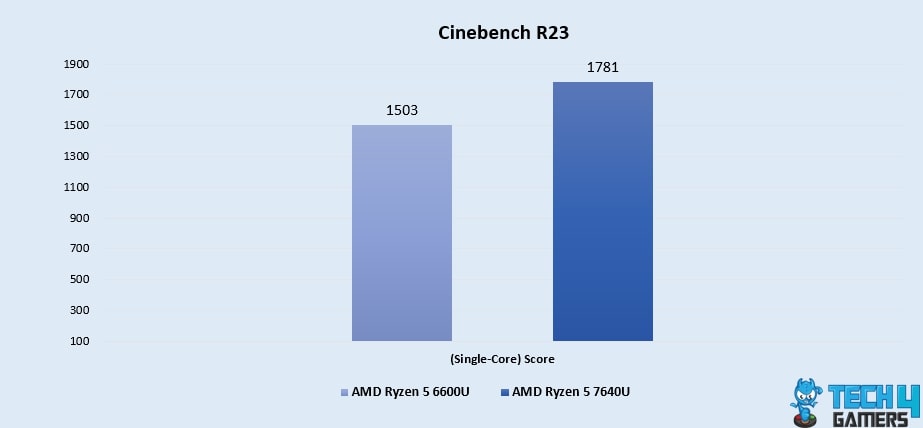
- When we tested the processors in the Cinebench test, the Ryzen 5 7640U led the pack with an impressive 18% boost, achieving a score of 1781, while the Ryzen 5 6600U trailed behind at 1503, showcasing the former’s superior single-core performance.
Cinebench R23 (Multi-Core)
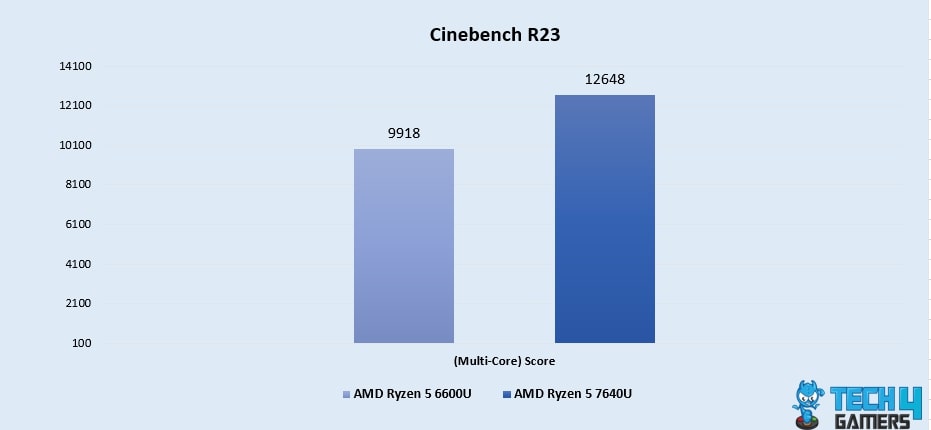
- In the multi-core domain of our Cinebench test, the Ryzen 5 7640U takes a significant leap with a 28% lead, scoring 12648, outperforming the Ryzen 5 6600U’s score of 9918, demonstrating its superior multitasking capabilities and earning our confidence.
