- Two Nvidia patents aim to reduce GPU loads and improve gaming performance, likely for a future GPU lineup.
- The first one discusses smarter ray-traced shadows that use shadow maps to estimate where they should fall.
- The second patent proposes calculating lighting by organizing it into grids and sampling it more efficiently.
Ray tracing has revolutionized gaming with insane upgrades to visuals, but it is also notoriously resource-intensive. However, Nvidia is exploring different solutions to make ray tracing more efficient and manageable for GPUs.
We have identified two Nvidia patents that propose more intelligent, ray-traced shadows and lighting, designed to consume fewer resources. The company aims to make GPUs more efficient in handling ray tracing, ultimately boosting gaming performance.
The first patent discusses using a shadow map to estimate where ray-traced shadows should fall instead of calculating every ray through alpha-tested geometry. Visibility and distance values are passed to a denoiser to smooth out shadows and make them look realistic.
A shadow map stores the distance of geometry as seen from the point of view of a light source. The shadow map lookups are also used to determine a visibility value for the pixel and a distance value for the pixel. These values are then passed to a denoiser, which […] smooth[s] out a resulting image during the rendering process.
Why it matters: These Nvidia patents could significantly reduce the resources required for ray tracing and lighting in future GPUs, making them more effective in handling AAA games.
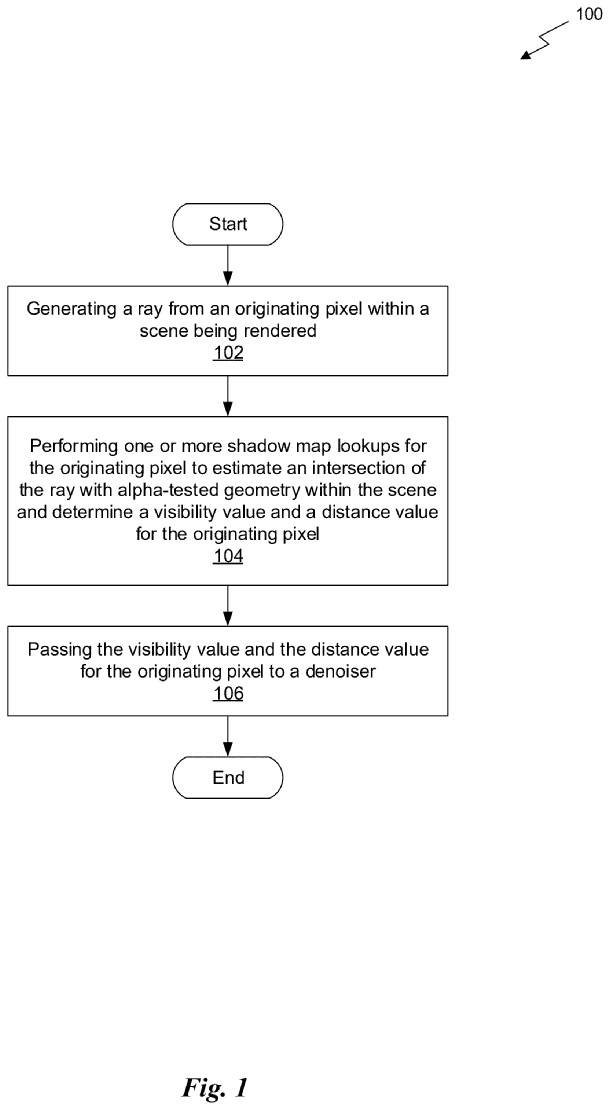
The patent called “PERFORMANCE OF RAY-TRACED SHADOW CREATION WITHIN A SCENE” claims that using shadow maps improves the realism and performance of ray tracing with alpha-tested geometry.
Nvidia argues that several time-consuming operations currently need to be performed to determine accurate shadows in ray tracing, consuming a significant amount of resources during the rendering process.
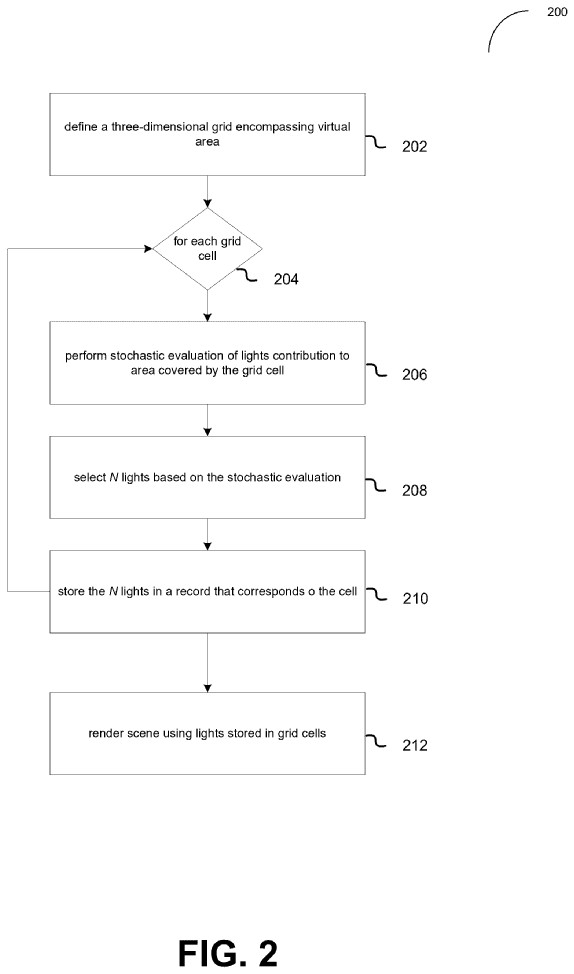
The second patent, called “GRID-BASED LIGHT SAMPLING FOR RAY TRACING APPLICATIONS,” describes using a smarter and more scalable way to handle lighting by organizing lights into a grid and sampling them more efficiently.
rendering a pixel within a particular subdivision is done by selecting lights from the subdivisions, such as grid cells, that surround and/or encompass the pixel. a number of lights are selected from subdivisions including or immediately surrounding the point, using a stochastic technique such as resampled importance sampling (“RIS”).
Each cell stores a subset of lights that are selected stochastically based on their contribution, prioritizing lights that significantly affect a cell using multiple sampling techniques. Pixels are illuminated during rendering, with more lights taken from closer cells.
This approach dramatically reduces the number of lights that need evaluation to make ray tracing faster and more scalable.
Nvidia argues that rendering scenes with large numbers of lights is currently computationally intensive, especially when dealing with ray-traced applications.
Nvidia has secured numerous unique patents in the past, including one to enhance GPU buffer memory management for improved gaming performance.
Do you think the new Nvidia patents will make ray tracing more efficient and accessible? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below, or join the discussion on the Tech4Gamers forum.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
Shameer Sarfaraz has previously worked for eXputer as a Senior News Writer for several years. Now with Tech4Gamers, he loves to devoutly keep up with the latest gaming and entertainment industries. He has a Bachelor’s Degree in Computer Science and years of experience reporting on games. Besides his passion for breaking news stories, Shahmeer loves spending his leisure time farming away in Stardew Valley. VGC, IGN, GameSpot, Game Rant, TheGamer, GamingBolt, The Verge, NME, Metro, Dot Esports, GameByte, Kotaku Australia, PC Gamer, and more have cited his articles.




