- A new Nvidia patent aims to improve GPU buffer management for higher gaming and rendering performance.
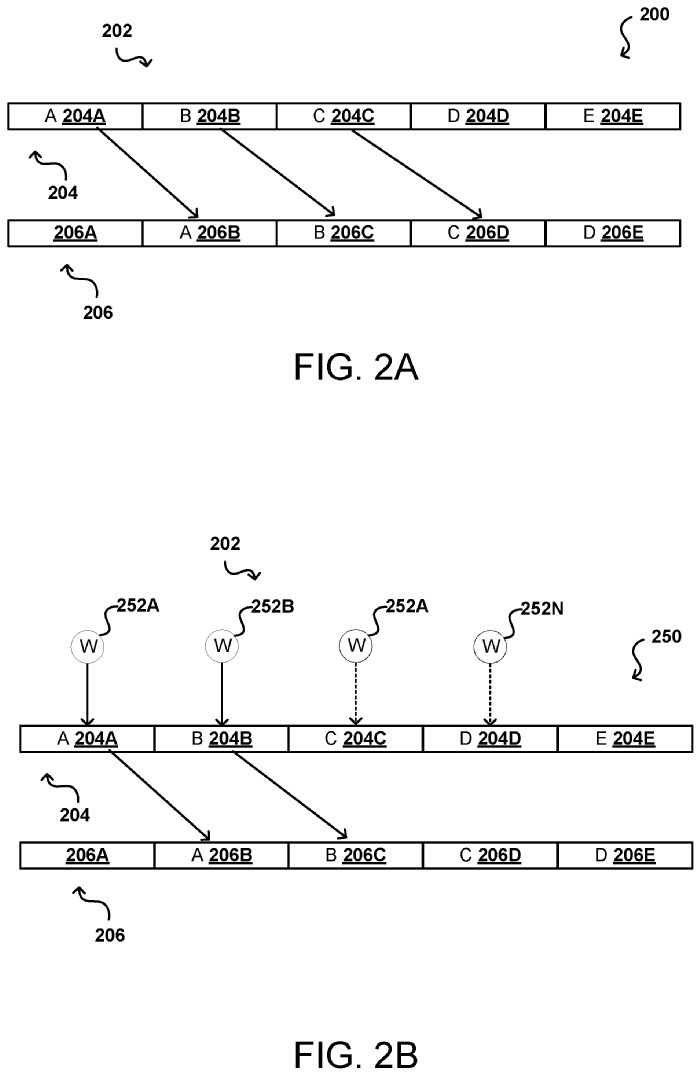
- Multiple threads efficiently rearrange data segments within the buffer without needing extra memory or causing errors.
- The software-based logarithmic solution avoids the need for a second buffer and supports parallel processing.
Whether it’s a software-based solution or hardware improvements, Nvidia is always looking for unique ways to push its GPUs to new extremes. Now, it has published a new patent that wholly upgrades how GPU memory functions.
We have discovered a new Nvidia patent that aims to enhance GPU buffer management by reducing the required space and errors associated with data movement. The buffer is divided into fixed-sized chunks with a boolean flag to check its status.
Then, worker threads race to grab data chunks, mark them as ‘picked up’ with atomic operations, and move them to a new spot after ensuring there are no overwrites.
The system also groups reused chunks together to create a larger block of empty space for new data that may need contiguous memory.
Systems and methods may implement workers to read a data segment into individual registries and then write the data segments to a different location within the memory buffer without the use of a second memory buffer. As a result, embodiments allow for a single read/write operation to move different data segments.
Why it matters: Nvidia patenting a smarter way to move data around inside a GPU’s memory could massively improve the performance of its future gaming GPU lineup.