Geekbench 5 (Single-Core)
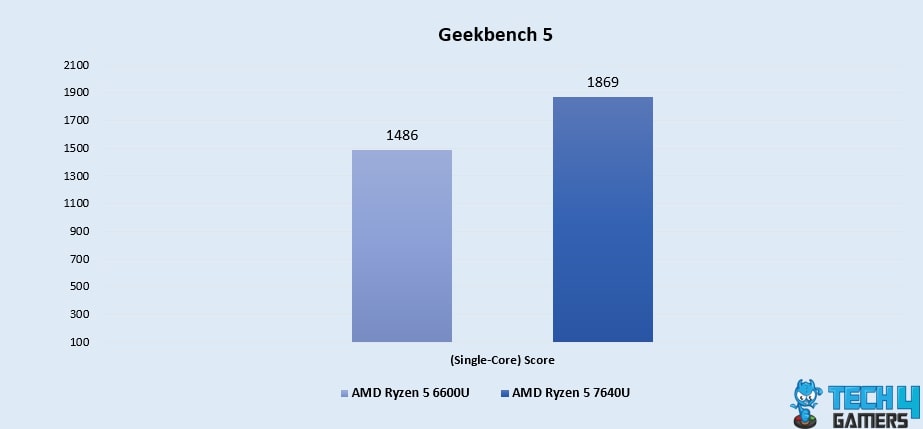
- While going over single-core tasks, the Ryzen 5 7640U again impresses with a 26% surge, reaching a score of 1869, while the Ryzen 5 6600U scores 1486, highlighting the former’s faster single-core processing.
Geekbench 5 (Multi-Core)
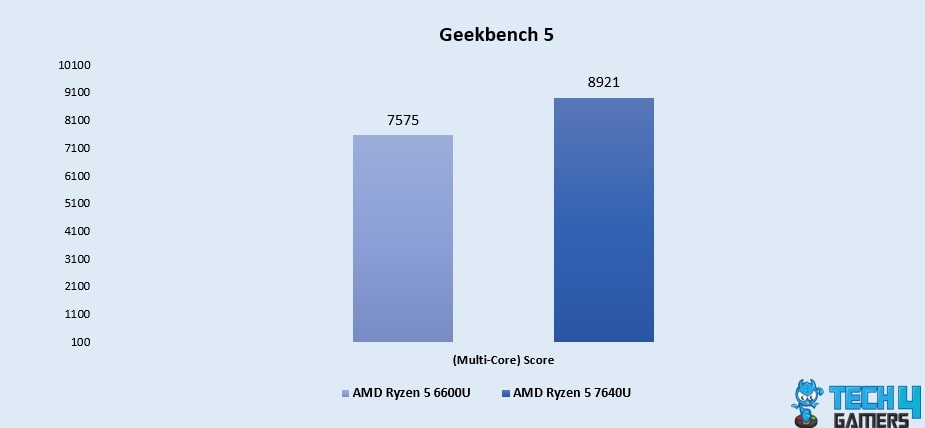
- In the realm of multitasking, the Ryzen 5 7640U maintains its lead with an 18% advantage, scoring 8921, while the Ryzen 5 6600U scores 7575, reinforcing its superior performance in handling parallel tasks.
Ryzen 5 7640U Vs Ryzen 5 6600U: Which Chip Is Suitable For You?
AMD Ryzen 5 7640U: We tested the Ryzen 5 7640U and discovered that it boasts a state-of-the-art performance and power efficiency of the chips. Utilizing the support for the DDR5-5600 and LPDDR5x-7500 memory, the Ryzen 5 7640U delivers better working speeds, outpacing the Ryzen 7 6800U’s performance.
AMD Ryzen 5 6600U: Conversely, the Ryzen 5 6600U impresses with a configurable TDP ranging from 15W to 28W, ensuring optimal power efficiency, while the Ryzen 5 7640U offers configurability from 15W to 30W. That’s why we put the processor forward in terms of power conservation.
In our rigorous benchmarks, the Ryzen 5 7640U showcases its superiority with a lead in single-core and a substantial lead in multi-core performance over the Ryzen 7 6800U, making it our versatile choice for various computing tasks.
More From AMD Ryzen 5 7640U:
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Comparisons Expert]
Shehryar Khan, a seasoned PC hardware expert, brings over three years of extensive experience and a deep passion for the world of technology. With a love for building PCs and a genuine enthusiasm for exploring the latest advancements in components, his expertise shines through his work and dedication towards this field. Currently, Shehryar is rocking a custom loop setup for his built.
Get In Touch: shehryar@tech4gamers.com







