- A new AMD patent proposes a hybrid scheduler system to make future processors more efficient in handling tasks.
- It describes a smarter way to assign tasks to different core types by switching between two schedulers dynamically.
- This approach reduces power consumption and increases responsiveness by using the right cores at the right time.
PC processors have come a long way, with modern ones featuring multiple cores designed to handle different tasks. However, effective communication and efficient usage of these cores is tough, but AMD has proposed a new system to greatly improve performance.
We have found a new AMD patent that describes using a hybrid software and hardware scheduling system to make processors more effective in task handling. Tasks are smartly assigned to different core types by using both scheduling policies dynamically instead of one.
A system contains energy-efficient and high-performance cores, including accelerators like GPUs and NPUs. Normally, the OS uses quality of service (QoS) tags to assign demanding tasks to fast cores and low-priority ones to energy-efficient cores.
However, when accelerators are being used, this tagging can mislead the scheduler and waste power. AMD suggests a system management unit (SMU) that monitors hardware in real time and dynamically overrides the software scheduler.
Unlike conventional techniques, the described techniques of hybrid scheduling for heterogeneous processor systems enable a hybrid approach for thread scheduling that dynamically switches between the first scheduling policy and the second scheduling policy.
Why it matters: The new hybrid scheduler might boost the performance of future AMD Ryzen processors, making them more efficient in CPU-bound tasks.
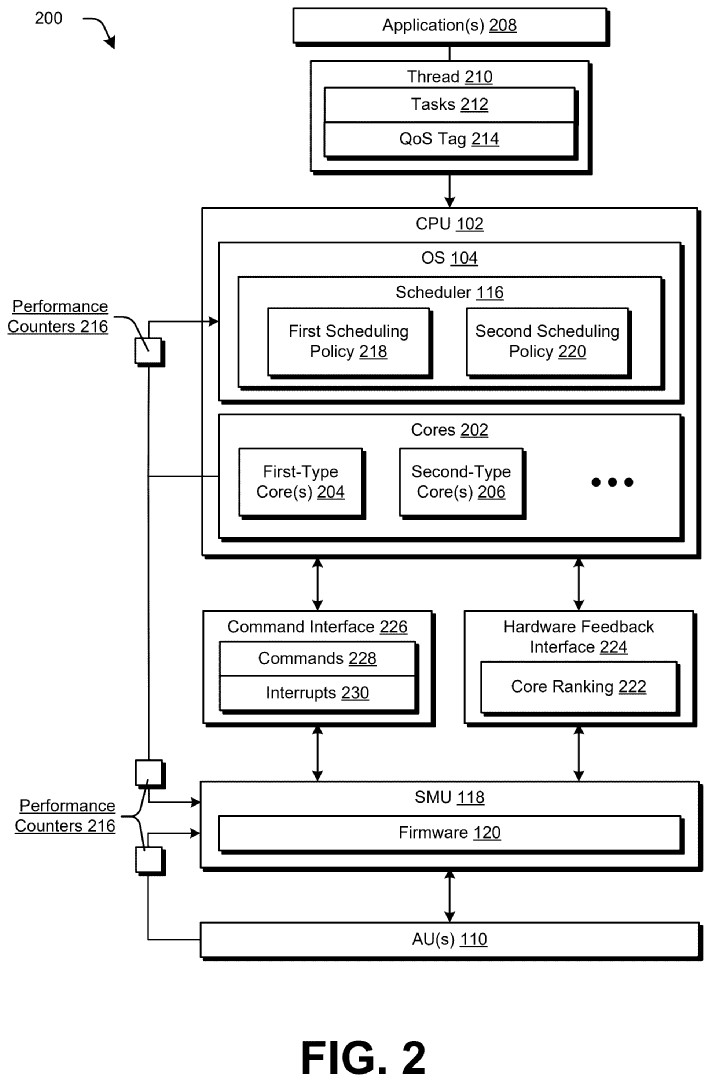
The patent “Hybrid Scheduling for Heterogeneous Processor Systems” ranks cores by efficiency and guides thread assignments when the hardware scheduler overrides the software ones.