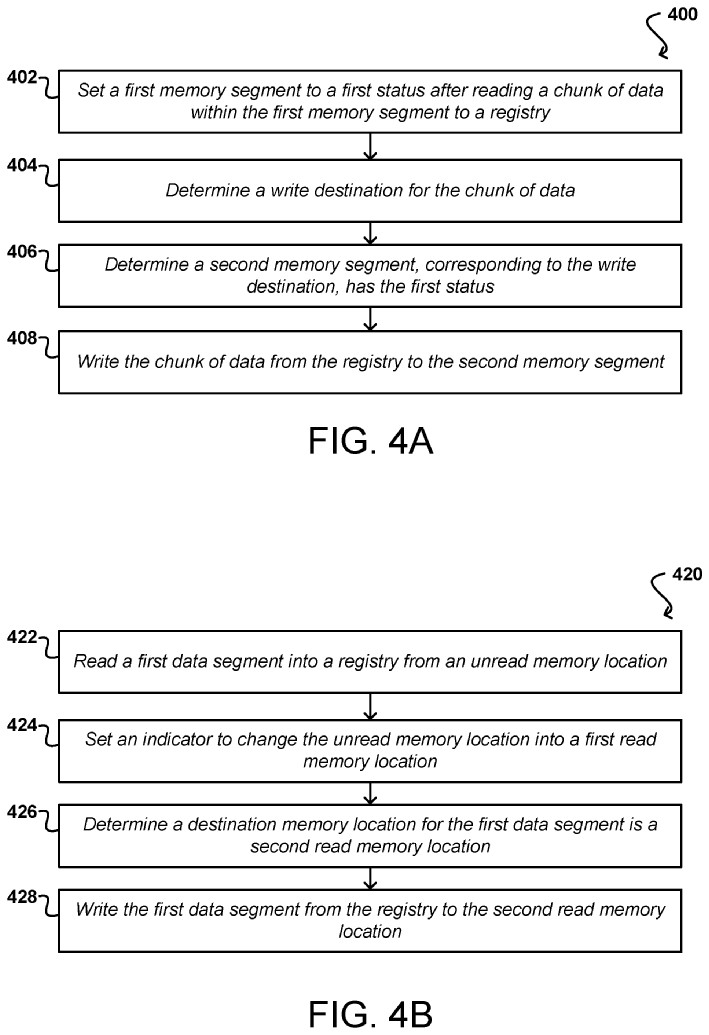
The patent called ‘IN-PLACE DATA MANAGEMENT WITHIN MEMORY BUFFERS’ claims that the entire described process happens in a single memory buffer, removing the need to rely on a second buffer. Also, it occurs in parallel, making the GPU memory pretty efficient.
Nvidia says moving reused data within the same buffer can cause errors when the source and destination overlap. So, the new system eliminates the need for traditional methods that risk overwriting data.
when rendering or adding information to the destination location, certain sub-buffers may be occupied, causing overlap between the source and destination locations, leading to read-after-write errors.
If realized, future Nvidia GPUs would come with more efficient memory, leading to improvements in gaming and complex rendering tasks.
Besides Nvidia, AMD has also published numerous unique patents in the past, including one about new blower fan designs for gaming laptops to address heating problems. There’s another patent about a smart cache cleaning system that can significantly improve processor performance.
Do you think the new Nvidia patent changing the way GPU buffer memory is handled will result in massive performance gains? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below, or join the discussion on the Tech4Gamers forum.
Thank you! Please share your positive feedback. 🔋
How could we improve this post? Please Help us. 😔
Shameer Sarfaraz has previously worked for eXputer as a Senior News Writer for several years. Now with Tech4Gamers, he loves to devoutly keep up with the latest gaming and entertainment industries. He has a Bachelor’s Degree in Computer Science and years of experience reporting on games. Besides his passion for breaking news stories, Shahmeer loves spending his leisure time farming away in Stardew Valley. VGC, IGN, GameSpot, Game Rant, TheGamer, GamingBolt, The Verge, NME, Metro, Dot Esports, GameByte, Kotaku Australia, PC Gamer, and more have cited his articles.




