The processing power of computers has significantly increased over time, allowing for more efficient multitasking and performance optimization. Threads are a key aspect of modern CPUs that plays a significant role in leading to this advancement. Consequently, they play a crucial role in determining the performance of a CPU.
What are Threads?
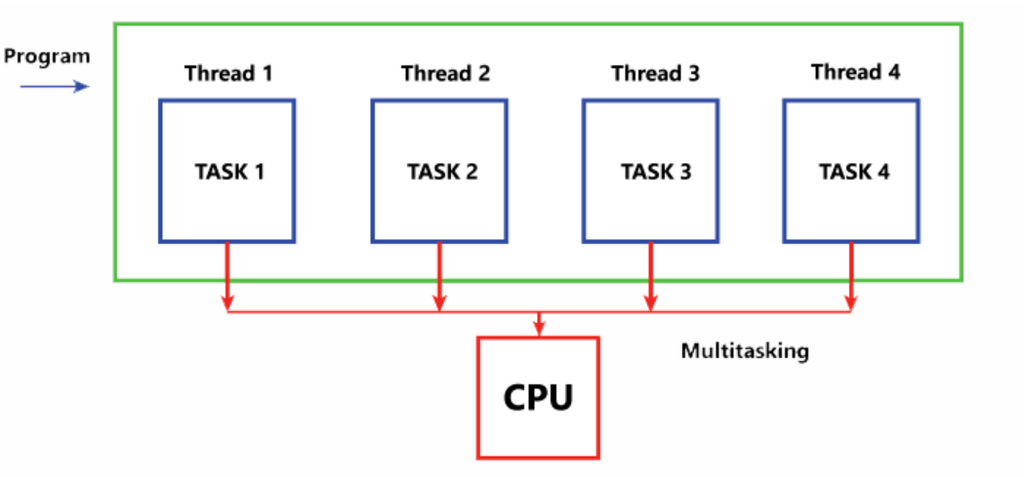
Threads are the smallest units of a computer program that can be executed independently by a CPU. Each thread represents a sequence of instructions that can be dispatched by the CPU for execution[1]. Every application generates its threads, independent instruction streams capable of being executed concurrently. In other words, threads are a way to introduce parallel computing by allowing multiple threads to be executed simultaneously by a CPU[2].
How Do Threads Affect Performance?
Threads can have a significant impact on the performance of a CPU. By enabling parallel computing, threads allow a processor to execute multiple tasks concurrently, which can result in faster processing times and improved performance[3]. For example, in a multi-threaded application, while one thread waits for data to be fetched from memory, another can execute instructions, reducing idle time and increasing overall efficiency[4].
Generally, more threads mean the CPU can handle more tasks simultaneously, reducing the overall processing time and improving performance[5]. However, the performance gain may not be linear and depends on factors like workload nature, software optimization for multi-threading, and CPU architecture efficiency.
CPU Cores vs Threads
A thread is mainly the smallest program unit that can be executed independently. In contrast, a CPU core is the individual processing unit inside the processor capable of executing instructions independently[6]. One core can handle one or more threads simultaneously, depending on whether it supports hyper-threading. Intel developed hyper-threading to allow a single core to execute multiple threads simultaneously.
How Many Threads Are Required for Gaming?
Most modern games are designed to take advantage of multi-threading, which means they can utilize multiple CPU threads to distribute the workload and improve performance. Generally, a CPU with at least 6 to 8 threads is typically sufficient for basic gaming needs. However, for more demanding games or tasks such as streaming, content creation, and video editing, CPUs with 10 or more threads are preferred[7].
In some cases, a processor with fewer threads but higher clock speeds may deliver better gaming performance than a processor with more threads but lower clock speeds. Therefore, it’s important to consider the overall system requirements of a game and the specific needs of your system when determining the optimal number of threads for gaming.
Related Helpful Resources By Tech4Gamers:
- CPU Cores
- How Much RAM Do You Need For Video Editing?
- GDDR6
- CPU Clock Speed: Definition & Everything To Know
- Hyper threading
References:
- Threads. University of Illinois Chicago. Retrieved from https://www.cs.uic.edu/~jbell/CourseNotes/OperatingSystems/4_Threads.html
- Cameron Wilson (Nov 2023). Multithreading and concurrency fundamentals. Retrieved from https://www.educative.io/blog/multithreading-and-concurrency-fundamentals
- Richard Bellairs (April 2019). What Is Parallel Programming and Multithreading. Retrieved from https://www.perforce.com/blog/qac/multithreading-parallel-programming-c-cpp
- A Low-Energy Multi-Threaded Processor Design for Application Specific Embedded Systems. Retrieved from https://www.graphyonline.com/archives/IJCSE/2018/IJCSE-131/
- Jason Potter (July 3, 2023). CPU Cores Vs. Threads – Everything You Need To Know. Retrieved from https://www.namehero.com/blog/cpu-cores-vs-threads-everything-you-need-to-know/
- The Difference Between CPU Cores and Threads. Retrieved from https://shardeum.org/blog/cpu-cores-and-threads/
- Short Guide to Choosing an Intel CPU-Powered Laptop. Retrieved from https://www.asus.com/content/short-guide-to-choosing-an-intel-cpu-powered-laptop/
FAQs
No, the number of threads in a CPU is determined during manufacturing and is almost impossible to temper once the CPU is manufactured.
Not necessarily. While more threads can help in improving performance in multi-threaded applications, not all applications are optimized for multi-threading. In some cases, more threads can even result in increased overhead and contention for system resources, leading to decreased performance.
You can check the number of threads in your CPU by checking the specifications of your processor or by using some system information tool like CPU-Z.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
[Wiki Editor]
Ali Rashid Khan is an avid gamer, hardware enthusiast, photographer, and devoted litterateur with a period of experience spanning more than 14 years. Sporting a specialization with regards to the latest tech in flagship phones, gaming laptops, and top-of-the-line PCs, Ali is known for consistently presenting the most detailed objective perspective on all types of gaming products, ranging from the Best Motherboards, CPU Coolers, RAM kits, GPUs, and PSUs amongst numerous other peripherals. When he’s not busy writing, you’ll find Ali meddling with mechanical keyboards, indulging in vehicular racing, or professionally competing worldwide with fellow mind-sport athletes in Scrabble. Currently speaking, Ali’s about to complete his Bachelor’s in Business Administration from Bahria University Karachi Campus.
Get In Touch: alirashid@tech4gamers.com


 Threads
Threads

![L3 Cache Explained [CPUs]](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/HOW-TO-1-3-218x150.jpg)
![Can Overclocking Damage The GPU? [Answered] Can Overclocking Damage The GPU](https://tech4gamers.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Can-Overclocking-Damage-The-GPU-218x150.jpg)