This hybrid method adapts the best scheduling policy depending on the workload, cutting power use, boosting responsiveness, and preventing thread misclassification with accelerators.
AMD argues that the current scheduling only relies on a single policy when managing tasks, which can be resource and power-intensive.
the described techniques reduce power consumption for the system while improving or maintaining system responsiveness in executing higher priority threads, as compared to conventional techniques that implement just one scheduling policy.
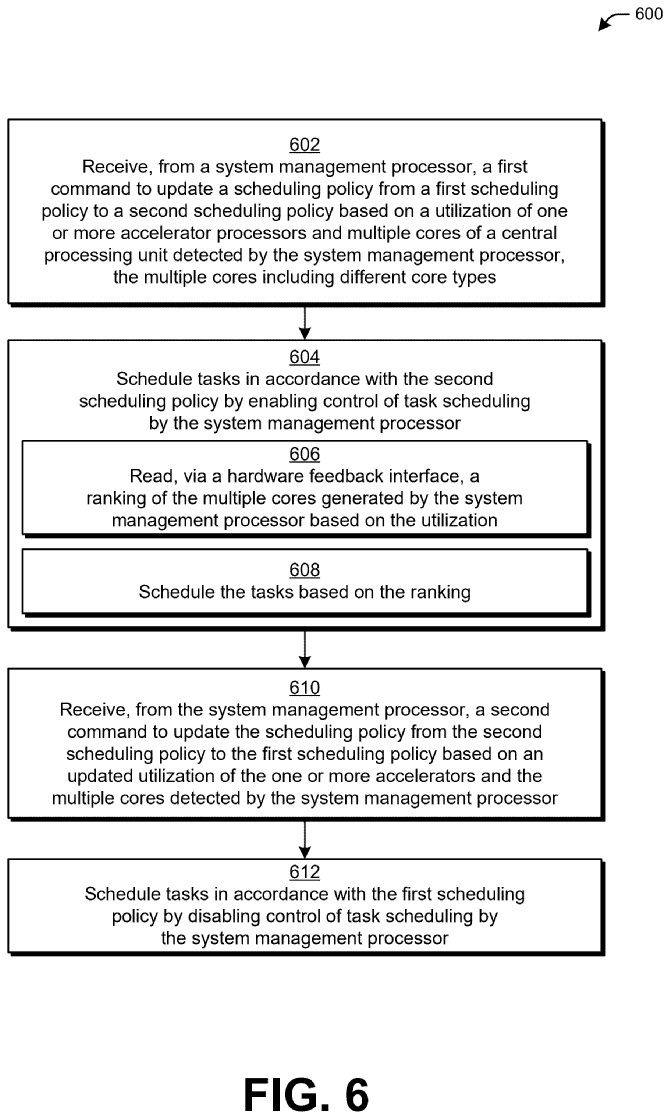
If realized, we may see this patent improve AMD’s future Ryzen processors with the dynamic scheduling strategy. This would result in better performance across gaming and other industries.
AMD has published many patents in the past, like one about smarter chip design to stop thermal paste and liquid metal from leaking out, and another one about a new RAM architecture as DDR5 approaches its bandwidth limit.
Do you think using a dynamic scheduler will give future AMD processors a noticeable performance boost? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below, or join the discussion on the Tech4Gamers forum.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
Shameer Sarfaraz has previously worked for eXputer as a Senior News Writer for several years. Now with Tech4Gamers, he loves to devoutly keep up with the latest gaming and entertainment industries. He has a Bachelor’s Degree in Computer Science and years of experience reporting on games. Besides his passion for breaking news stories, Shahmeer loves spending his leisure time farming away in Stardew Valley. VGC, IGN, GameSpot, Game Rant, TheGamer, GamingBolt, The Verge, NME, Metro, Dot Esports, GameByte, Kotaku Australia, PC Gamer, and more have cited his articles.




